Atlas-free brain tissue segmentation method
A separation method and image segmentation technology, applied in image analysis, image data processing, medical science, etc., can solve problems such as degradation of segmentation results, massive calculations, and inaccurate brains
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
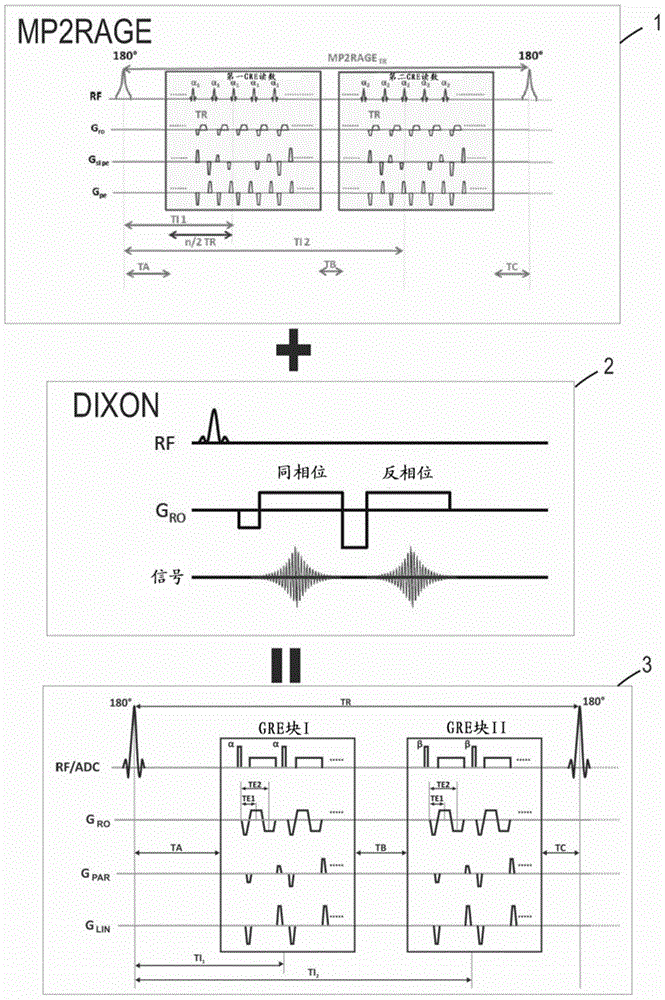
[0041] figure 1 and figure 2 A preferred embodiment of the non-spectral magnetic resonance imaging method according to the invention is schematically shown. The method is configured to image at least a portion of the brain and includes the steps of:
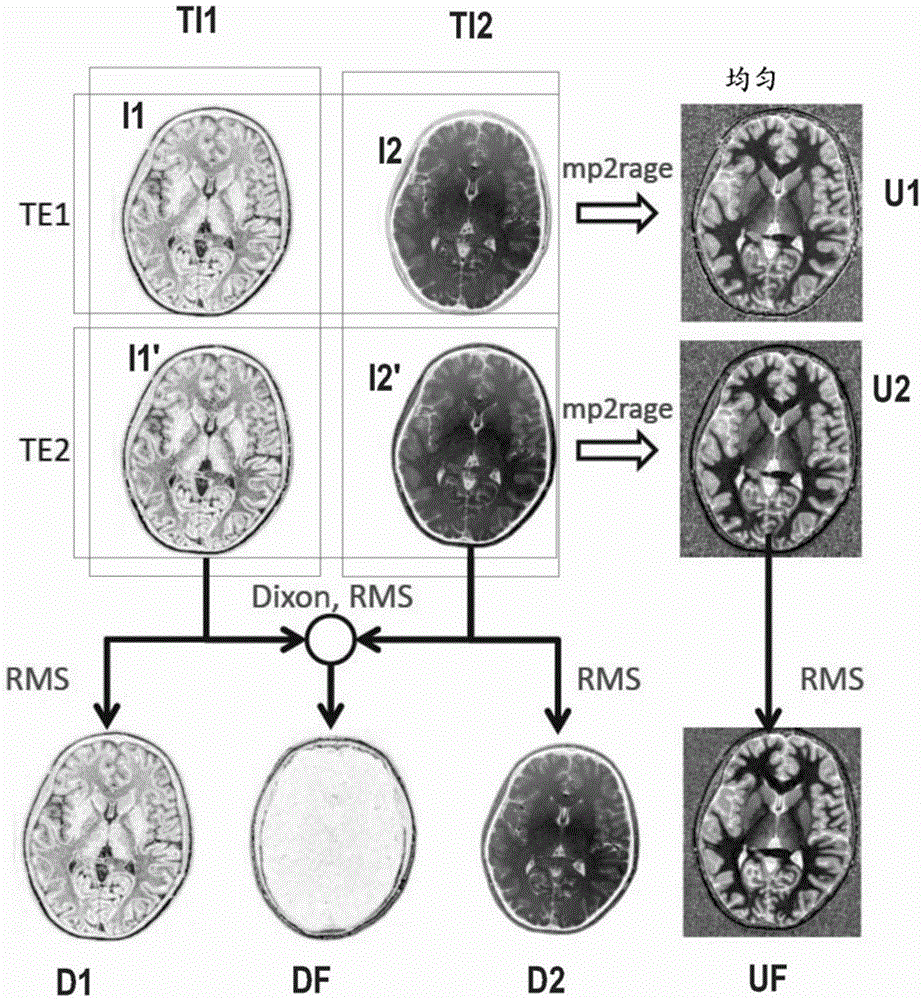
[0042] Using an MRI sequence 3, the MRI sequence 3 is configured to acquire two image volumes I1, I2, I1', I2' of the portion, respectively for each echo at different inversion times TI1, TI2 within a single acquisition First image volume I1, I1' and second image volume I2, I2' at time TE1, TE2, where the MRI sequence 3 is a double-echo MP2RAGE using the Dixon method 2 to acquire the fat-water separation image of the portion Sequence 1, said MP2RAGE sequence 1 is preferably performed using GeneRalized Autocalibrating Partially Parallel Acquisition (GRAPPA) and is specifically characterized by the following parameters:
[0043] TI1 / TI2 / TR=700 / 2500 / 5000ms,
[0044] TE1 / TE2=2.44 / 6.06ms,
[0045] GRAPPA has a reduction factor R...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com