Driving method for liquid crystal device, liquid crystal device, and electronic device
A technology of a liquid crystal device and a driving method, applied in circuits, electrical components, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as light leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
[0064] In this embodiment, an active matrix liquid crystal device including a thin film transistor (Thin Film Transistor; TFT) as a switching element of a pixel will be described as an example. This liquid crystal device is a liquid crystal device that can be suitably used as, for example, a light modulation element (liquid crystal light valve) of a projection display device (liquid crystal projector) described later.
[0065] LCD device
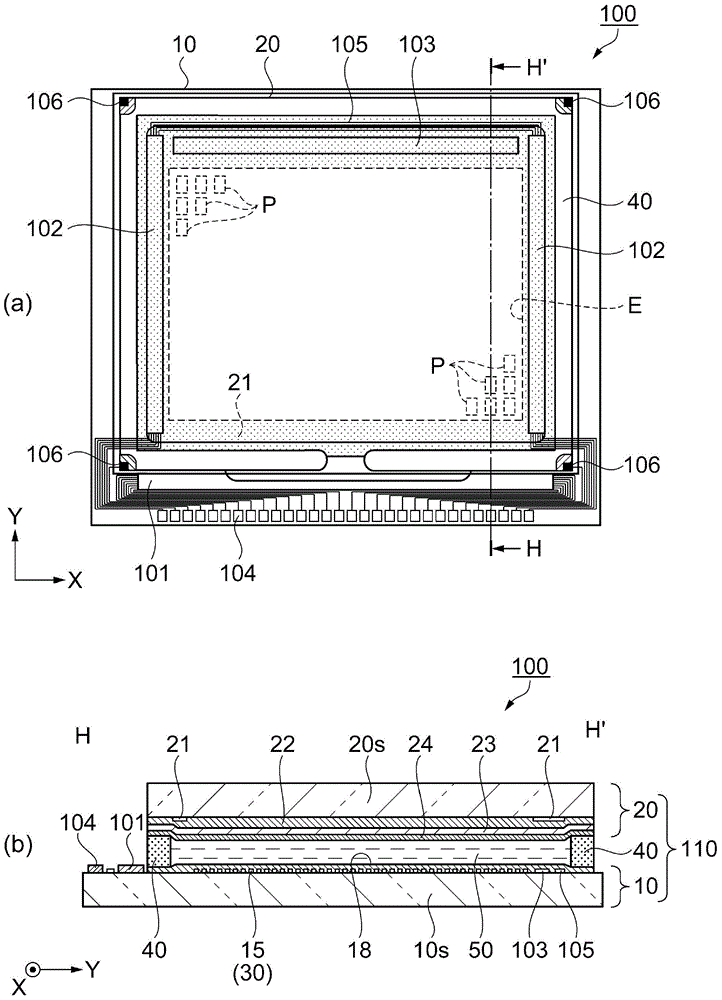
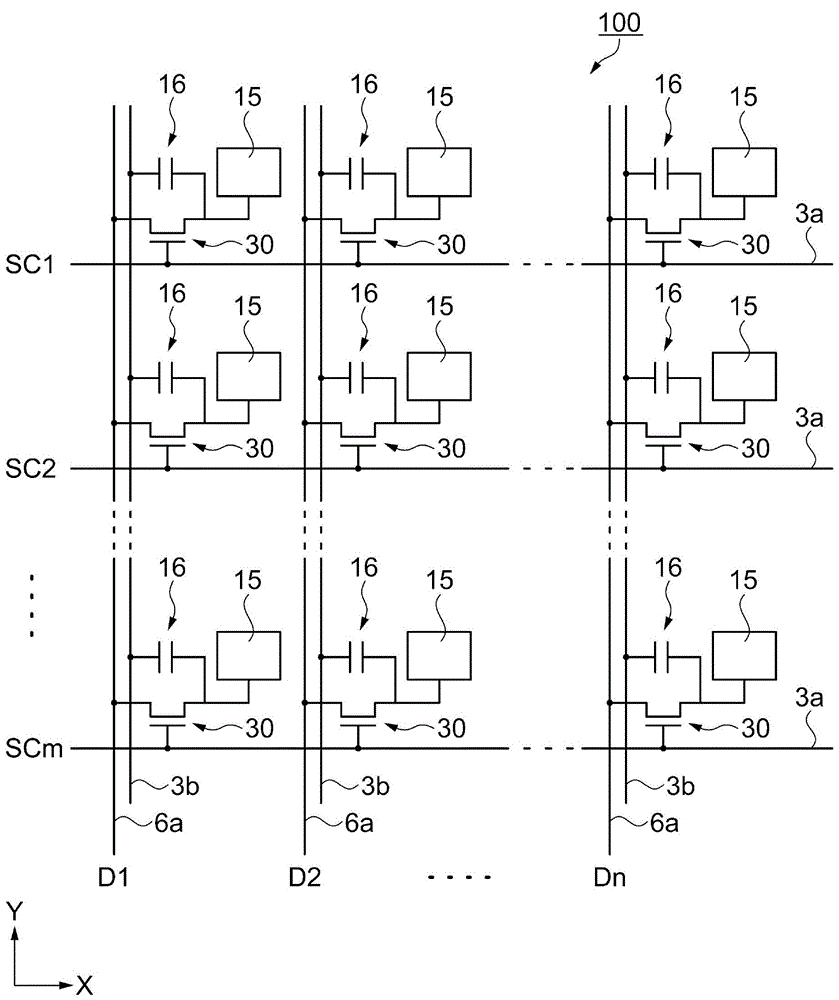
[0066] First, refer to figure 1 and figure 2 The liquid crystal device of this embodiment will be described. figure 1 (a) is a schematic plan view showing the structure of the liquid crystal device of the first embodiment, figure 1 (b) is along figure 1 (a) Schematic cross-sectional view along line H-H'. figure 2 It is an equivalent circuit diagram showing the electrical configuration of the liquid crystal device of the first embodiment.
[0067] Such as figure 1 As shown in (a) and (b), the liquid crystal device 100 of the present ...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0137] Next, refer to Figure 8 and Figure 9 The liquid crystal device of the second embodiment will be described. Figure 8 is a wiring diagram showing the structure of the electron partition in the liquid crystal device of the second embodiment, Figure 9 It is a schematic cross-sectional view showing the structure of the liquid crystal device of the second embodiment. The liquid crystal device of the second embodiment differs from the liquid crystal device 100 of the first embodiment in the arrangement of the dummy pixels DP. Therefore, the same reference numerals are assigned to the same configurations as those of the liquid crystal device 100 of the first embodiment, and detailed descriptions are omitted, and the parts different from those of the liquid crystal device 100 of the first embodiment will be described.
[0138] The optical design of the normally black mode is applied to the liquid crystal device 200 of the present embodiment. Such as Figure 8 As shown, ...
no. 3 Embodiment approach )
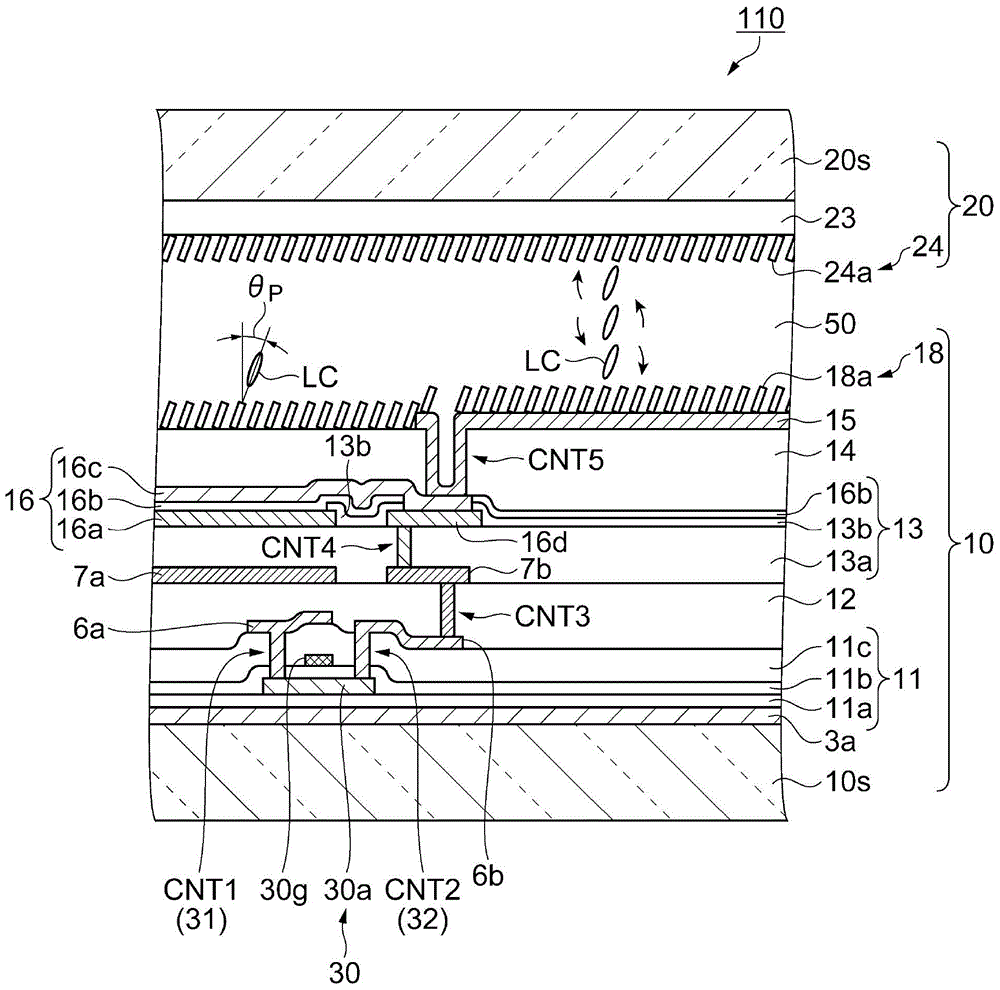
[0152] Next, refer to Figure 10 and Figure 11 The liquid crystal device of the third embodiment will be described. Figure 10 It is a schematic plan view showing the pixel structure in the liquid crystal device of the third embodiment, Figure 11 It is a schematic cross-sectional view showing the structure of the electron partition in the liquid crystal device of the third embodiment. also, Figure 11 is the same as the first embodiment Figure 6 Corresponding schematic sectional view.
[0153] The liquid crystal device of the third embodiment differs in the structure of the pixel P from the liquid crystal device 100 of the first embodiment. Therefore, the same reference numerals are assigned to the same configurations as those of the liquid crystal device 100 of the first embodiment, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
[0154] The liquid crystal device 300 of this embodiment employs an optical design in a normally black mode. Such as Figure 10 As sho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com