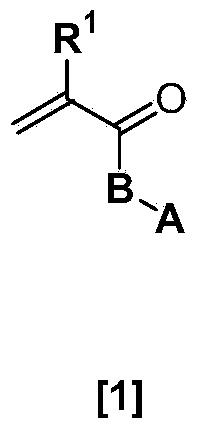
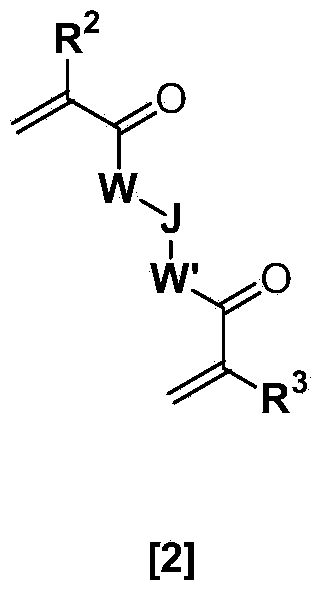
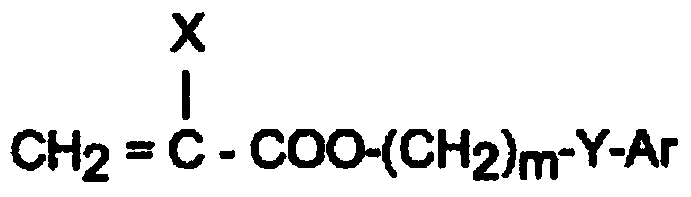Ophthalmic and otorhinolaryngological device materials containing a multi-arm peg macromer
A technology of ENT and ophthalmology, applied in the field of ophthalmology and ENT device materials containing multi-arm PEG macromers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Partially Methacrylated 2000M n Synthesis of 4-arm PEG, Batch #1
[0090] Commercially available 4-arm polyethylene glycol was degassed at 70°C for 4 days and then dissolved in about 100 ml THF. Triethylamine and p-methoxyphenol (ca. 50 mg) were added and the mixture was cooled to 0°C. Add methacryloyl chloride dropwise. Formation of triethylamine-HCl salt started immediately. The mixture was stirred at ambient temperature for 72 hours, then filtered through a plug of silica using a medium porosity sintered glass funnel. The silica was rinsed with dichloromethane so the total volume of the filtrate was about 500-700ml. The solvent was removed by rotary evaporation and the product was dried under vacuum for 3-4 days to give a light yellow liquid (yield 60%).
[0091] Reaction table showing the synthesis of 4-arm PEG using 1.5 equivalents of methacryloyl chloride
[0092]
Embodiment 2
[0094] Partially Methacrylated 2000M n Synthesis of 4-arm PEG, Batch #2
[0095] Procedure: same as Example 1. Pale yellow liquid (yield about 60%).
[0096] Reaction table showing the synthesis of 4-arm PEG using 3.5 equivalents of methacryloyl chloride
[0097]
Embodiment 3
[0099] IOL preparation
[0100] The multi-armed PEG derivatives from Examples 1 and 2 were formulated as shown in Tables 1 and 2. Specimens measuring a thickness of 0.9 mm were cured thermally at 70°C for 1 hour and at 110°C for 2 hours. Samples were extracted in acetone for 20 hours at 55°C, then slowly dried at ambient temperature for 20 hours, followed by vacuum (0.1 mm Hg) at 70°C for a minimum of 20 hours. The extractable weight percent, equilibrium water content (EWC), refractive index (R.I.) and plate appearance of the hydrated samples subjected to the 45-22°C ΔT test are shown in Table 3. The mechanical and thermal properties of selected compositions are shown in Table 4.
[0101] Table 1
[0102]
[0103] Table 2
[0104]
[0105]
[0106] table 3
[0107]
[0108] 1 Samples were equilibrated in deionized water for 9 days at 45°C, then cooled to ambient temperature and later examined by light microscopy using a 10X objective for 1-2 hours.
[0109] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com