Key protein identification method based on subcellular localization specificity
A technology of subcellular localization and identification method, applied in the field of key protein identification based on subcellular localization specificity, which can solve problems such as deviation of prediction results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
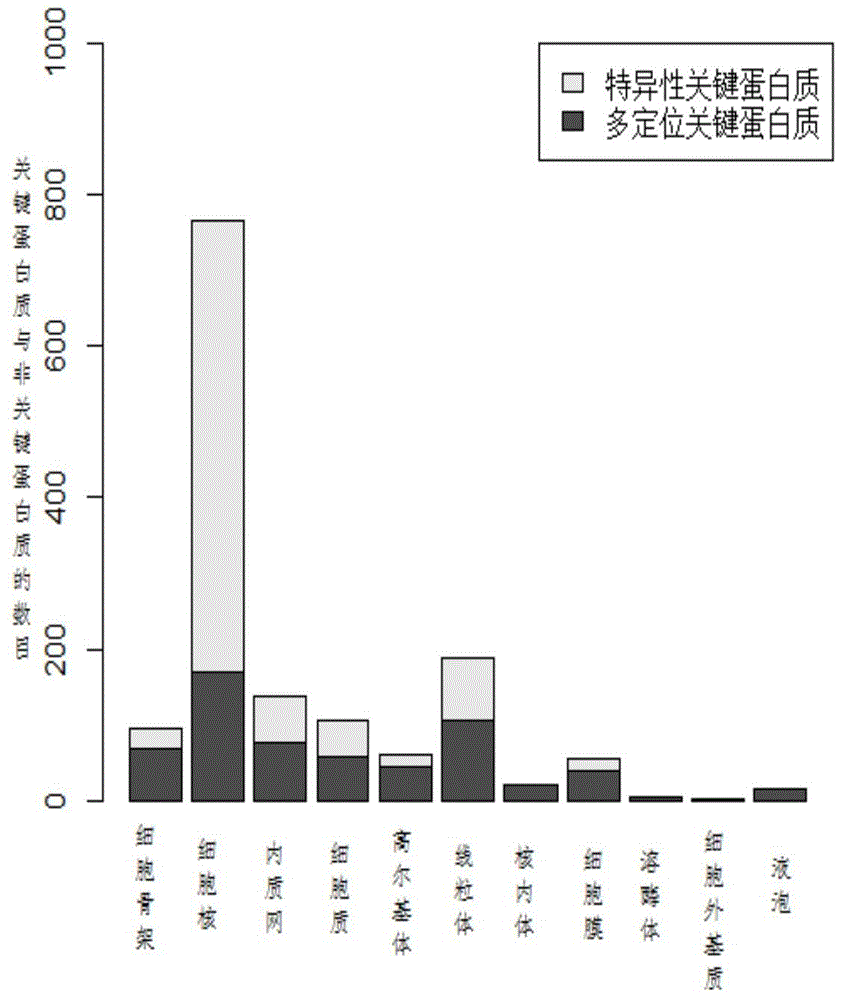
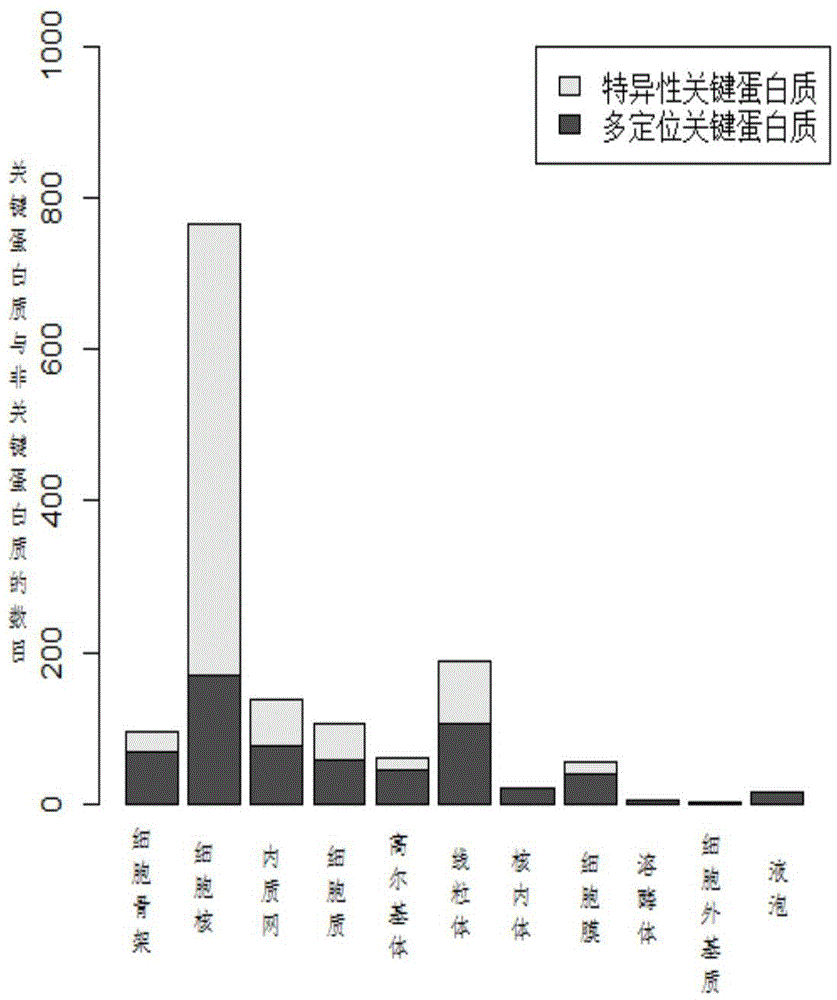
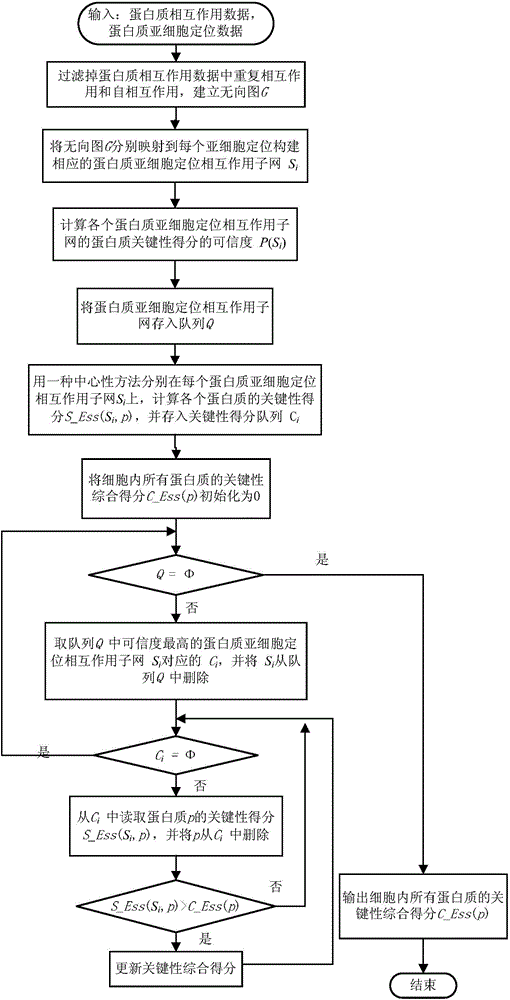
[0039] (1) Construction of protein subcellular localization interaction subnetwork and analysis of distribution characteristics of key proteins
[0040] Protein subcellular localization data for different species can be obtained from the COMPARTMENTS database. The COMPARTMENTS database integrates experimentally-based protein subcellular annotation information from UniProtKB, MGI, SGD, FlyBase, WormBase and other databases, covering protein subcellular localization information of eukaryotes such as humans, yeast, Drosophila, and mice. Public databases such as DIP and Biogrid contain protein interaction data for many species. Yeast is currently the most widely studied species, and its protein interaction network and key protein data are the most complete and reliable among many species. Therefore, data analysis and experimental verification are first based on yeast data. The protein interaction network of yeast comes from the data of DIP database in October 2010. Excluding sel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com