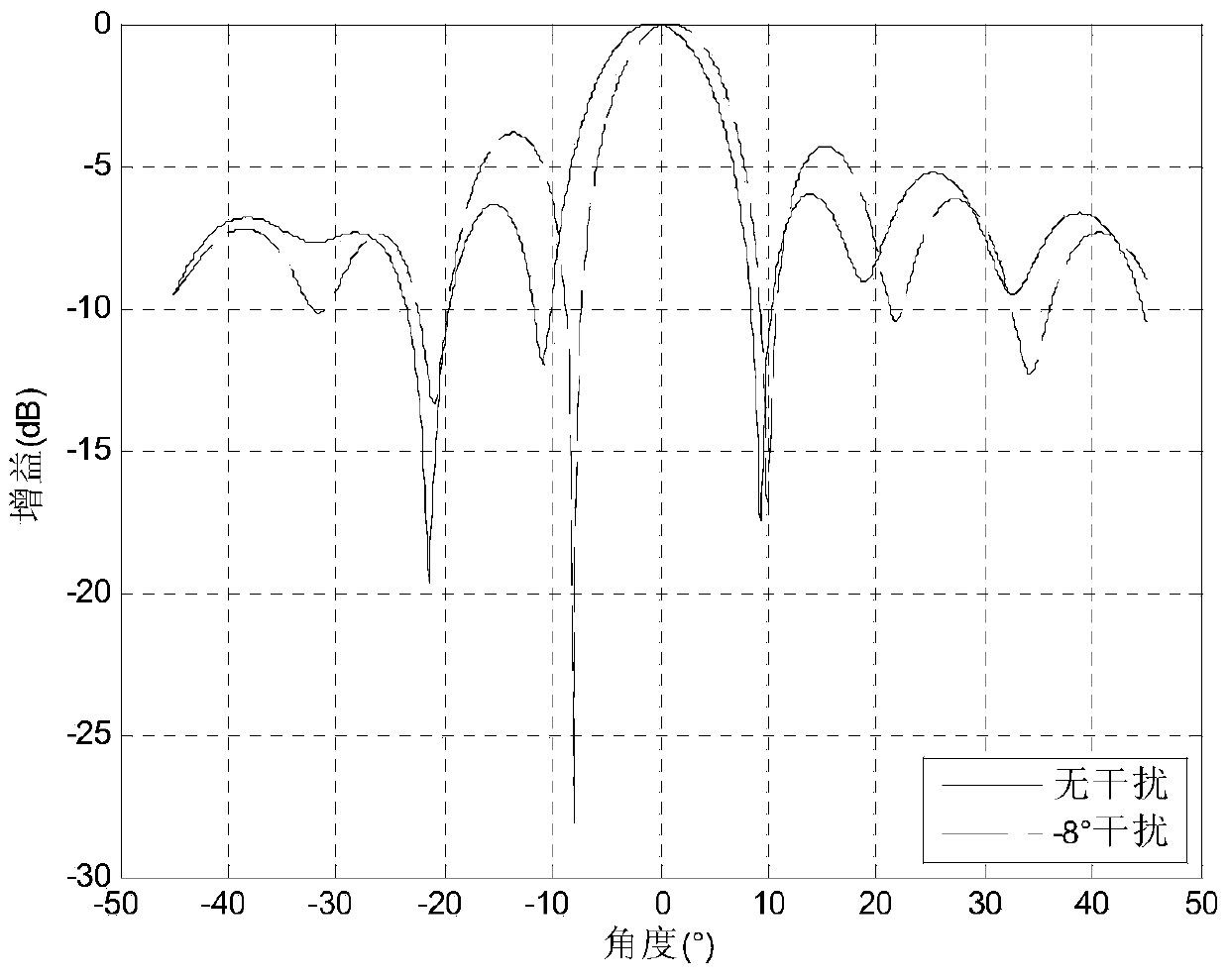
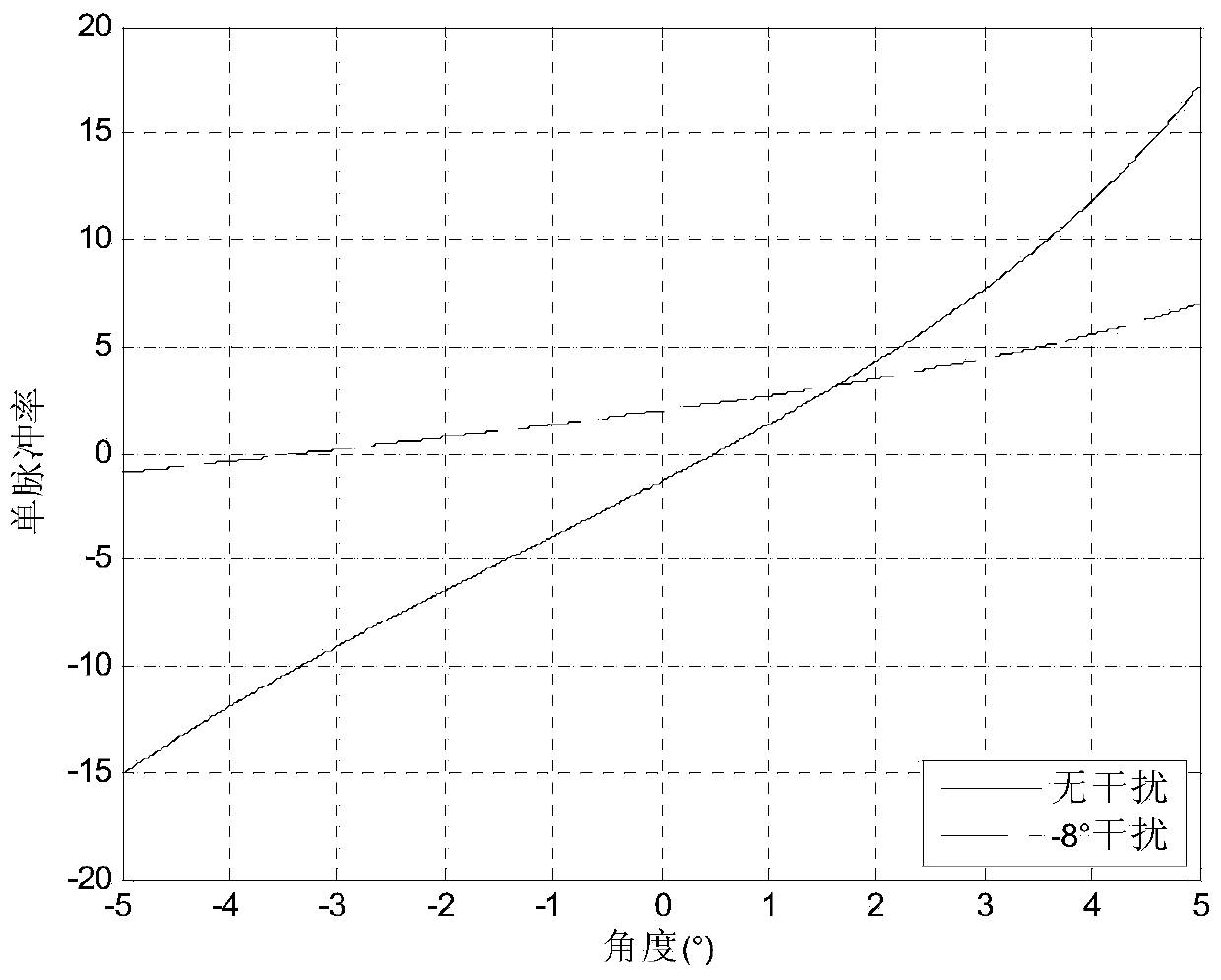
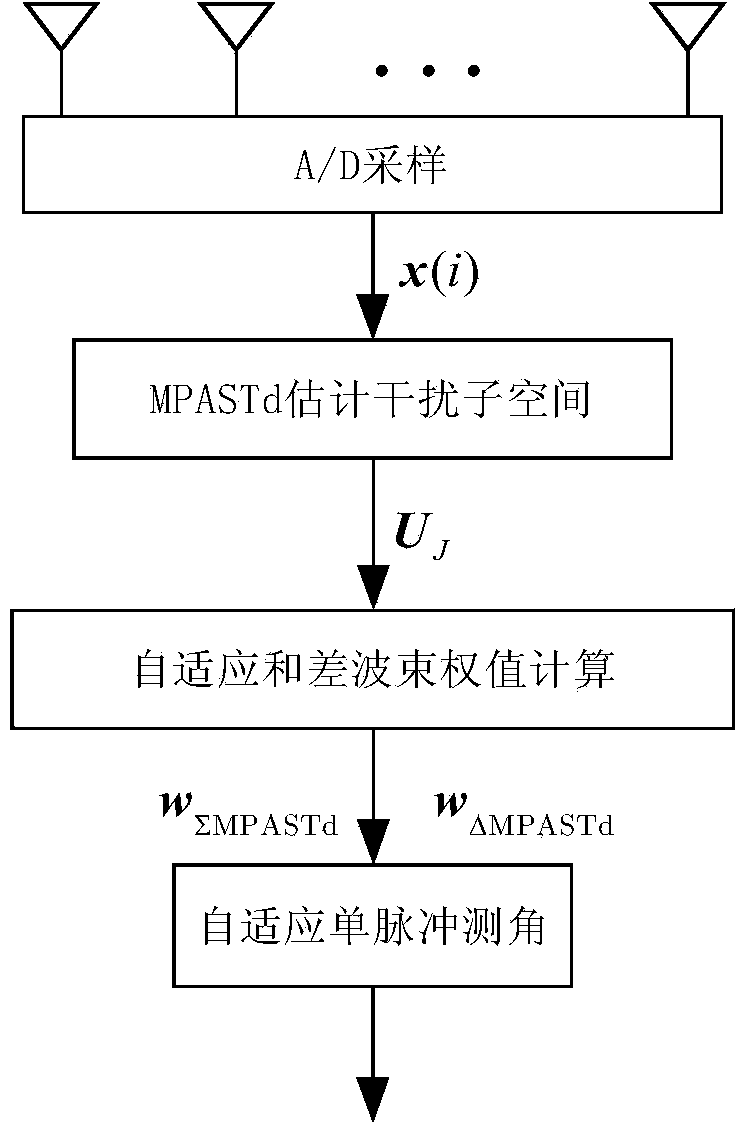
Interference subspace tracking-based high-efficiency self-adaptive monopulse angle measurement method
A technique for interfering with subspace and single-pulse angle measurement, which is applied in measuring devices, radio wave measurement systems, radio wave reflection/re-radiation, etc., and can solve problems such as large amount of computation and slow convergence speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
[0065] 1) Estimation of interference subspace based on MPASTd
[0066] Assuming that the uniform linear array is composed of N array elements, and the antennas of each array element are isotropic, the signal model of its detection unit can be expressed as follows:
[0067] z = a u b+n (1) In the formula, z represents the output signal of the detection unit array, b represents the complex envelope of the target, u represents the direction parameter and u=sinθ, θ is the azimuth angle of the target, Superscript T Represents the transposed symbol, λ is the wavelength of the transmitted signal, d is the distance between array elements, and n represents interference plus noise. Assume that the interference plus noise obeys a Gaussian distribution with a mean value of 0 and a covariance of Q, and the interference, noise and target are not correlated with each other.
[0068] The MPASTd algorithm is improved on the basis of PASTd. For radar application scenarios, first use the sa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com