Programming method for flash memory device
A flash memory device and programming method technology, applied in static memory, read-only memory, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of flash memory device upgrade and key size reduction, large depletion layer width, device punch-through, etc., to improve reliability, increase Cell density, the effect of increasing storage capacity and density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example Embodiment
[0026] Embodiment one
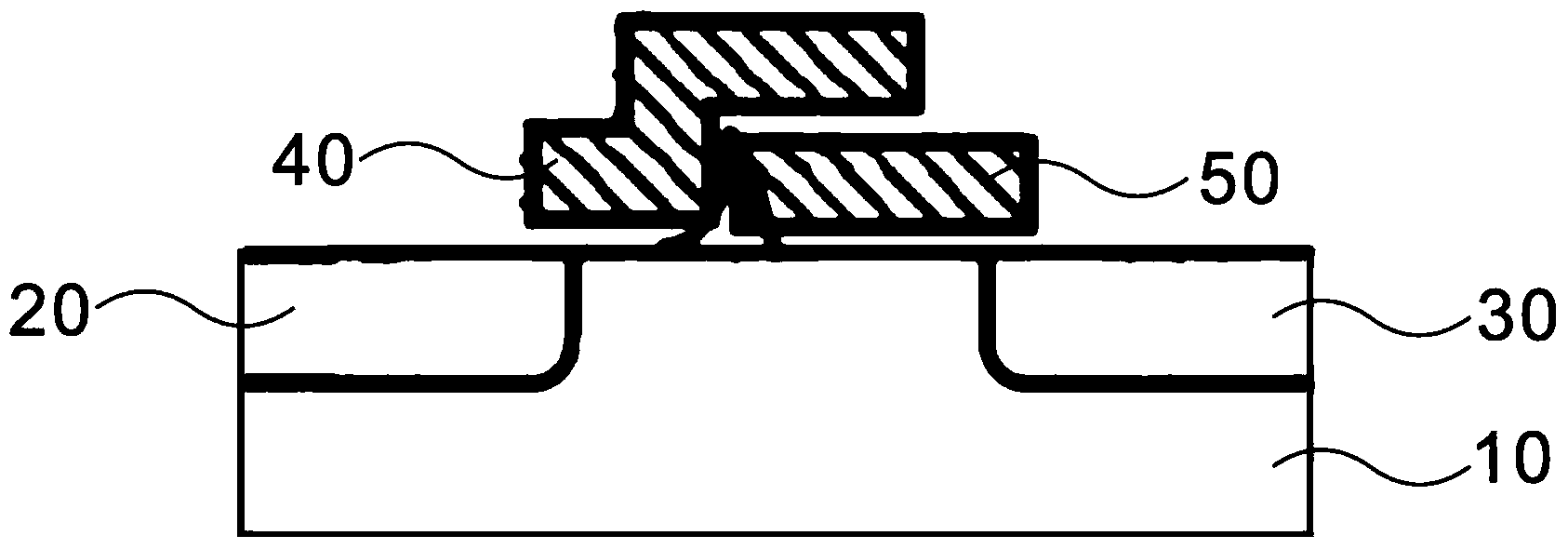
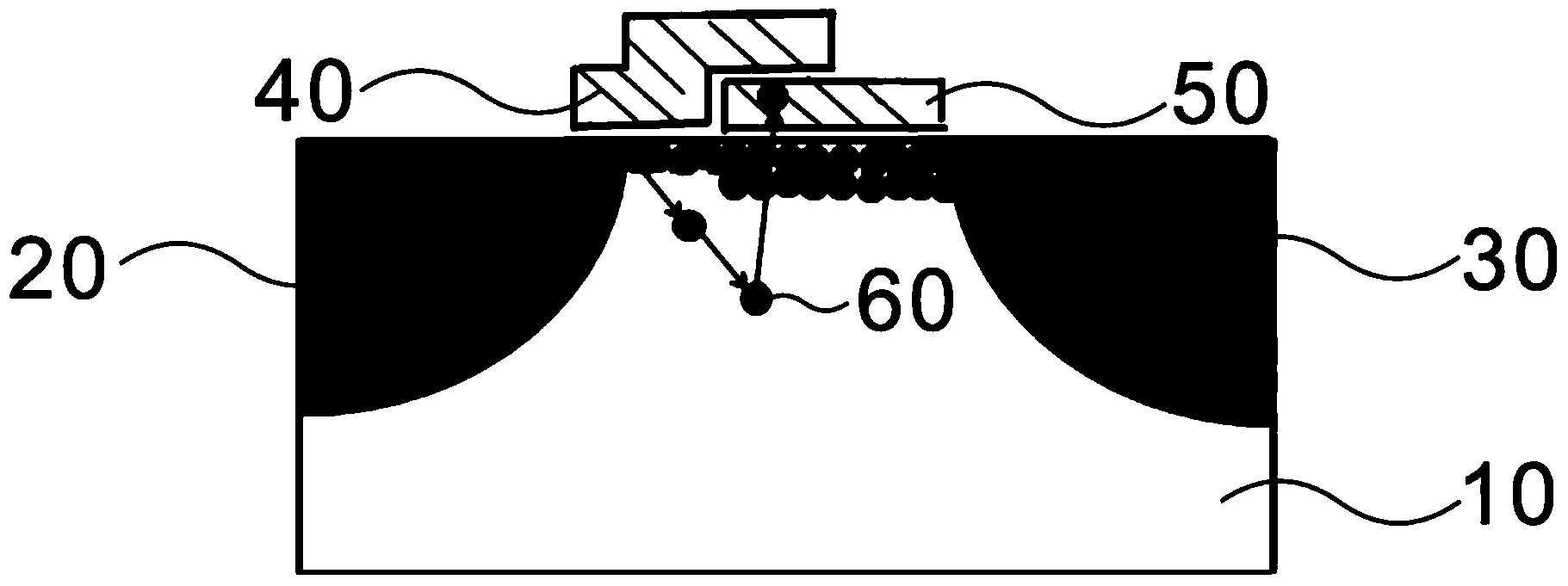
[0027] The semiconductor substrate 10 is a P-type substrate, the material of the control gate 40 and the floating gate 50 is polysilicon, and the material of the oxide layer is silicon dioxide, wherein the control gate 40 has a length of 10 nm and a height of 90 nm, and the floating gate 50 has a height of 70 nm and a length of 40 nm. , the thickness of the oxide layer is 2nm; during the programming operation, the threshold voltage Vth of the flash memory device is 0.7V, the applied voltage to the drain terminal 30 is 2V, the applied voltage to the floating gate 50 is 3V, and the applied voltage to the control gate 40 is The voltage is 0.7V, the voltage applied to the semiconductor substrate 10 is 1.5V, and the voltage applied to the source terminal 20 is 0V.
Example Embodiment
[0028] Embodiment two
[0029] The semiconductor substrate 10 is a P-type substrate, the material of the control gate 40 and the floating gate 50 is polysilicon, and the material of the oxide layer is silicon dioxide, wherein the control gate 40 has a length of 10 nm and a height of 90 nm, and the floating gate 50 has a height of 70 nm and a length of 40 nm. , the thickness of the oxide layer is 3.5nm; during the programming operation, the threshold voltage Vth of the flash memory device is 0.7V, the applied voltage to the drain terminal 30 is 3V, the applied voltage to the floating gate 50 is 2V, and the control gate 40 The applied voltage is 1V, the applied voltage of the semiconductor substrate 10 is 1V, and the source terminal 20 is applied with a voltage of 0V.
[0030] The manufacturing method of the flash memory device provided by the present invention is an existing manufacturing method of the flash memory device, which can be obtained by those skilled in the art throu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com