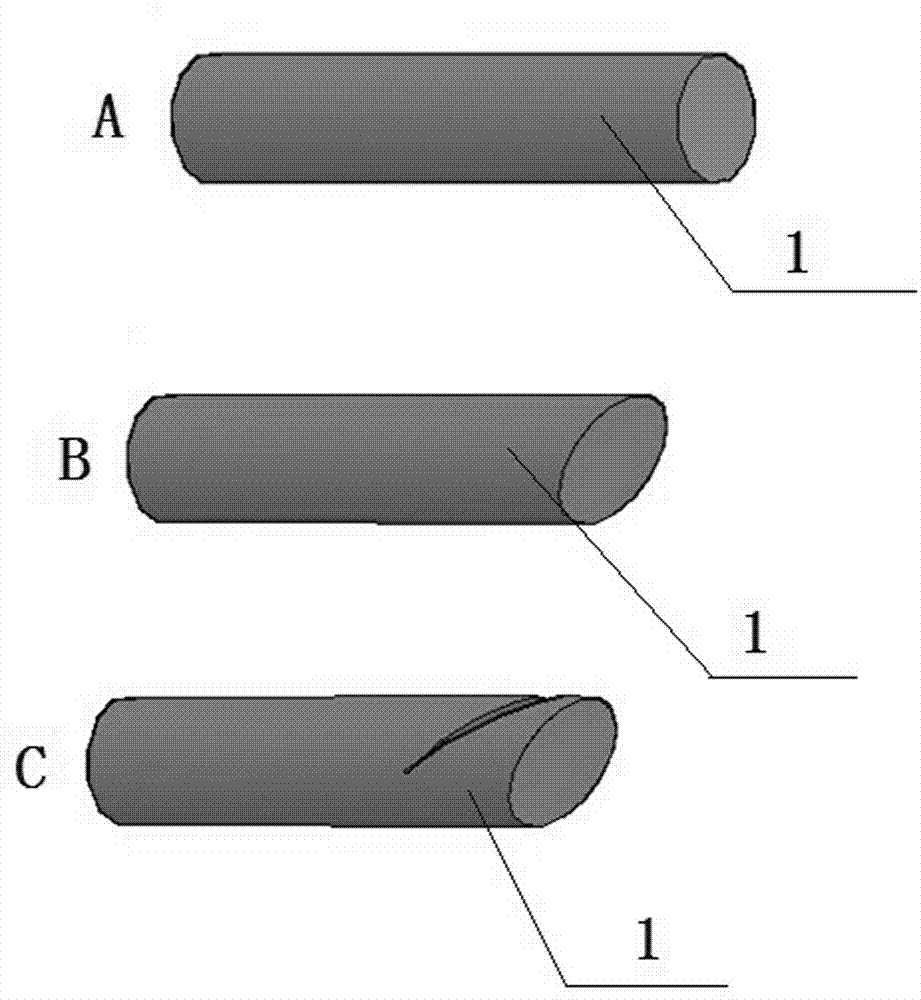
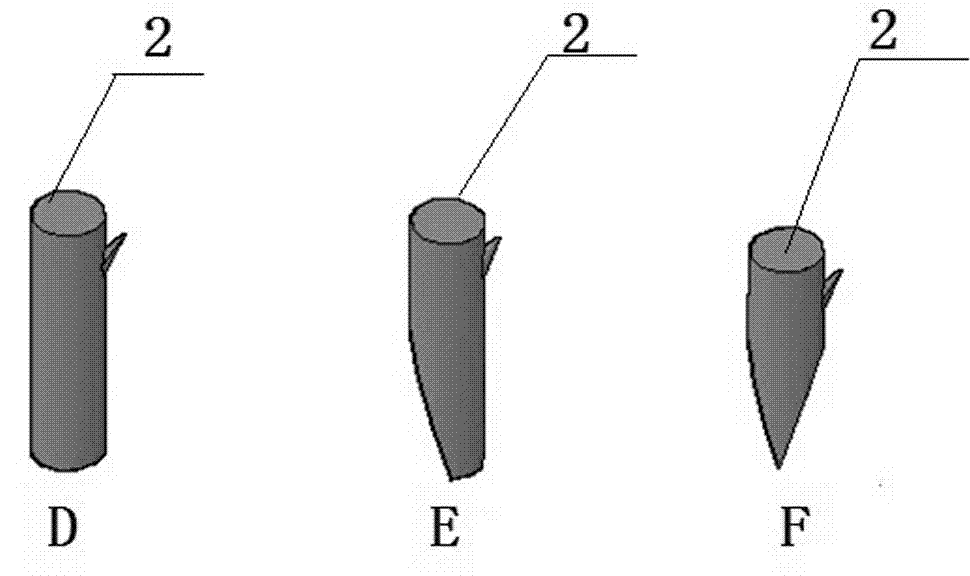
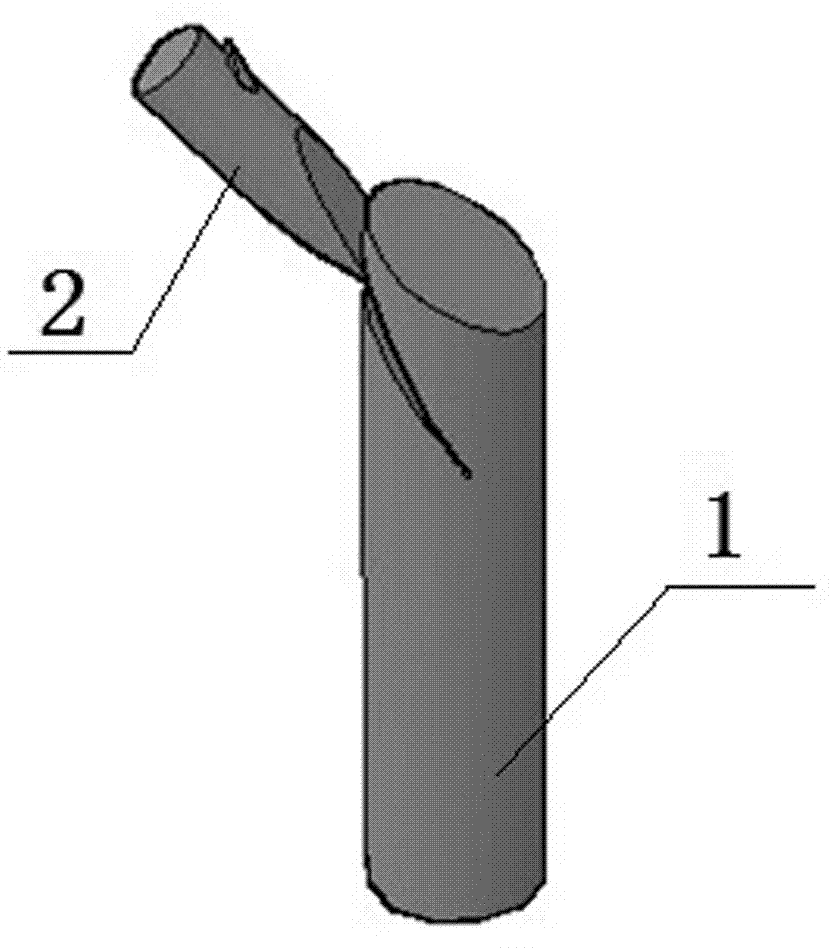
Method for grafting other species on stiff branch of tree
A hard branch grafting and tree technology, which is applied in the field of tree hard branch grafting to other varieties, can solve the problems of branch rot, new branches are easy to be broken by the wind, and heavy pruning workload, etc., to achieve the effect of vigorous life and vitality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] During the production period, "twig single-bud hard branch grafting and replanting technology" for pear, apple, apricot, plum and jujube.
[0029] 1. Grafting time: pears, apricots, and plums are grafted when the flower buds are enlarged and the inflorescences are exposed to the initial flowering stage; apples are grafted from the leaf development stage to the early flowering stage; jujube is carried out from the germination stage to the leaf development stage. If the grafting time is too early, the sap does not start to flow, and the rootstock and scion are not easy to heal; if the grafting time is too late, flowering consumes a lot of nutrients in the tree body, affecting survival and the growth of new branches after survival.
[0030] 2. Selection of rootstocks for "twigs": For fruit trees that are planned to change varieties, keep the original tree shape and tree structure basically unchanged, and according to the original tree crown and branch spatial distribution, ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] During the production period, "twig single-bud hard branch grafting and replanting technology" for pear, apple, apricot, plum and jujube.
[0040] 1. Grafting time: pears, apricots, and plums are grafted when the flower buds are enlarged and the inflorescences are exposed to the initial flowering stage; apples are grafted from the leaf development stage to the early flowering stage; jujube is carried out from the germination stage to the leaf development stage. If the grafting time is too early, the sap does not start to flow, and the rootstock and scion are not easy to heal; if the grafting time is too late, flowering consumes a lot of nutrients in the tree body, affecting survival and the growth of new branches after survival.
[0041] 2. Selection of rootstocks for "twigs": For fruit trees that are planned to change varieties, keep the original tree shape and tree structure basically unchanged, and according to the original tree crown and branch spatial distribution, ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] During the production period, "twig single-bud hard branch grafting and replanting technology" for pear, apple, apricot, plum and jujube.
[0051] 1. Grafting time: pears, apricots, and plums are grafted when the flower buds are enlarged and the inflorescences are exposed to the initial flowering stage; apples are grafted from the leaf development stage to the early flowering stage; jujube is carried out from the germination stage to the leaf development stage. If the grafting time is too early, the sap does not start to flow, and the rootstock and scion are not easy to heal; if the grafting time is too late, flowering consumes a lot of nutrients in the tree body, affecting survival and the growth of new branches after survival.
[0052] 2. Selection of rootstocks for "twigs": For fruit trees that are planned to change varieties, keep the original tree shape and tree structure basically unchanged, and according to the original tree crown and branch spatial distribution, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com