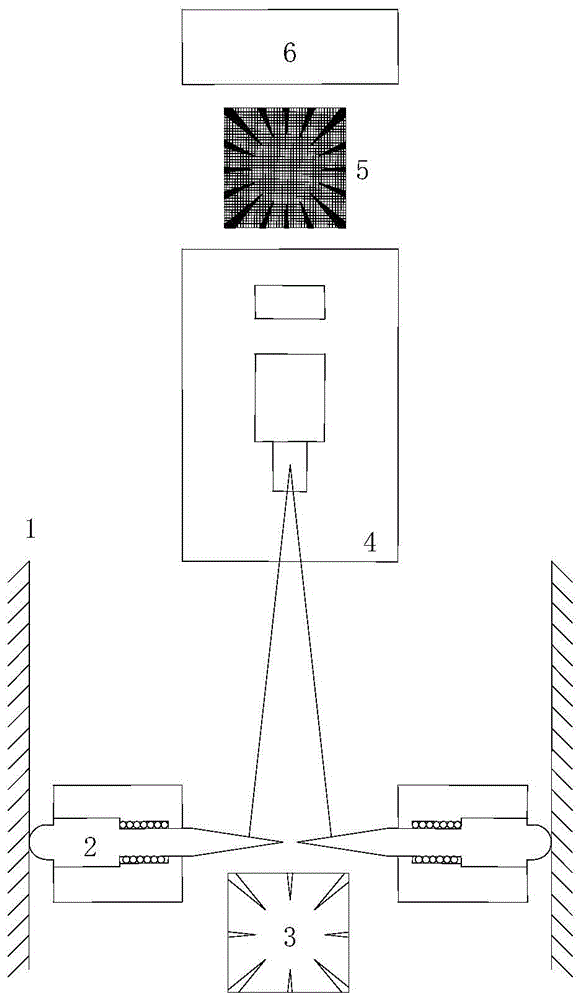
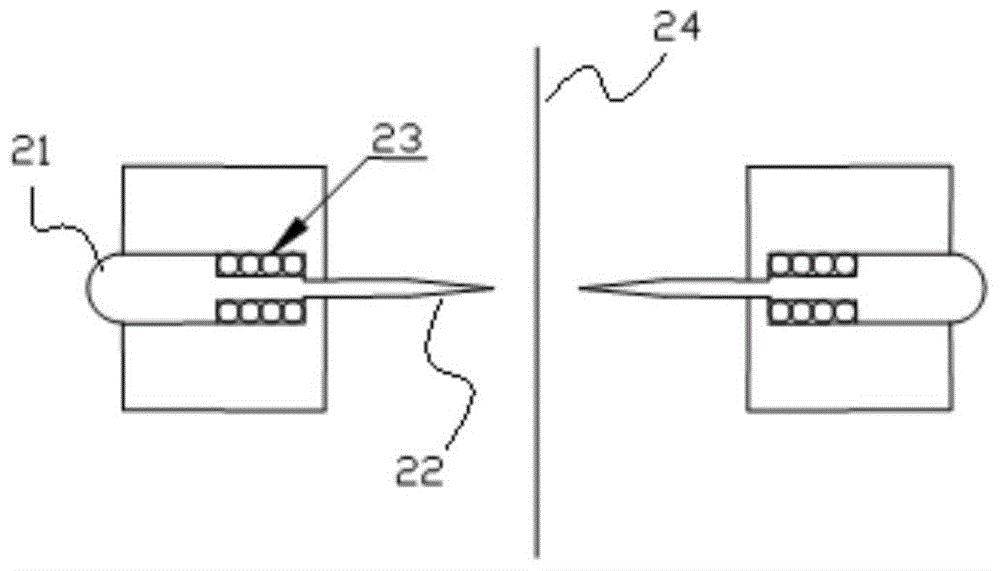
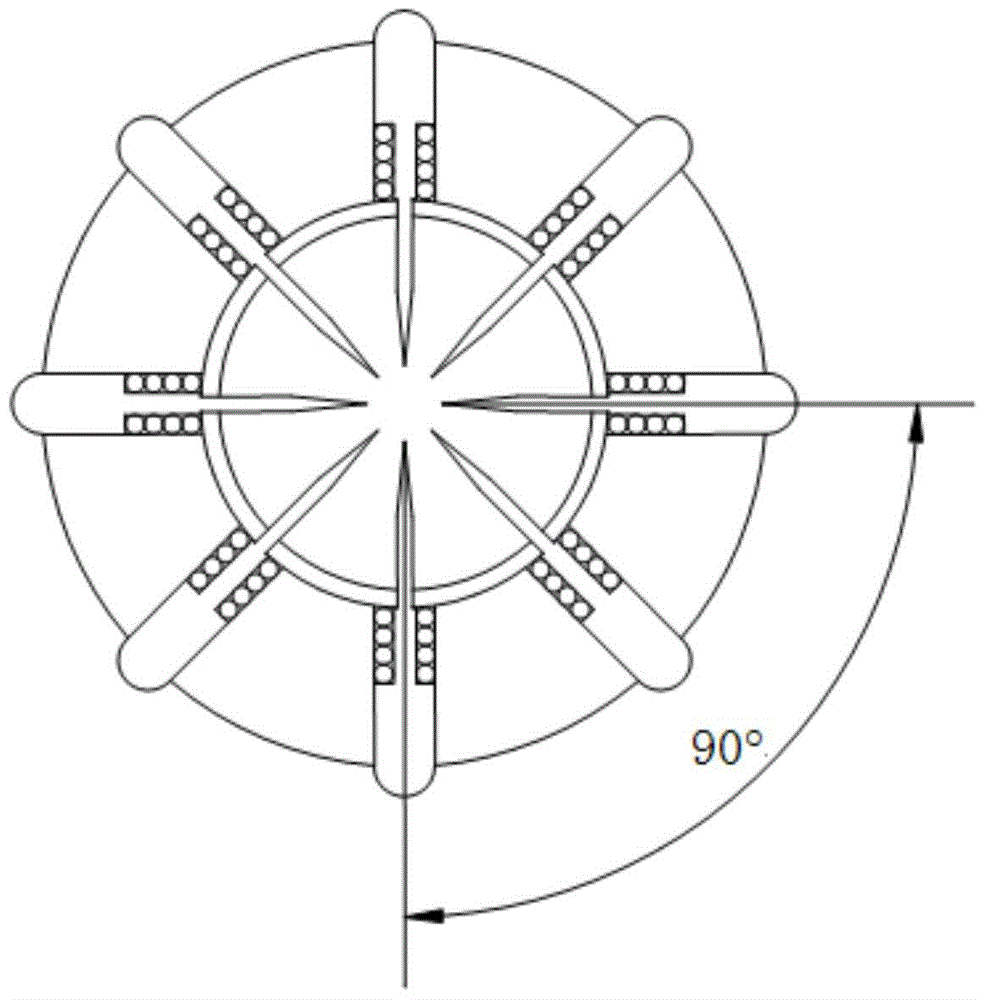
An in-situ stress test method for optical microscopic measurement of aperture deformation
A technique of optical microscopy and aperture measurement, which is applied in the measurement device, the use of optical devices, and the measurement of force by measuring the change of optical properties of materials when they are stressed. In order to achieve the effect of reducing the requirements of the test environment, improving the test ability, significant scientific significance and economic and practical value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0116] Embodiment 1: step 1, comprehensive selection
[0117] In order to break through the extreme environment of high temperature and high pressure in ultra-deep holes and realize the purpose of in-situ stress measurement based on the principle of aperture deformation, high temperature and high pressure resistant aperture deformation sensing technology, positioning technology and micro deformation measurement technology are necessary. However, considering the particularity of the environment in the borehole and the complexity of ground stress measurement, we chose to separate the aperture deformation sensing part from the positioning and deformation measurement part, and carry out high temperature and high pressure resistance treatment and packaging respectively to solve the problem in this extreme environment. geostress test problems. To this end, a combination of aperture deformation stylus sensing method, non-contact optical microscopic imaging technology, micro deformati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com