A SERS substrate material and its hot spot excitation method and characterization
A base material and hotspot technology, applied in the field of SERS base materials, can solve the problems that the expected effect cannot be fully achieved, difficult to synthesize metal nanomaterials, difficult to operate and control, etc., and achieve the effect of wide applicable wavelength range, low cost and mild conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
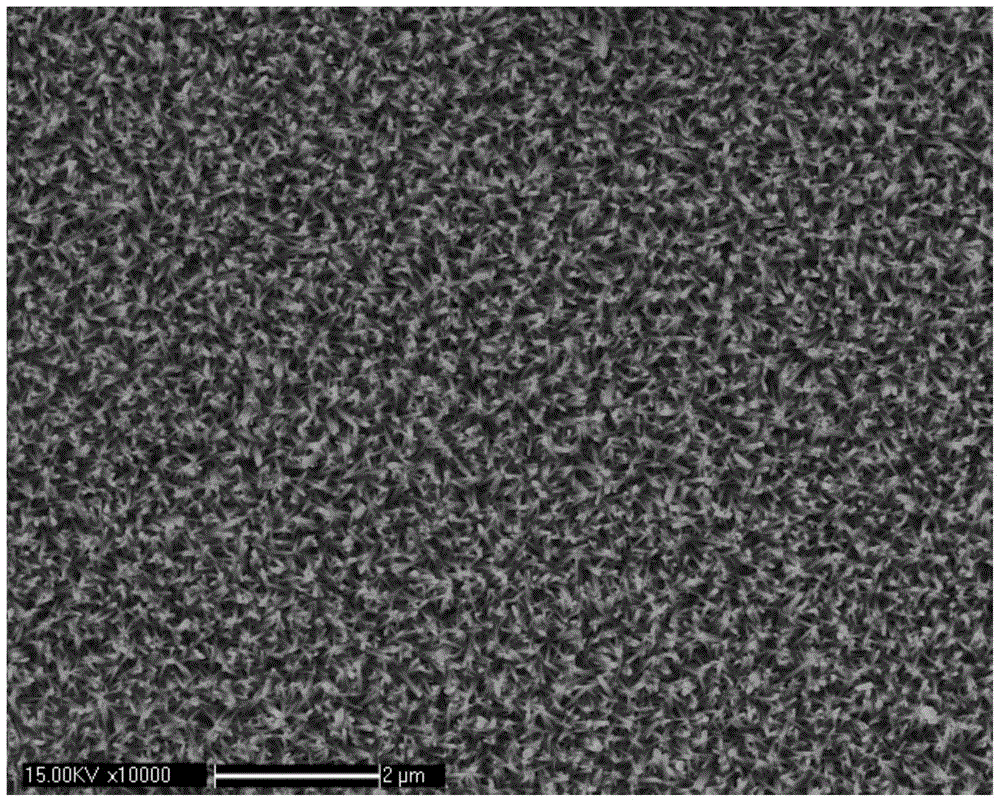
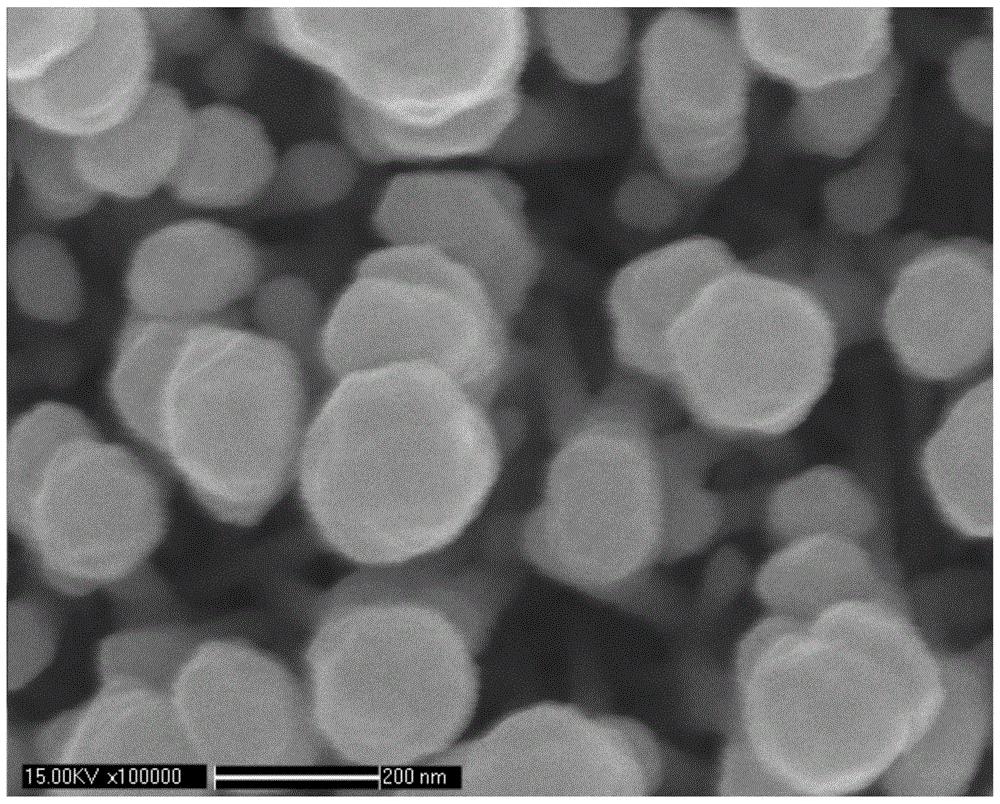
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
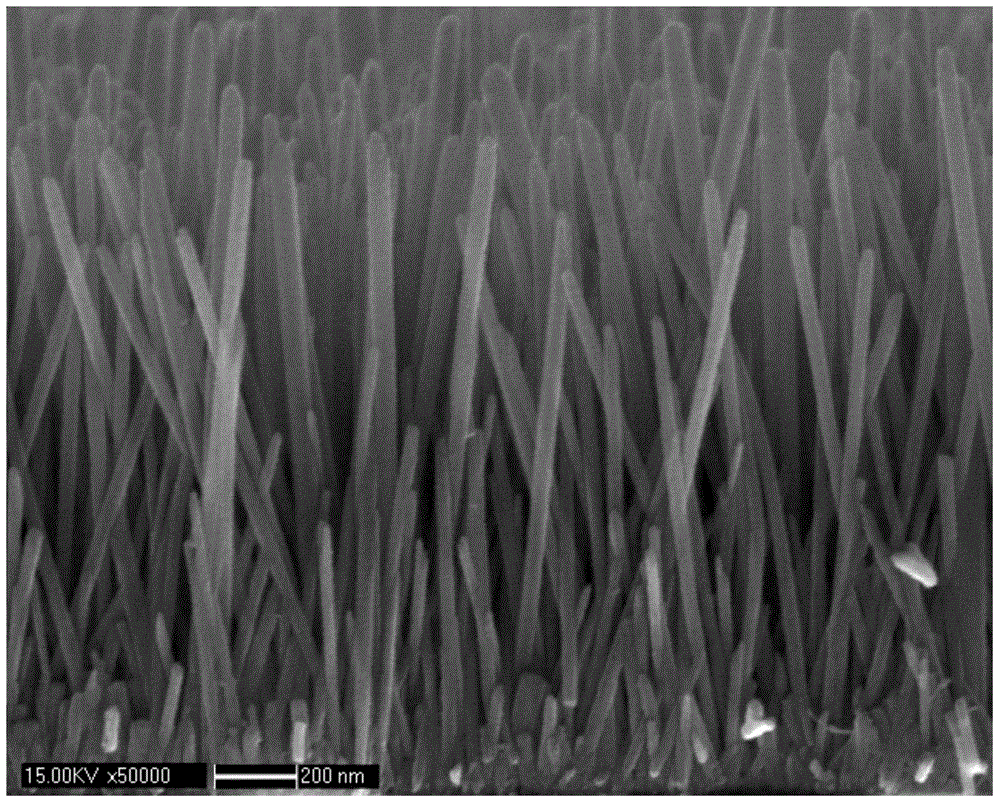
[0054] Step 1: Cut the silicon wafer into 1.5cm×1.5cm strips, ultrasonically clean them one by one with acetone, alcohol, and deionized water and dry them, and place them vertically in an airtight container for later use;
[0055] Step 2: Make a zinc seed layer on the clean silicon wafer in step 1, and evacuate the magnetron sputtering chamber to a chamber pressure of 1×10 -1 ~1×10 -4 mmHg, use metal zinc with a purity of 99.99% as the target to vapor-deposit the silicon wafers placed in the chamber of the magnetron sputtering instrument after step 1, and the vapor-deposition time is not less than 2 minutes;
[0056] Step three: through Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O (purity of 99.998%) powder was dissolved in deionized water to prepare 0.025mol / L of Zn(NO 3 ) 2 Solution, prepare an equimolar hexamethylenetetramine (HMT) solution at the same time, put the silicon chip processed in step 2 into the mixed solution, the surface of the silicon chip needs to be completely immersed, and ca...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Immerse the substrate material prepared in Example 1 into the probe 4-ATP modification solution, the soaking time is controlled to 4-12 hours, and a surface monomolecular layer with probe molecules is obtained through self-assembly, and the monomolecular layer is passed through the mercapto group. Adsorbed on the ZnO-Ag surface of the base material to form a composite base material. Using water as the solvent to excite the hot spot, quantify 5 microliters to the central surface of the composite substrate material, and perform time-resolved Raman spectroscopy test at the same time, observe as follows: Figure 4 It can be found that the intensity of the Raman spectrum does not change substantially as shown by the change of the spectral intensity over time, while Figure 4 The small inset in the upper right corner is the experimental diagram of the contact angle between solvent water and the base material. As shown in the figure, the contact angle between water and the com...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Immerse the substrate material prepared in Example 1 into the probe 4-ATP modification solution, the soaking time is controlled at 4-12 hours, and a surface monomolecular layer with probe molecules is obtained through self-assembly, and the monomolecular layer is passed through the mercapto group. Adsorbed on the ZnO-Ag surface of the base material to form a composite base material. Using ethanol as the hot spot solvent, first test the contact angle between ethanol and the composite substrate material, such as Figure 5 The inset in the upper right corner shows that the contact angle between ethanol and the composite substrate is zero degrees, indicating that ethanol can completely wet the composite substrate material. Quantitatively add 5 microliters of ethanol to the central surface of the composite substrate material, and simultaneously perform time-resolved Raman spectrum testing to observe the changes in Raman spectrum intensity over time. Figure 5 It can be seen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com