Method for preparing nanoscale zero-valent iron and nanoscale duplex metal Cu/Fe
A nano-scale, zero-valent iron technology, applied in nanotechnology and other directions, can solve the problems of easy agglomeration and uneven particle distribution, and achieve the effects of rapid reaction, uniform particle size distribution and simple preparation method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
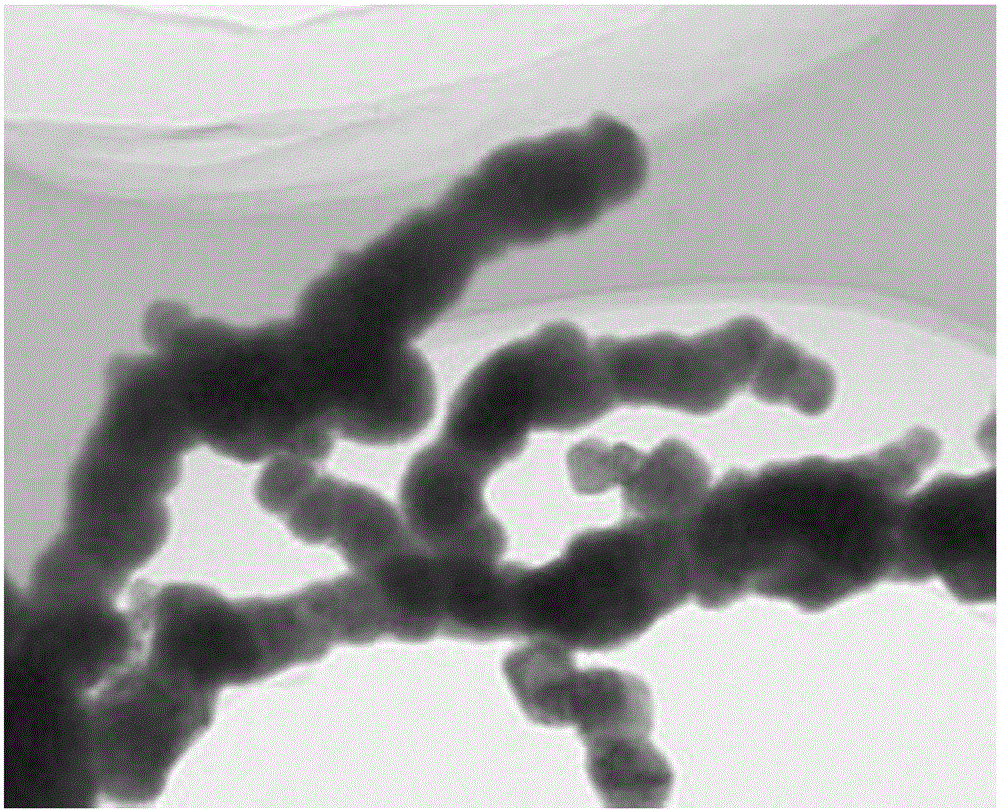
[0042] Under the action of ultrasonic (40KHz, 150W) and continuous stirring under nitrogen, the temperature of the water bath is 30°C, and the concentration of 200mL is 0.50mol L -1 NaBH 4 The aqueous solution was added dropwise within 25min to a container containing 200mL 0.25mol·L -1 FeSO 4 ·7H 2 In a 500mL three-necked flask of O aqueous solution, continue to react for 10 minutes after the dropwise addition, and then nano-sized zero-valent iron particles can be prepared. The prepared nano-sized zero-valent Wash thoroughly with ionic water for 4 times, then fully wash with 200mL absolute ethanol for 4 times, and then store in absolute ethanol.
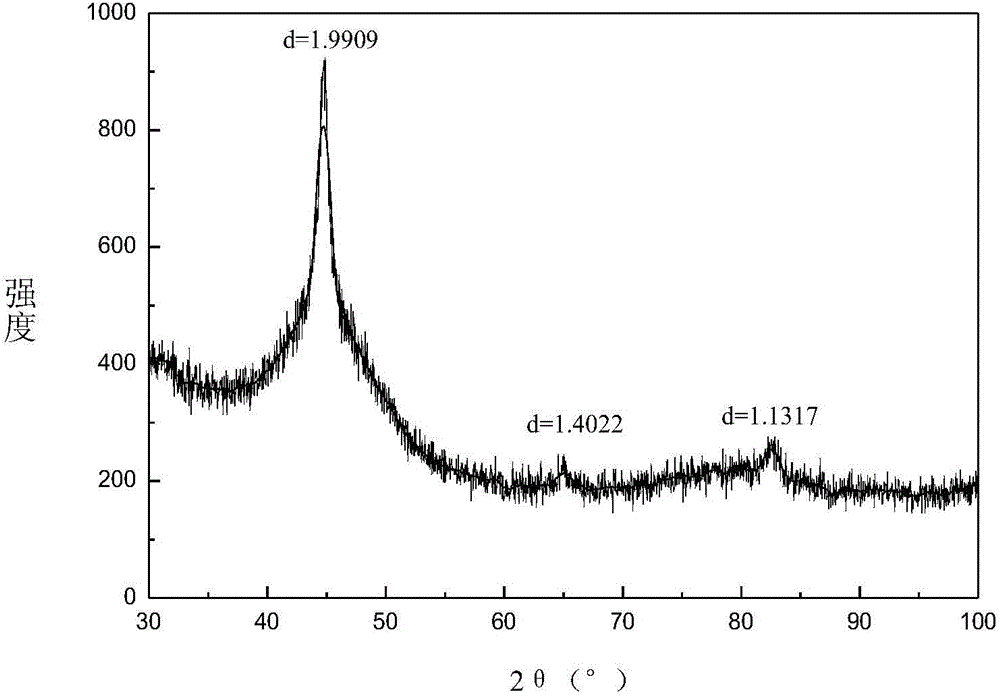
[0043] XRD spectrum as figure 1 shown. The XRD test results show that: when the scanning diffraction angle (2θ) is 30-100°, the corresponding 2θ when the diffraction peaks appear are 44-46°, 64-66°, 81-83°, corresponding to the standard PDF card of iron It was found that the corresponding 110-plane diffraction (44.6732°), 200-p...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Under the action of ultrasonic (40KHz, 100W) and continuous stirring under nitrogen, the temperature of the water bath is 30°C, and the concentration of 200mL is 0.50mol L -1 NaBH 4 The aqueous solution was added dropwise within 25min to a container with an equal volume of 0.25mol·L -1 FeSO 4 ·7H 2 In a 500mL three-neck flask of O aqueous solution, continue to react for 10 minutes after the dropwise addition, and then nano-scale zero-valent iron particles can be prepared. Fully washed, then fully washed with absolute ethanol, and stored in absolute ethanol.
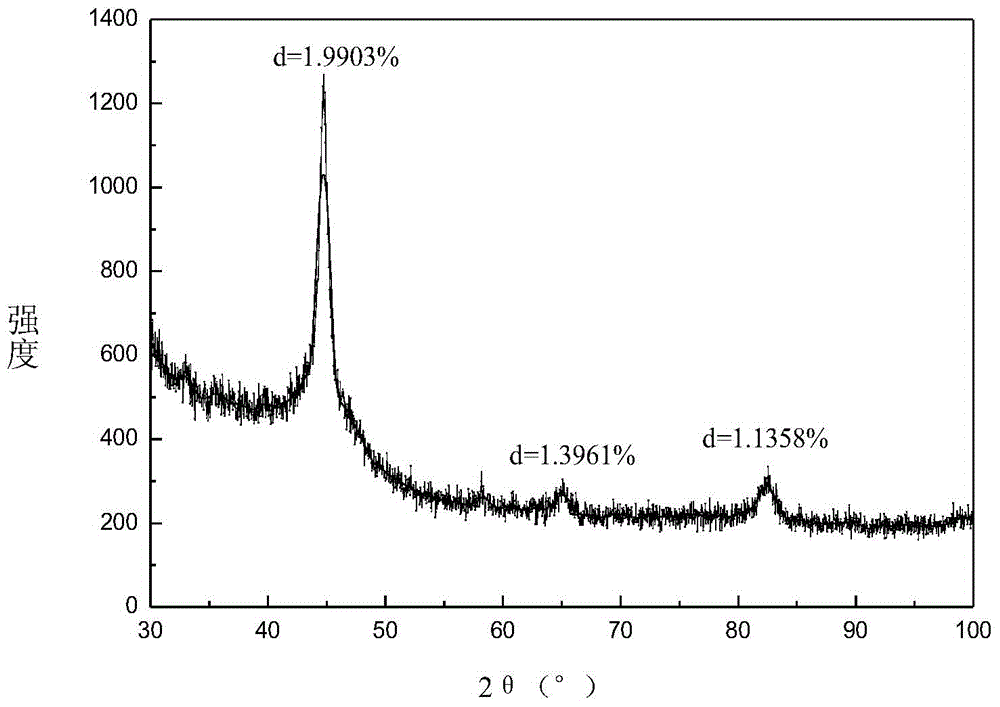
[0048] The XRD test results show that: when the scanning diffraction angle (2θ) is 30-100°, the corresponding 2θ when the diffraction peaks appear are 44-46°, 64-66°, 81-83°, corresponding to the standard PDF card of iron It was found that the corresponding 110-plane diffraction (44.6732°), 200-plane diffraction (65.0211°) and 211-plane diffraction (82.3326°) corresponded exactly, indicating that the particles ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Under the action of ultrasonic (20KHz, 150W) and continuous stirring nitrogen, the temperature of the water bath is 30 ℃, and the concentration of 200mL is 0.50mol L -1 NaBH 4 The aqueous solution was added dropwise within 25min to a container with an equal volume of 0.25mol·L -1 FeSO 4 ·7H 2 In a 500mL three-neck flask of O aqueous solution, continue to react for 10 minutes after the dropwise addition, and then nano-scale zero-valent iron particles can be prepared. Fully washed, then fully washed with absolute ethanol, and stored in absolute ethanol.
[0053] The XRD test results show that: when the scanning diffraction angle (2θ) is 30-100°, the corresponding 2θ when the diffraction peaks appear are 44-46°, 64-66°, 81-83°, corresponding to the standard PDF card of iron It was found that the corresponding 110-plane diffraction (44.6732°), 200-plane diffraction (65.0211°) and 211-plane diffraction (82.3326°) corresponded exactly, indicating that the particles were e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com