Method for preparing nanometer zero-valent iron based on liquid-phase complexation reduction method
A technology of nano-zero-valent iron and reduction method, which is applied in the field of preparation of nano-zero-valent iron and nano-zero-valent iron particles by liquid-phase complexation reduction method, which can solve the problems of time-consuming operation, easy agglomeration, easy oxidation, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of convenient operation, simple equipment and uniform distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] In 20mL of distilled water, add 0.6934g FeSO 4 (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ·6H 2 0 and 0.8032g sulfosalicylic acid, adjust the pH of the solution to be 6, then add 20mL of THF, stir to make it fully mixed. Weigh 0.2gNaBH 4 Dissolve in the mixed system of 20mL THF and water (volume ratio 1:1), and finally drop the sodium borohydride solution into the complex ferrous salt solution at a rate of 2-3 drops / second, and control The reaction time is 15 min, and the nano-iron particles are washed three times with distilled water and absolute ethanol respectively, and then the nano-iron particles are stored in absolute ethanol.
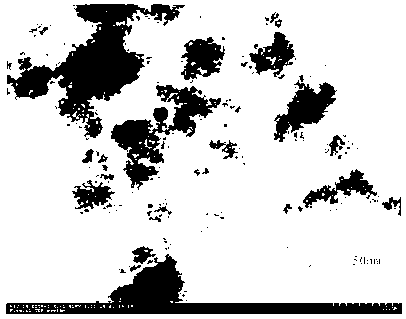
[0043] The test result of TEM shows that the range of particle size is about 5-20m, and the average particle size is 16nm.
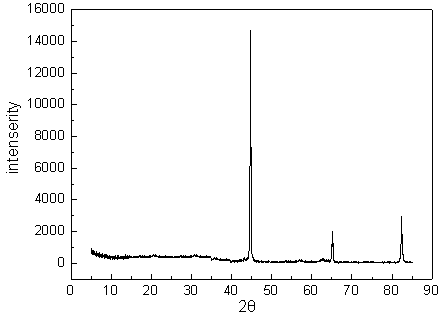
[0044] The XRD test results show that: when the scanning diffraction angle 2θ is 30°~100°, the corresponding 2θ when the diffraction peaks appear are 44.4732°, 65.8241°, and 82.9826°, respectively, and compared with the standard PDF card ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] In 13mL of distilled water, add 0.6986g FeSO 4 (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ·6H 2 0 and 0.8046g sulfosalicylic acid, adjust the pH of the solution to be 6, then add 27mL of THF, stir to make it fully mixed. Weigh 0.2gNaBH 4 Dissolve in the mixed system of 20mL THF and water (volume ratio 1:1), and finally drop the sodium borohydride solution into the complex ferrous salt solution at a rate of 2-3 drops / second, and control The reaction time is 15 min, and the nano-iron particles are washed three times with distilled water and absolute ethanol respectively, and then the nano-iron particles are stored in absolute ethanol.
[0048] The test result of TEM shows that the range of particle size is about 5-20m, and the average particle size is 15nm.
[0049] The XRD test results show that: when the scanning diffraction angle 2θ is 30°~100°, the corresponding 2θ when the diffraction peaks appear are 45.1752°, 65.0724°, and 82.1429°, respectively. Compared with the standard PDF card of i...
Embodiment 3
[0052] In 27mL of distilled water, add 0.7023g FeSO 4 (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ·6H 2 0 and 0.8174g sulfosalicylic acid, adjust the pH of the solution to be 6, then add 13mL of THF, stir to make it fully mixed. Weigh 0.2gNaBH 4 Dissolve in a mixed system of 20mL THF and water (volume ratio 1:1), and finally drop the sodium borohydride solution into the complex ferrous salt at a rate of 2-3 drops / second, and control the reaction after dropping The time is 15 minutes. After washing the nano-iron particles with distilled water and absolute ethanol three times respectively, the nano-iron particles are stored in absolute ethanol.
[0053] The test result of TEM shows that the range of particle size is about 5-20m, and the average particle size is 18nm.
[0054] The XRD test results show that: when the scanning diffraction angle 2θ is 30°~100°, the corresponding 2θ when the diffraction peaks appear are 44.2485°, 65.7484°, and 82.6836°, which are found by comparing the standard PDF card o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com