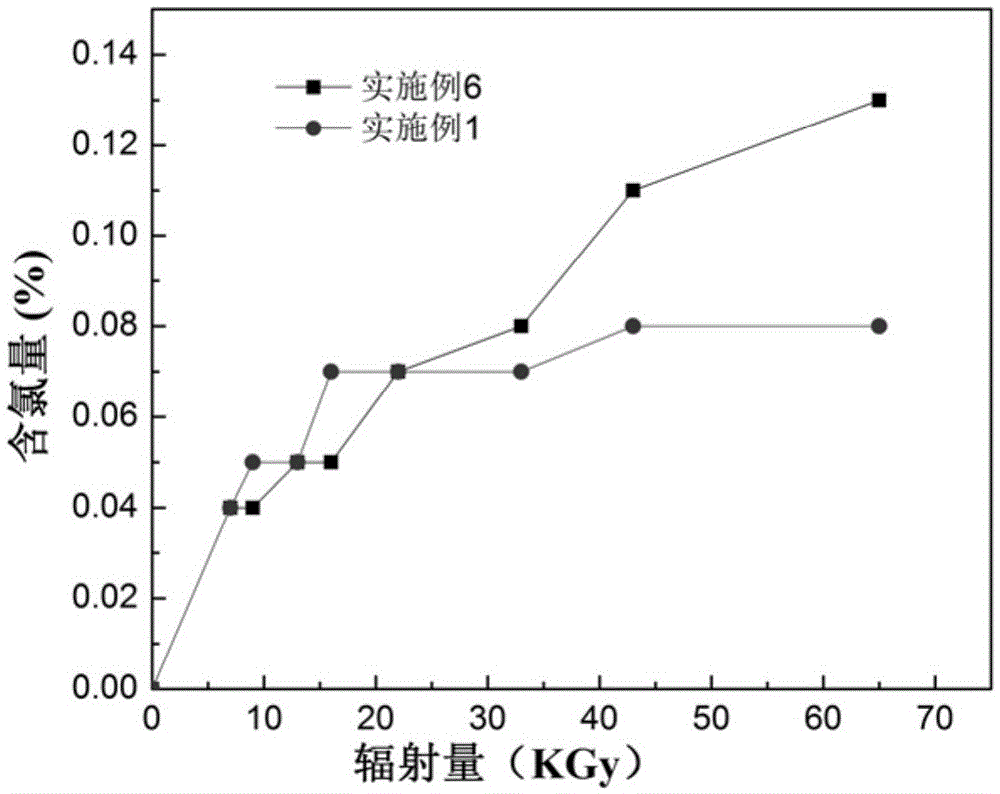
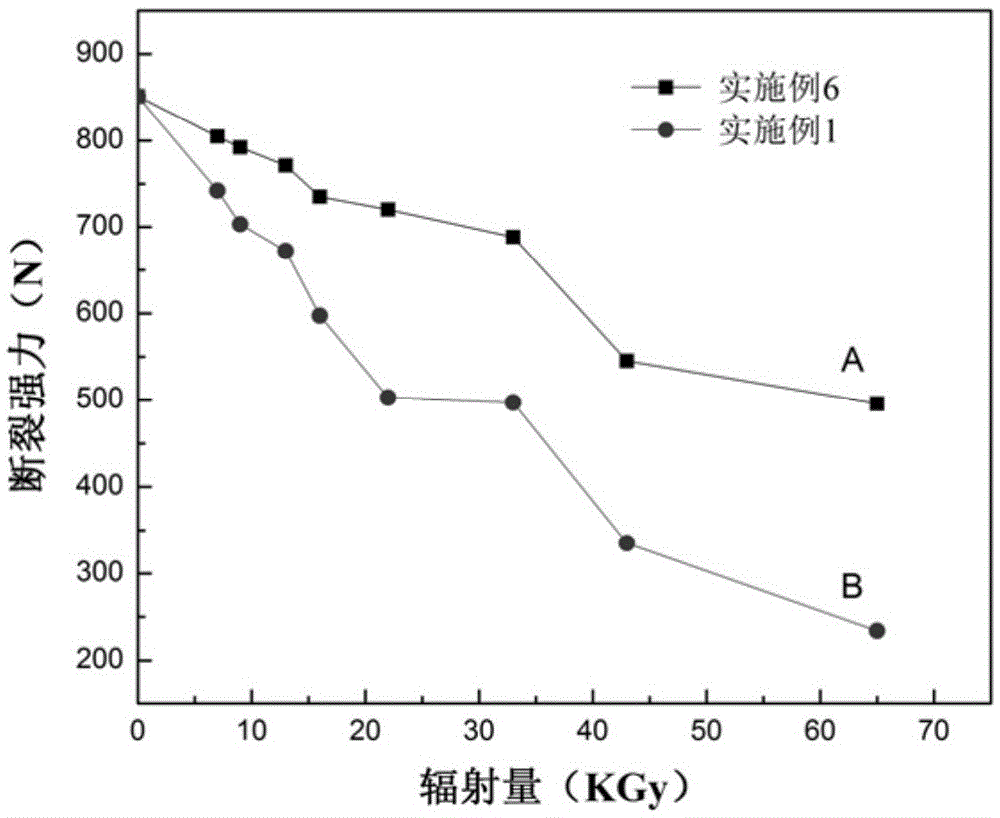
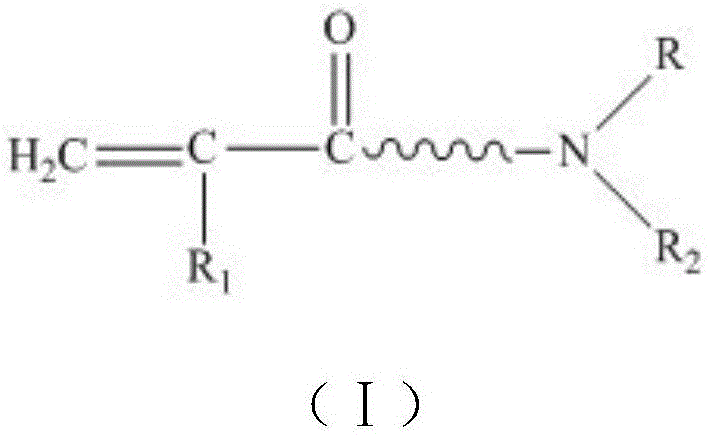
A method for preparing antibacterial textiles using electron radiation technology
A technology of antibacterial textiles and electron radiation, applied in the direction of textiles and papermaking, fiber treatment, physical treatment, etc., can solve the problems of increasing finishing and wastewater treatment costs, uncontrollable factors and side reactions, and difficult control of product quality, etc., to achieve easy Effects of control, high product yield, and improved antibacterial performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0043] 0.5 mol of methacrylamide and 0.05 mol of initiator were dissolved in 100 ml of water, and reacted at 70° C. for 5 min to prepare an oligomer antibacterial liquid. The natural fiber textile to be treated (cotton fabric, purchased from Zhejiang Guandong Printing and Dyeing Garment Co., Ltd.) was processed by 100KGy electron irradiation, immersed in the above-mentioned antibacterial solution for 6 hours, taken out, and dried in a dryer at 60 °C for 30 min. Wash the surface with a large amount of deionized water, soak it in a 0.5% sodium hypochlorite solution after drying, take it out after soaking for 1 hour, wash it with a large amount of water, and dry it in a dryer at 45°C for 1 hour. Antibacterial pure cotton fabrics were obtained. The available chlorine content of the antibacterial pure cotton fabric was measured by iodometric method.
Embodiment 3
[0049] 0.5mol of acrylamide (structure shown below) and 0.025mol of initiator were dissolved in 100ml of water, and reacted at 60°C for 30min to prepare a working solution. After the synthetic fiber (polypropylene non-woven fabric) to be treated is irradiated by 80KGy, and immersed in the above working solution for 2 hours, the polypropylene fabric is taken out, and its surface is washed with a large amount of deionized water. After drying, soak it in a 0.5% sodium hypochlorite solution by mass, take it out after soaking for 1 hour, wash it with a large amount of water, and dry it in a 45°C dryer for 1 hour to obtain an antibacterial polypropylene fabric. The effective chlorine content of the antibacterial polypropylene fabric measured by iodometric method was 0.14%.
[0050]
[0051] 2. Example of co-radiation process
[0052] 1. Example 4
[0053] Immerse the cotton fabric in an aqueous solution containing 10% of 3-acrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride (structure sho...
Embodiment 5
[0056] Immerse the cotton fabric in a solution containing 5% 1,1,2,2-tetramethylpiperidinol acrylate (the structure is shown in Figure IV) / acrylic acid, take it out and press it (the nip rate is 120%). After 65KGy electron irradiation, it was placed in a dryer at 60°C for 30min. After drying, it was soaked in 0.5% sodium hypochlorite solution by mass, soaked for 1 hour, taken out, washed with a large amount of water, and dried in a 45°C dryer for 1 hour to obtain antibacterial cotton fabric. The available chlorine content of the antibacterial cotton fabric measured by iodometric method was 0.23%.
[0057]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com