Channel access method, device and system
A channel access and channel technology, applied in transmission path sub-channel allocation, wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as adjacent frequency band signal interference, access request frame interference, collision, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
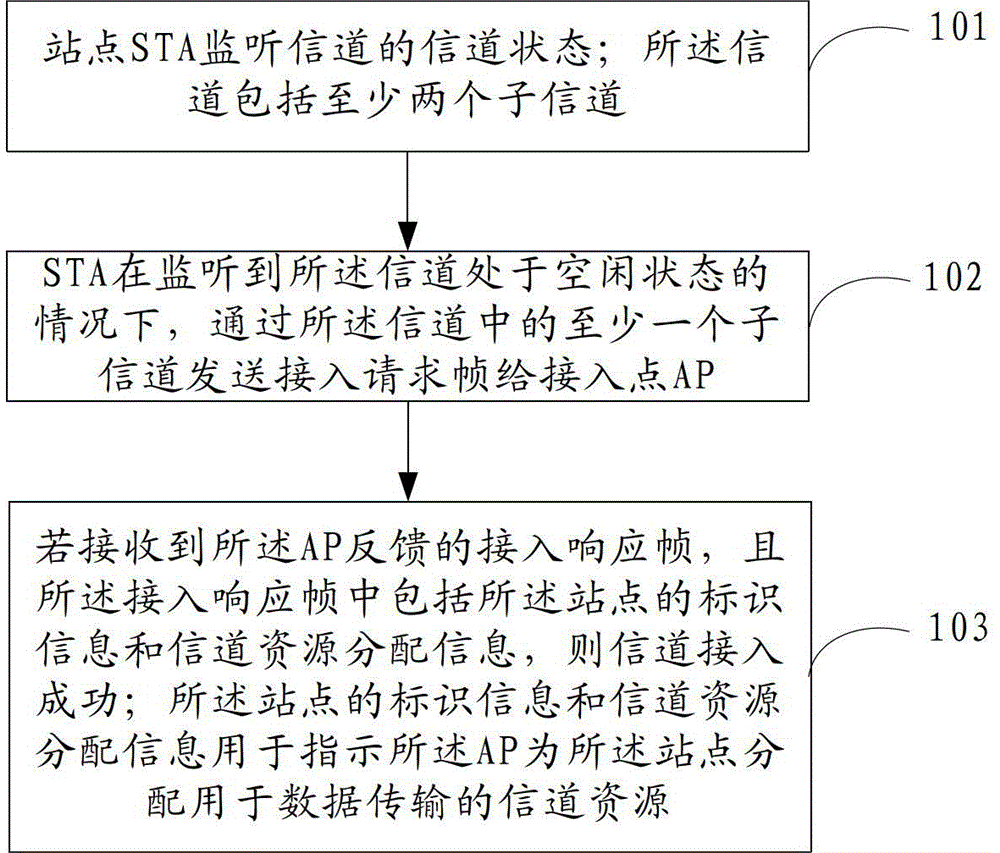
[0129] Step 501, 8 STAs monitor the busy / idle status of the channel. If the idle time of the channel reaches the DIFS time, go to step 502, otherwise stay at step 501.
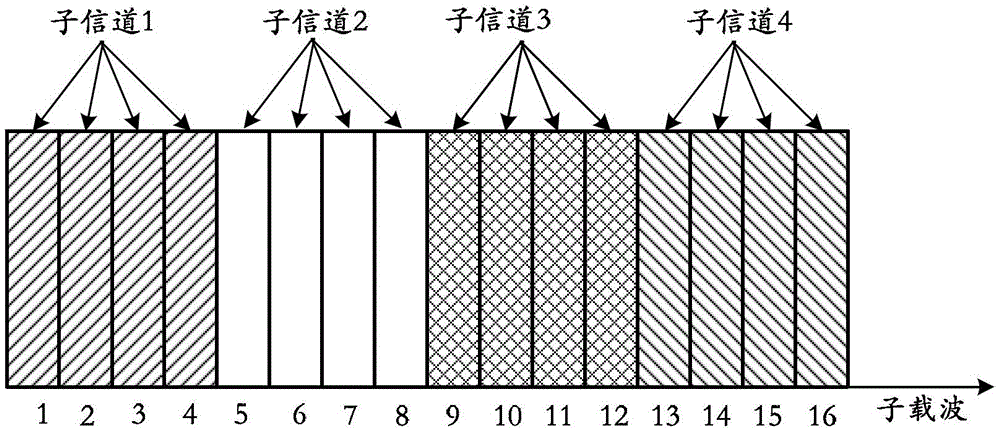
[0130] Specifically, the channel is divided into 4 sub-channels, and the 4 sub-channels are mutually orthogonal. When the energy signal strength in the channel is greater than or equal to the preset threshold, the channel is considered to be in a busy state; when the energy signal strength in the channel is less than the preset threshold, the channel is considered to be in an idle state.
[0131] Step 502 , assuming that STA1 , STA2 , STA3 and STA4 all select the backoff time to be 2T, and the backoff time selected by STA5 , STA6 , STA7 and STA8 are all greater than 2T, perform a backoff process.
[0132] Step 503. After 2T time, the STA with a backoff time of 2T randomly selects a subchannel to send an RTS frame to the AP, and then proceeds to step 504; the STA with a backoff time greater than 2T proceeds to...
Embodiment 2
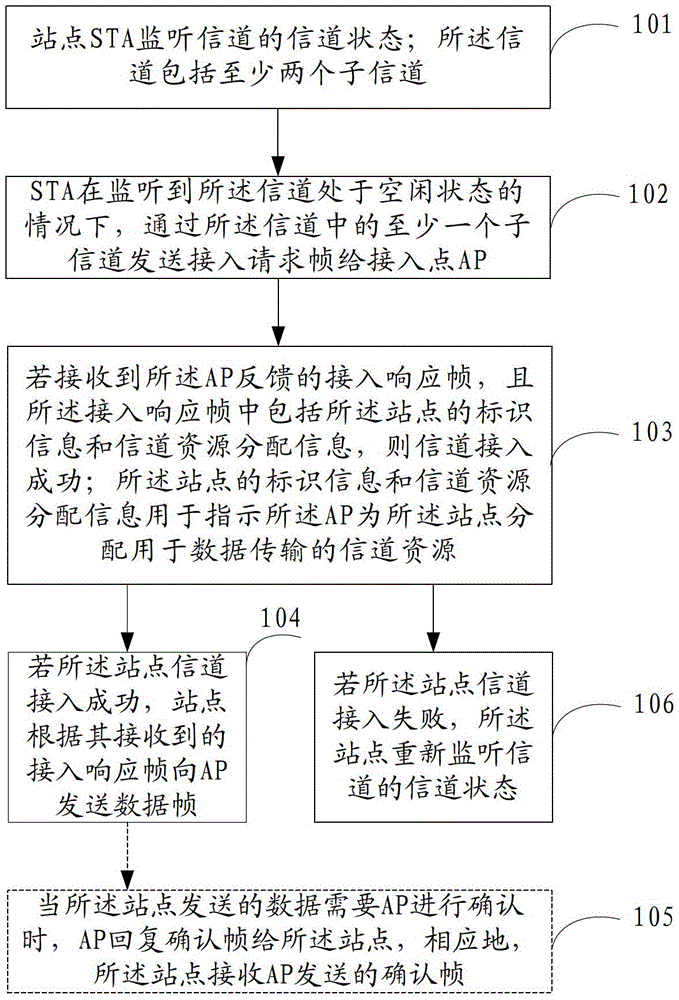
[0141] This embodiment provides a method for data transmission when channel access is successful, including: steps 501-504 in Embodiment 1, which are steps 601-604 in this embodiment, which will not be repeated here. Such as Figure 6 As shown, this embodiment also includes:
[0142] Step 605, STA1 and STA2 according to the received G-CTS frame, after waiting for the channel to be free for SIFS time, STA1 sends DATA1 frame to AP on sub-channel 1 and sub-channel 2, STA2 sends DATA2 frame on sub-channel 3 and sub-channel 4 to AP. Correspondingly, the AP receives the DATA1 frame sent by STA1 and the DATA2 frame sent by STA2.
[0143] Specifically, STA1, STA2, STA3, and STA4 receive the G-CTS frame sent by the AP through the channel. Since the G-CTS frame only contains the channel resource allocation information for STA1 and STA2, it does not contain the channel resource allocation information for STA3 and STA4. Resource allocation information, so after STA1 and STA2 wait for t...
Embodiment 3
[0150] Next, the present invention also provides another specific embodiment, which describes in detail the method for data transmission when the channel access is successful.
[0151] In this embodiment, steps 501-504 in Embodiment 1 are included, which are steps 701-704 in this embodiment, which will not be repeated here. Such as Figure 7 As shown, this embodiment also includes:
[0152] Step 705. According to the received G-CTS frame, STA1 and STA2 send the DATA1 frame to the AP on the entire channel after STA1 waits for the channel to be idle for SIFS time, and STA2 waits for the channel to be idle for SIFS time before sending the DATA2 frame on the entire channel to AP. Correspondingly, the AP receives the DATA1 frame sent by STA1 and the DATA2 frame sent by STA2, such as Figure 7 shown in .
[0153] If the data sent by STA1 and STA2 (for example: broadcast frame, multicast frame) does not require the AP to confirm, then the AP only needs to receive the data sent by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com