T-connection power grid transient state quantity unit protection method utilizing voltage and current abrupt change quantity wavelet coefficient correlation analysis
A technology of wavelet coefficient and correlation analysis, applied to electrical components, emergency protection circuit devices, etc., can solve the problems of linkage protection failure, unpredictable compensation voltage phase change, refusal to operate, etc., to improve accuracy, improve reliability, reduce risk effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
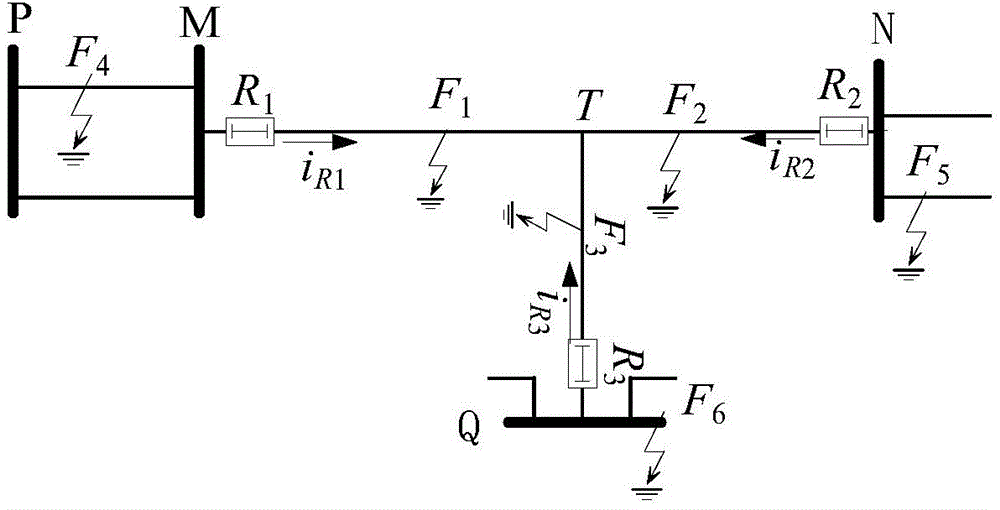
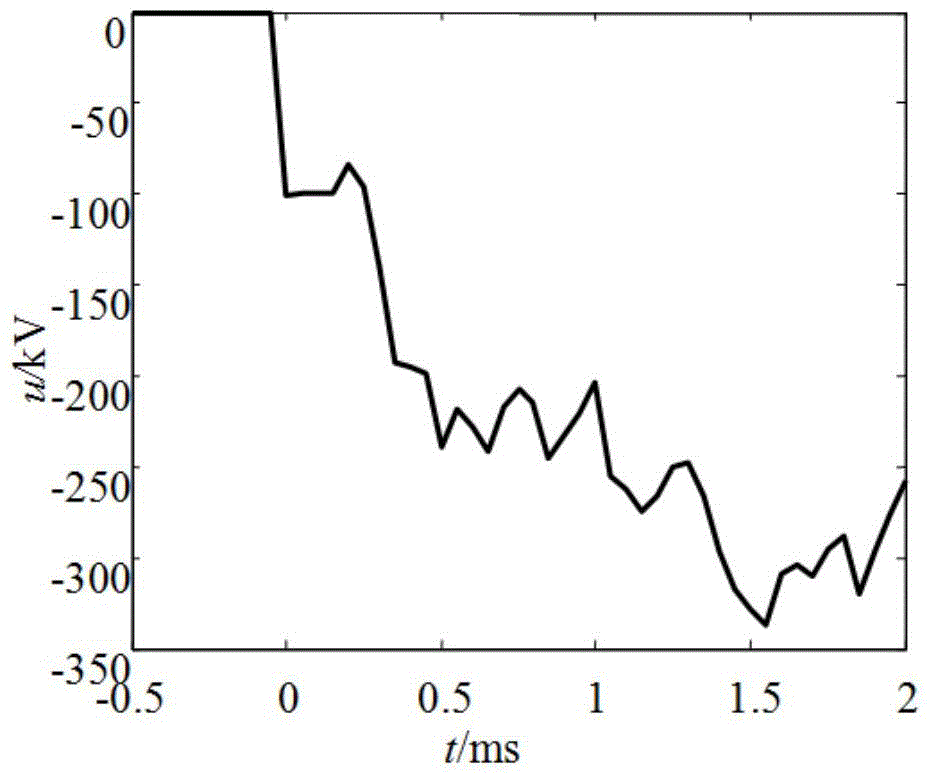
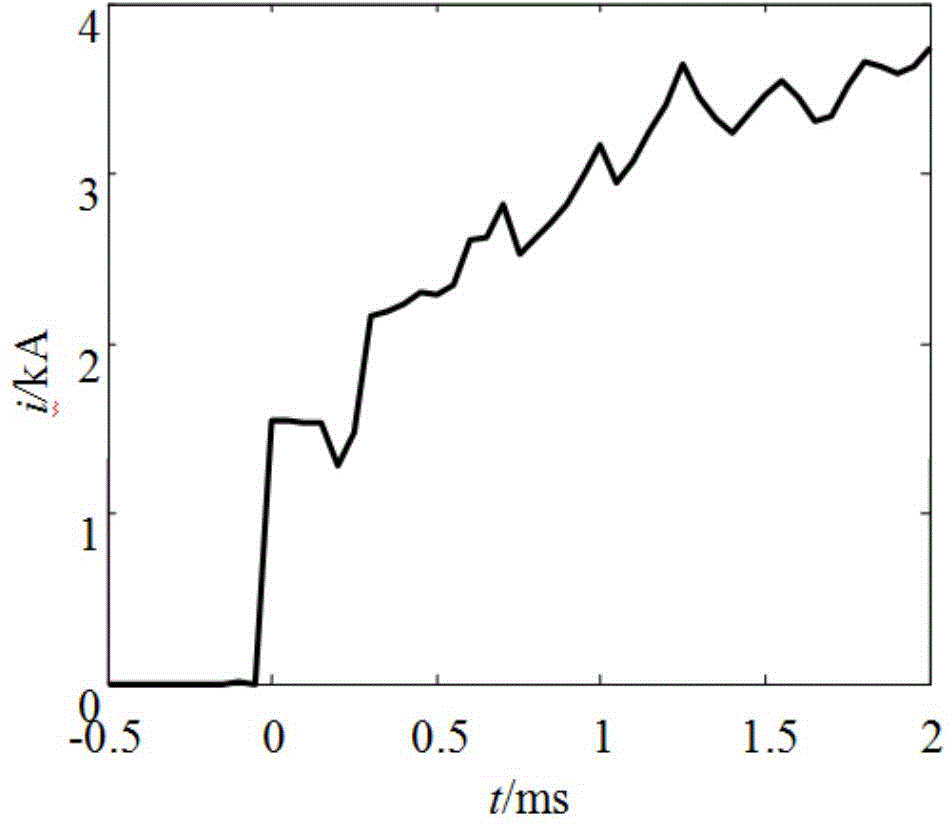
[0038] Example 1: Establish as figure 1 The T-connection grid line model shown. In the system, the line length l MN = 120km, l TQ = 80km, l PM =70km. It is stipulated that the positive direction of the current is that the busbar points to the line. Now assume that a phase A metallic ground fault F occurs on the line MT 40km away from the M terminal 1 , the fault initial phase angle is 90°, and the sampling frequency is 20kHz. By the M-terminal directional element R 1 , N-terminal directional element R 2 and Q-terminal directional element R 3 The voltage and current transient quantities in the 0.5ms time window after the fault are obtained as follows: Figure 2-7 shown. The 8-layer wavelet decomposition is performed on it, and the wavelet basis function is selected as db4, and the wavelet coefficients of voltage and current mutations in the first scale are obtained as follows: Figure 8-10 shown. Obtained by correlation analysis, the correlation coefficient r u,i_M...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2: The same T-connection grid line model as Embodiment 1. Now assume that a phase A metallic ground fault F occurs at 20km away from the N terminal on the TN section line 2 , the fault initial phase angle is 90°, and the sampling frequency is 20kHz. Respectively by the M, N, Q terminal directional element R 1 , R 2 , R 3 Obtain the transient quantities of voltage and current within the time window of 0.5ms after the fault, and perform 8-layer wavelet decomposition on it, and select the wavelet basis function as db4, and obtain the correlation coefficient of the wavelet coefficients of voltage and current mutations at the first scale as r u,i_M =-0.9960, r u,i_N = -0.9984 and r u,i_Q =-0.9984, satisfy - 1 ≤ r u , i _ ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3: The same T-connection grid line model as Embodiment 1. Assume that a phase A metallic ground fault F occurs at a distance of 20km from the M terminal on the PM section of the line 4 , the fault initial phase angle is 90°, and the sampling frequency is 20kHz. Respectively by the M, N, Q terminal directional element R 1 , R 2 , R 3 Obtain the transient quantities of voltage and current within the time window of 0.5ms after the fault, and perform 8-layer wavelet decomposition on it, and select the wavelet basis function as db4, and obtain the correlation coefficient of the wavelet coefficients of voltage and current mutations at the first scale as r u,i_M =0.9999, r u,i_N = -0.9998 and r u,i_Q =-1, not satisfied - 1 ≤ r u , i ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com