Deep wavelet neural network-based polarimetric SAR (synthetic aperture radar) image classification method
A wavelet neural network and classification method technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of inability to extract high-dimensional features and low classification accuracy, and achieve the effects of improving classification accuracy, strong approximation and fault tolerance, and good robustness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
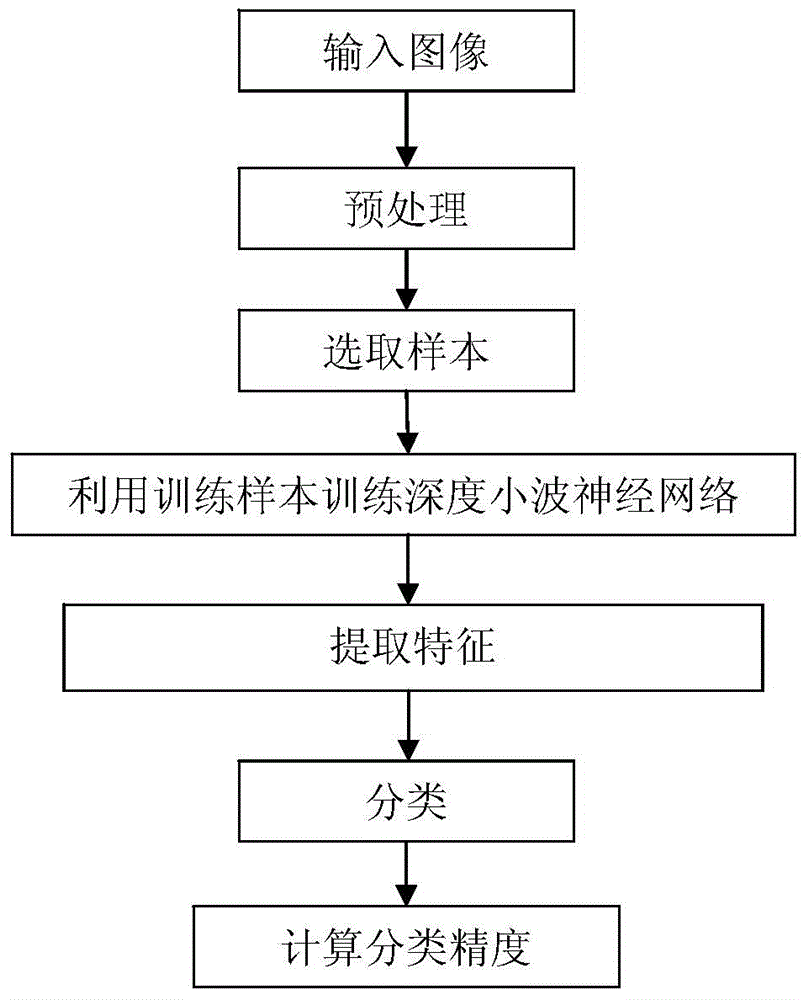
[0035] The present invention is a kind of classification method of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar SAR image based on depth wavelet neural network, referring to the attached figure 1 , describe in detail the specific implementation steps of the present invention:
[0036]Step 1: Input an image, actually input a coherence matrix of a polarimetric SAR image to be classified, see for details figure 2 , figure 2 Shown is the L-band multi-view polarimetric SAR image in the Flevoland, Netherlands region obtained by the AIRSAR platform in 1989. The coherence matrix of the image is a matrix with a size of 3×3×N, and N is the polarimetric synthetic aperture radar SAR image The total number of pixels.
[0037] Step 2: Preprocessing, use a Lee filter with a window size of 7×7 to filter the above coherence matrix to obtain the filtered coherence matrix, in specific simulation experiments, you can use 3×3, 5×5, 7 The coherence matrix of the polarimetric SAR image is filtered wit...
Embodiment 2
[0055] The polarization synthetic aperture radar SAR image classification method based on deep wavelet neural network is the same as embodiment 1, wherein the calculation hidden layer output formula described in step 4b and step 4e is as follows:
[0056] ψ ( j ) = exp ( - ( Σ k = 1 m W jk ′ x k - b j a j ...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The polarization synthetic aperture mine SAR image classification method based on the depth wavelet neural network is the same as embodiment 1-2, and the mean square error formula described in step 4c and step 4f is as follows:
[0064] E = Σ s = 1 S Σ i = 1 n ( h ( i ) - x i ) 2
[0065] Among them, E represents the mean square error of the sample, where E is a general representation of the mean square error, and the error of the first layer network is represented by E 1 Indicates that the error of the first layer network is expressed by E 2 Indicat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com