Active noise reduction device and active noise reduction method
A technology of noise reduction and signal processing device, which is applied to hearing devices, transportation and packaging, active noise control and other directions of active noise cancellation, which can solve the problem of smaller update amount and achieve the effect of reducing noise.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
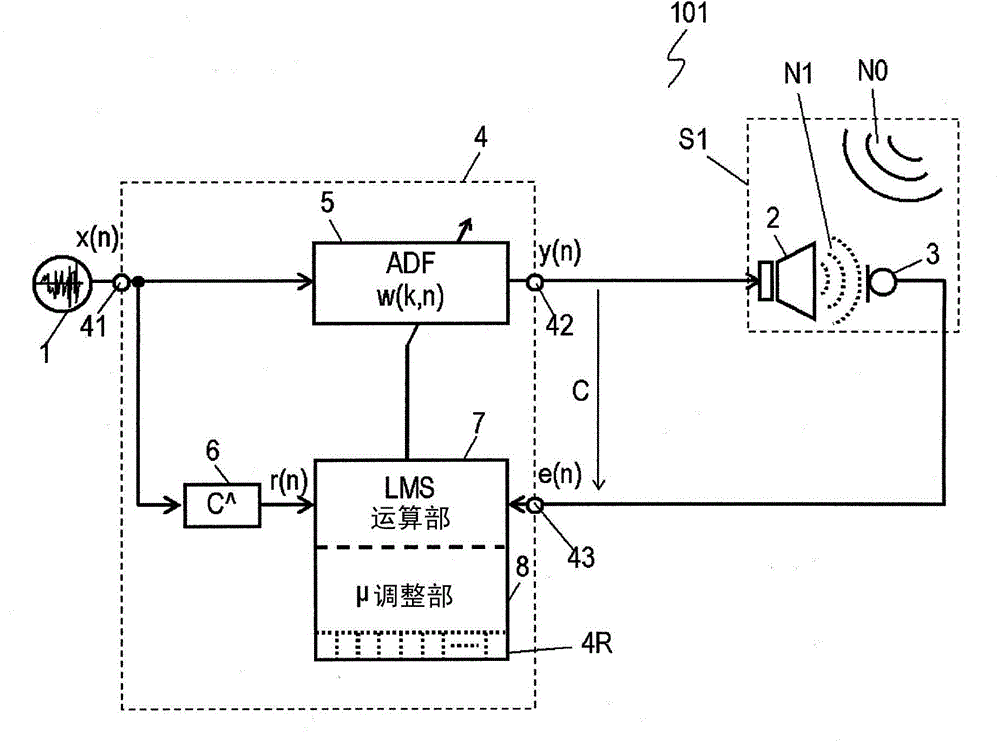
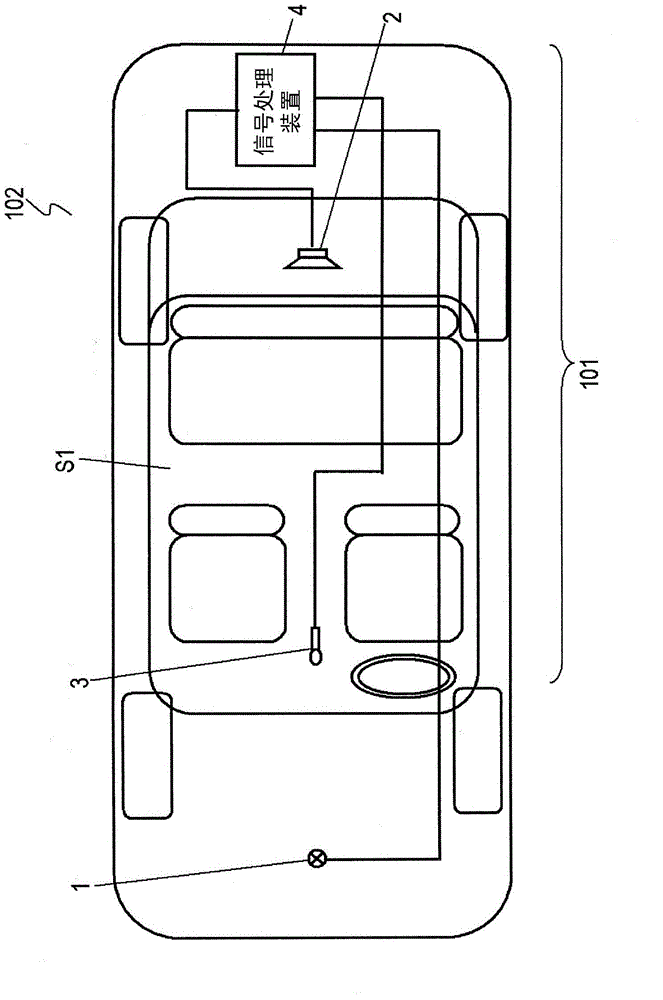
[0057] figure 1 It is a block diagram of the active noise reduction device 101 in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the mobile body 102 equipped with the active noise reduction device 101 . The mobile body 102 in Embodiment 1 is a vehicle having a space S1 such as a vehicle interior. The active noise reduction device 101 is composed of a reference signal source 1 , a secondary noise source 2 , an error signal source 3 , and a signal processing device 4 . The signal processing means 4 outputs a secondary noise signal y(i) based on the reference signal x(i) and the error signal e(i). The noise N0 is reduced by causing the secondary noise N1 generated by reproducing the secondary noise signal y(i) by the secondary noise source 2 to interfere with the noise N0 generated in the space S1.
[0058] The reference signal source 1 is a transducer (transducer) that outputs a reference signal x(i) related to the presence of noise N0 , and is...
Embodiment approach 2
[0163] Figure 9 It is a block diagram of the active noise reduction device 201 in Embodiment 2 of this invention. Figure 10 is a schematic diagram of a mobile body 202 equipped with an active noise reduction device 201 . exist Figure 9 and Figure 10 in, right with figure 1 and figure 2 The same parts of the active noise reduction device 101 and the moving body 102 in the illustrated first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals.
[0164] The active noise reduction device 101 in Embodiment 1 includes one reference signal source 1 , one secondary noise source 2 , one error signal source 3 , and a signal processing device 4 . The active noise reduction device 201 can pass through the signal processing device 204, at least one reference signal source 1 ξ , at least one secondary noise source2 η , and at least one error signal source 3 ζ To reduce the noise of space S1.
[0165] The active noise reduction device 201 in Embodiment 2 is equipped with four...
Embodiment approach 3
[0349] Figure 12 It is a block diagram of the active noise reduction device 301 in Embodiment 3 of the present invention. Figure 13 is a schematic diagram of a mobile body 302 equipped with an active noise reduction device 301 . exist Figure 12 and Figure 13 in, right with figure 1 and figure 2 The same parts of the active noise reduction device 101 and the moving body 102 in the illustrated first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals. The mobile body 302 in Embodiment 3 is a vehicle having a space S1 such as a vehicle interior. The active noise reduction device 301 is composed of a secondary noise source 2 , an error signal source 3 , and a signal processing device 304 . The signal processing device 304 outputs a secondary noise signal y(i) according to the error signal e(i). The noise N0 is reduced by causing the secondary noise N1 generated by regenerating the secondary noise signal y(i) by the secondary noise source 2 to interfere with the nois...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com