Haematococcus pluvialis cell wall breaking method
A technology of Haematococcus pluvialis and cells, which is applied in the field of cell wall breaking of Haematococcus pluvialls, which can solve the problems of affecting yield, difficult crushing, and affecting the extraction rate of astaxanthin, and achieves rapid and efficient wall breaking without foreign matter The effect of adding and effectively protecting biologically active ingredients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The method for breaking the cell wall of Haematococcus pluvialis comprises the following steps:
[0038] Step (1), take 50kg of Haematococcus pluvialis wet algae mud after pressure filtration, and its solid content is 60%, so as to obtain 30kg of solid content, put it in the freezer and freeze at -25°C for 12 hours, and measure the wet algae The temperature of the mud is -18°C, crushed into powder;
[0039] Take 45kg of edible alcohol and 55kg of water to make 100kg of alcohol solution with a mass concentration of 45%, put it in the freezer, freeze at -35°C for 12 hours, and measure the alcohol solution to be -25°C; then wet the algae mud at -18°C , scattered among them;
[0040] Step (2), adding food-grade antioxidant vitamin E to the alcohol solution in step (1), the addition amount is 90g, to obtain a feed liquid;
[0041] In step (3), the material liquid obtained in step (2) is ground and mixed evenly by a colloidal mill, and then the wall is broken once with a hi...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The method for breaking the cell wall of Haematococcus pluvialis comprises the following steps:
[0045] Step (1), take 32kg of edible alcohol and 48kg of water to make 80kg of alcohol solution with a mass concentration of 40%, put it in the freezer, freeze at -35°C for 10 hours, and measure the alcohol solution to be -25°C; then take dry rain Haematococcus powder algal powder 20kg is dispersed in it;
[0046] Step (2), adding food-grade antioxidant phospholipids to the alcohol solution in step (1) in an amount of 20 g to obtain a feed liquid;
[0047] In step (3), the material liquid obtained in step (2) is ground and mixed evenly by a colloidal mill, and then the wall is broken once with a high-pressure homogeneous nanomachine at a pressure of 120-130mpa to obtain Haematococcus pluvialis cells Wall-breaking liquid material; the wall-breaking process is carried out under the conditions of cold chain low temperature and light-proof sealing.
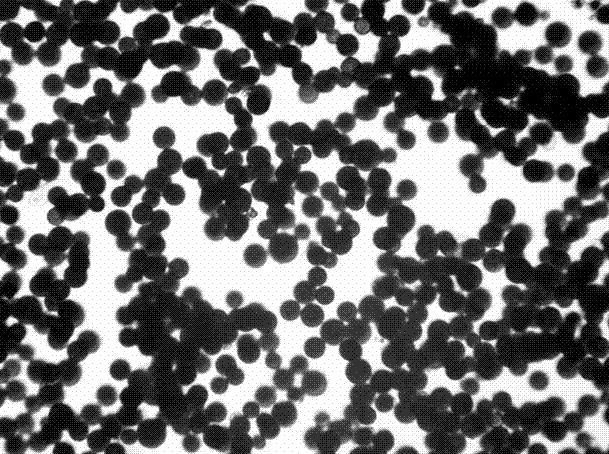
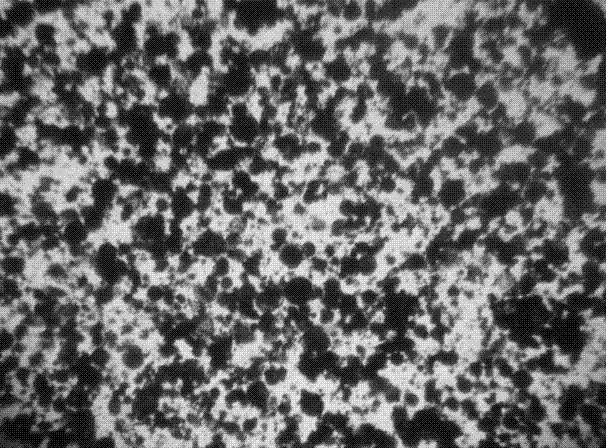
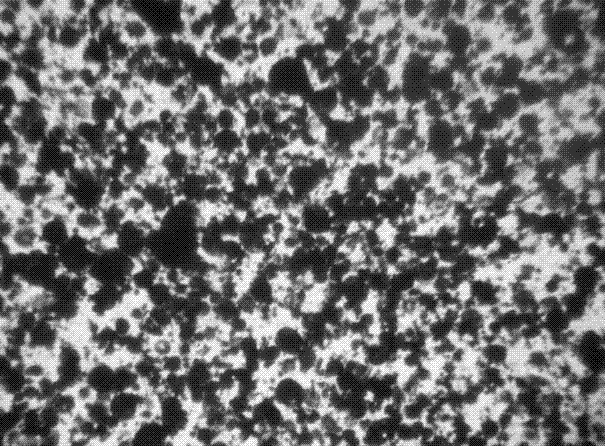
[0048] Through microscope...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The method for breaking the cell wall of Haematococcus pluvialis comprises the following steps:
[0051]Step (1), take 24kg of edible alcohol and 56kg of water to make 80kg of alcohol solution with a mass concentration of 30%, put it in the freezer, freeze it at -35°C for 18 hours, and measure the alcohol solution to be -30°C; then take the dry 25kg of Haematococcus pluvialis flake algae powder are dispersed in it;
[0052] Step (2), adding food-grade antioxidant butylated hydroxyanisole to the alcohol solution in step (1) in an amount of 60 g to obtain a feed liquid;
[0053] In step (3), the material liquid obtained in step (2) is ground and mixed evenly by a colloidal mill, and then the wall is broken once with a high-pressure homogeneous nanomachine at a pressure of 120-130mpa to obtain Haematococcus pluvialis cells Wall-breaking liquid material; the wall-breaking process is carried out under the conditions of cold chain low temperature and light-proof sealing.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com