Display device, pixel circuit and driving method thereof
A technology of pixel circuits and driving transistors, applied in static indicators, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of non-compensation, uneven threshold voltage of TFT devices, uneven panel display, etc., and achieve the effect of compensating for unevenness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
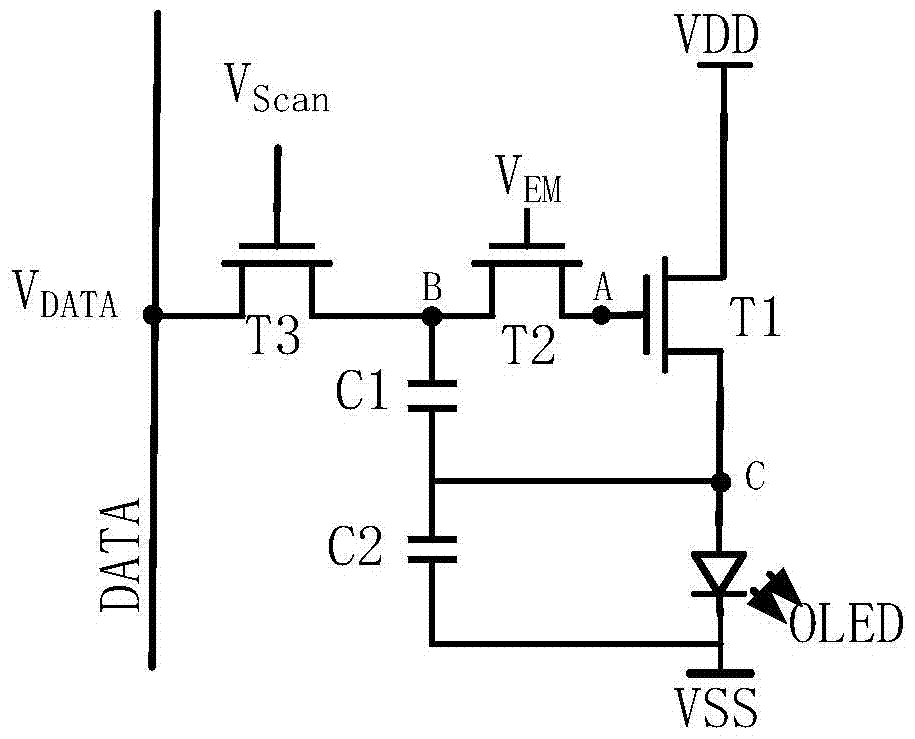
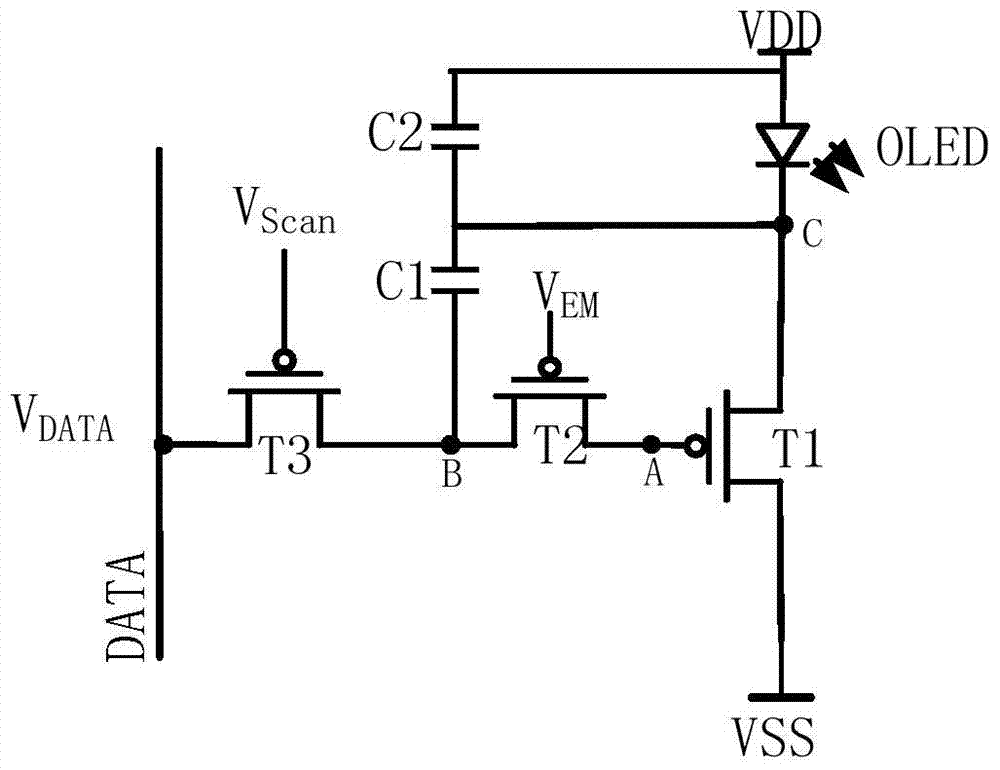
[0040] Please refer to Figure 1a with Figure 1b , The structure diagram of a pixel circuit disclosed in this embodiment includes: a driving transistor T1 and a light-emitting element OLED connected in series between a first level terminal VDD and a second level terminal VSS, and a second transistor T2, a third transistor Transistor T3 and storage capacitor C1. among them, Figure 1a In the pixel circuit shown, each transistor (the driving transistor T1, the second transistor T2, and the third transistor T3) is an N-type thin film transistor; Figure 1b In the pixel circuit shown, each transistor (the driving transistor T1, the second transistor T2, and the third transistor T3) is a P-type thin film transistor.
[0041] The first electrode of the driving transistor T1 is connected to the first terminal of the light emitting element OLED to form a third node C, and the second electrode of the driving transistor T1 and the second terminal of the light emitting element OLED are resp...
Embodiment 2
[0066] In the first embodiment, the initialization potential of the third node C is provided by the first level terminal VDD or the second level terminal VSS. The difference between this embodiment and the above embodiment is that the pixel circuit disclosed in this embodiment further includes a fourth The transistor T4 provides a corresponding potential to the third node C. Please refer to Figure 3a with Figure 3b , Is a structural diagram of a pixel circuit disclosed in this embodiment.
[0067] The first electrode of the fourth transistor T4 is connected to the third node C, the second electrode of the fourth transistor T4 is used to input the initialization potential, and the control electrode of the fourth transistor T4 is used to input the initialization control signal V Ini . In the initialization phase, the fourth transistor T4 responds to the initialization control signal V Ini The effective level of the fourth transistor T4 is turned on, and the second pole of the...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Please refer to Figure 6a with Figure 6b , The pixel circuit structure diagram disclosed in this embodiment is different from the above embodiment in that the second pole of the fourth transistor T4 is used for coupling to the data line DATA, and the initialization potential of the second pole of the fourth transistor T4 is set by the data line Provided by DATA.
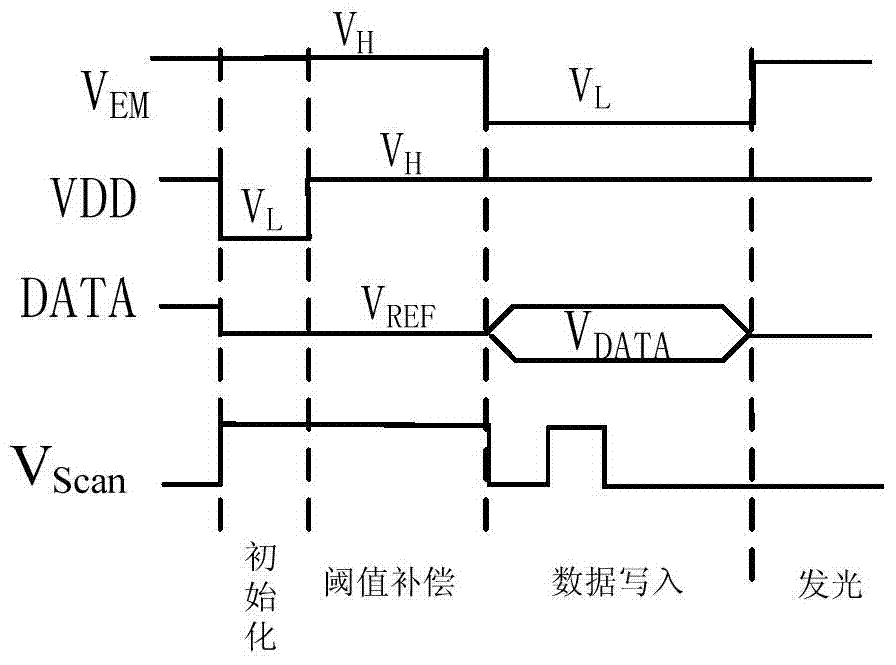
[0075] Please refer to Figure 7 , This example Figure 6a As shown in the driving timing diagram of the pixel circuit, the driving process of the pixel circuit of this embodiment is basically the same as that of the second embodiment. The difference is that in the initialization phase, the initialization potential of the third node C (for example, the low level V L ) Is provided by the data line DATA. In the threshold compensation stage and the data writing stage, the data line DATA provides the reference potential V to the third transistor T3 respectively REF And data voltage V DATA .
[0076] Figure 6a The s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com