Critical burial depth computing method for groundwater recharging vegetation
A groundwater and vegetation technology, applied in computing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as lack of analysis and calculation methods, and achieve the effect of clear physical process and mechanism of action, reliable theoretical and technical support
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
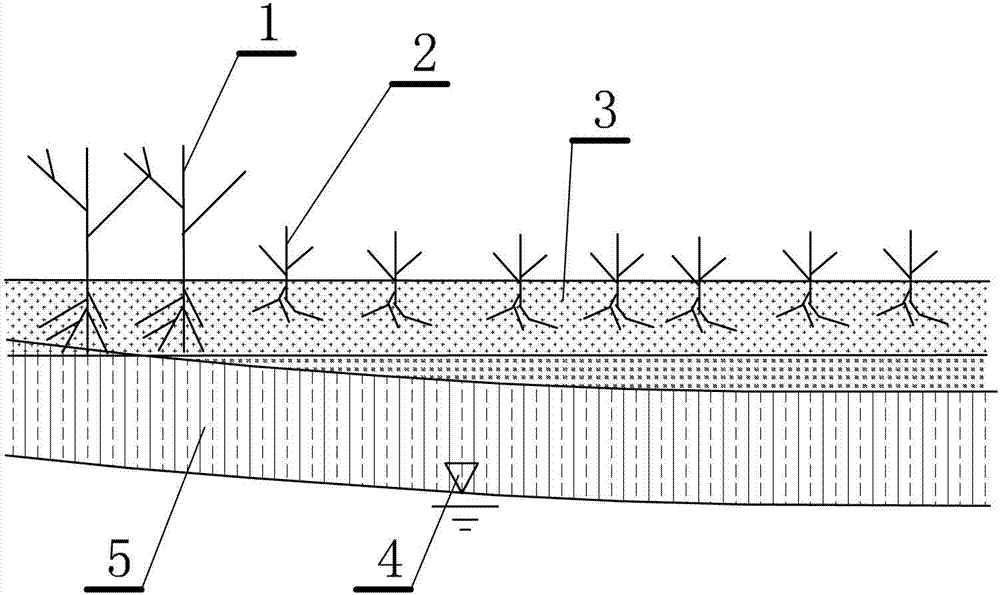
[0027] This embodiment is a method for calculating the critical buried depth of groundwater recharge vegetation, the process is as follows figure 1 shown.
[0028] The thickness of the vegetation root action layer is observed on the spot, and the maximum rise height of soil capillary water is used as the thickness index of the diving active layer to carry out model analysis and calculation. The specific steps of the method described in this embodiment are as follows:
[0029] Data collection steps: used to collect various parameters of the known soil and vegetation communities, including: soil vegetation physiological data: thickness of root action layer, soil physical data: soil measured effective particle size, soil measured total porosity.
[0030] In this embodiment, the detected natural soil is called "known soil". The actual measurement of known soil is very important and is the collection of basic data, which should be as accurate as possible.
[0031] The root syste...
Embodiment 2
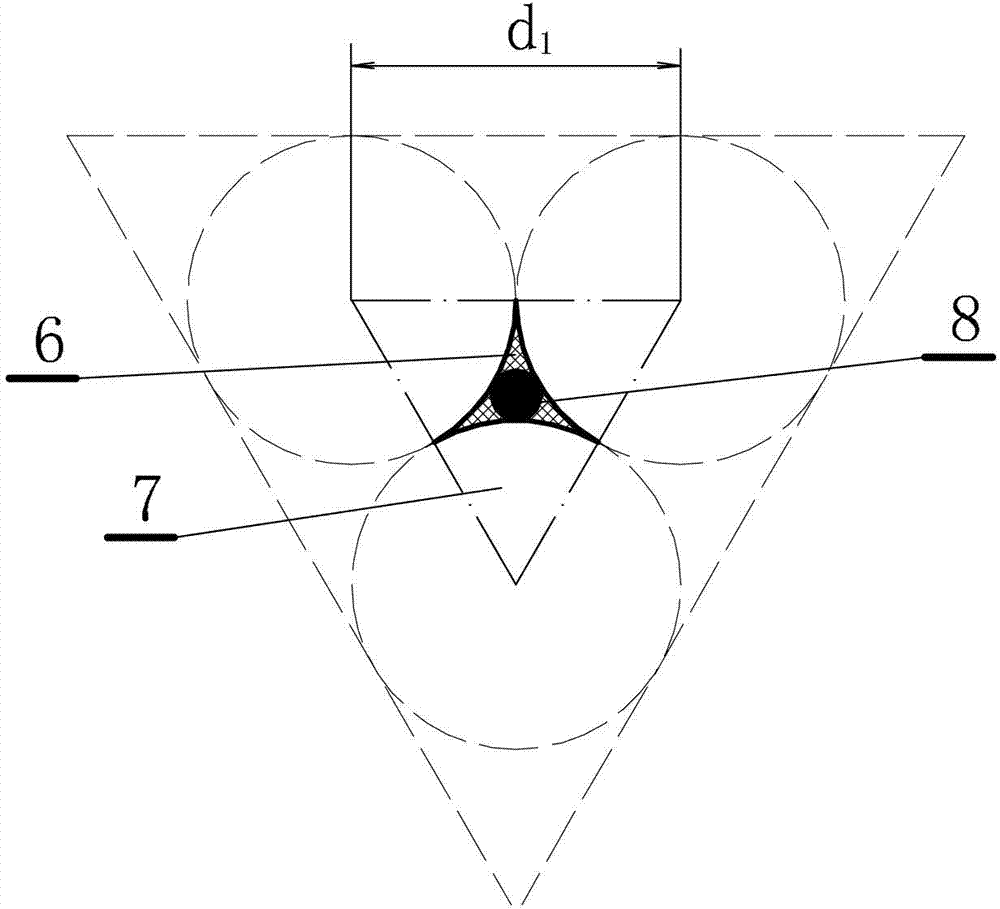
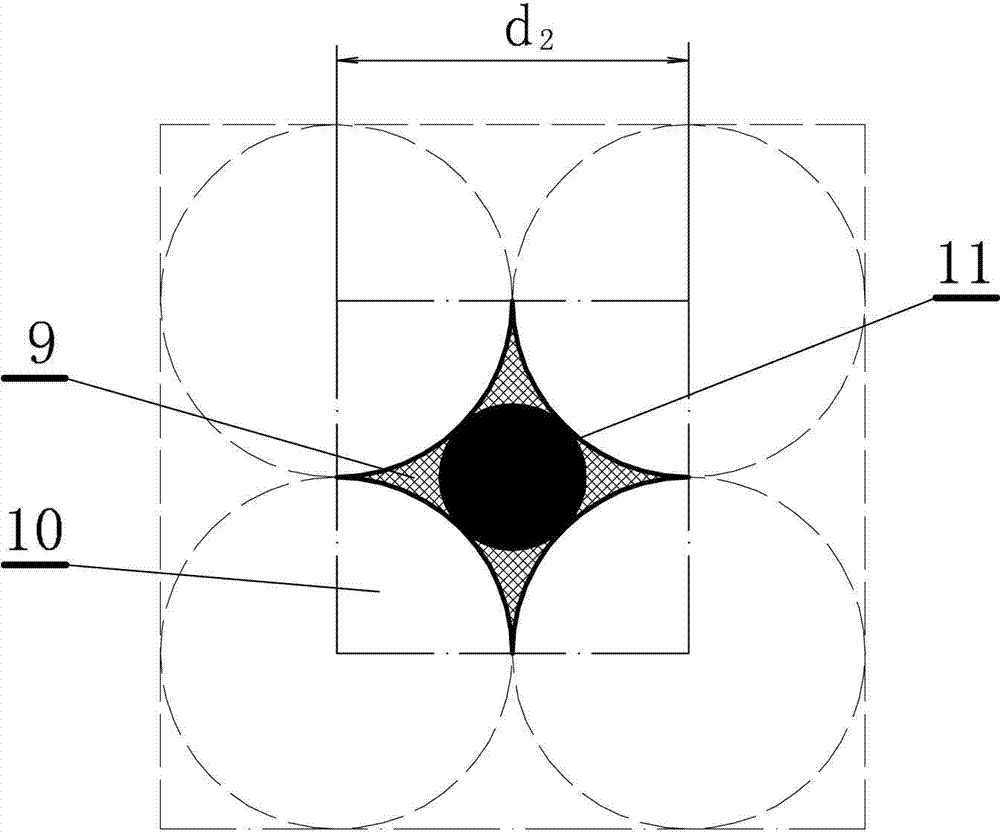
[0065] This embodiment is an improvement of the first embodiment, and is a refinement of the "regular arrangement model of soil particles" of the first embodiment. The soil particles in the "regular arrangement model of soil particles" described in this embodiment have a triangular arrangement structure.
[0066] The regular arrangement model of soil particles described in this embodiment is a regular triangular arrangement structure, and its plan view is as follows image 3 shown. The soil structure arranged in a regular triangle can be regarded as a height d 1 , the length of the upper and lower sides is d 1 3 1 / 6 spheres 7 are embedded in the regular triangular prism, and the rest ( image 3 The part of the grid in ) is the pores 6, while the part 8 between the three balls ( image 3 The blackened part in ) can be considered as effective pores.
Embodiment 3
[0068] This embodiment is an improvement of the second embodiment, which is about the refinement of the soil particles with a triangular arrangement structure in the second embodiment. The total porosity of the soil particles in the triangular arrangement structure described in this example is 39.5%.
[0069] Total porosity of triangularly arranged soil particles n for:
[0070] .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com