Polybenzoxazine composition
Technology of a polymer composition, benzoxazine, applied in the field of preparation of polymer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0158] All parts, percentages, ratios, etc. in the examples are by weight unless otherwise indicated.
[0159] The amount of catalyst used in the binder is determined by equivalents (eq) based on the number of moles of reactive groups per mole of reactant molecules, for example, 2 equivalents of a difunctional reactant represents one mole of that reactant, and one A mole of trifunctional reactant would represent 3 equivalents of that reactant. The catalyst was treated as a monofunctional catalyst.
[0160] A double dash symbol in the table indicates that the sample was not tested.
[0161] Materials were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Milwaukee, WI unless otherwise stated.
[0162] testing method
[0163] Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC Analysis) of Curing
[0164] The thermal properties of the composition during curing were determined by placing an amount of the composition in an open aluminum pan in a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) and heating from 25°...
example 1
[0215] Powders of finely ground BZ-1 (23.1) and sulfur (3.2 grams) were mixed in an equimolar ratio and stirred and shaken in a Wig-L-Bug shaker for approximately 1 minute. Approximately 15.4 milligrams (mg) of the mixture was heated to 320°C in a DSC (Seiko) as described above. The DSC trace showed an exotherm with a high temperature peak at about 211°C, a cure onset temperature of about 140°C, and a total energy released during cure of 221 J / gram. The trace also shows a less sharp endotherm with a peak at about 113°C, which corresponds to the recorded melting point of sulfur.
example 2
[0217] BZ-2 (33.3 grams) and finely ground sulfur (3.2 grams) were mixed in an equimolar ratio and stirred vigorously for about 1 minute. Approximately 20.3 mg of the mixture was heated to 320°C in DSC as described in Example 1. The DSC trace shows an exotherm with double high temperature peaks at about 170°C and 225°C and a cure onset temperature of about 130°C. The total energy released during curing was 221 J / gram. The trace also shows a less sharp endotherm with a peak at about 113°C, which corresponds to the recorded melting point of sulfur.
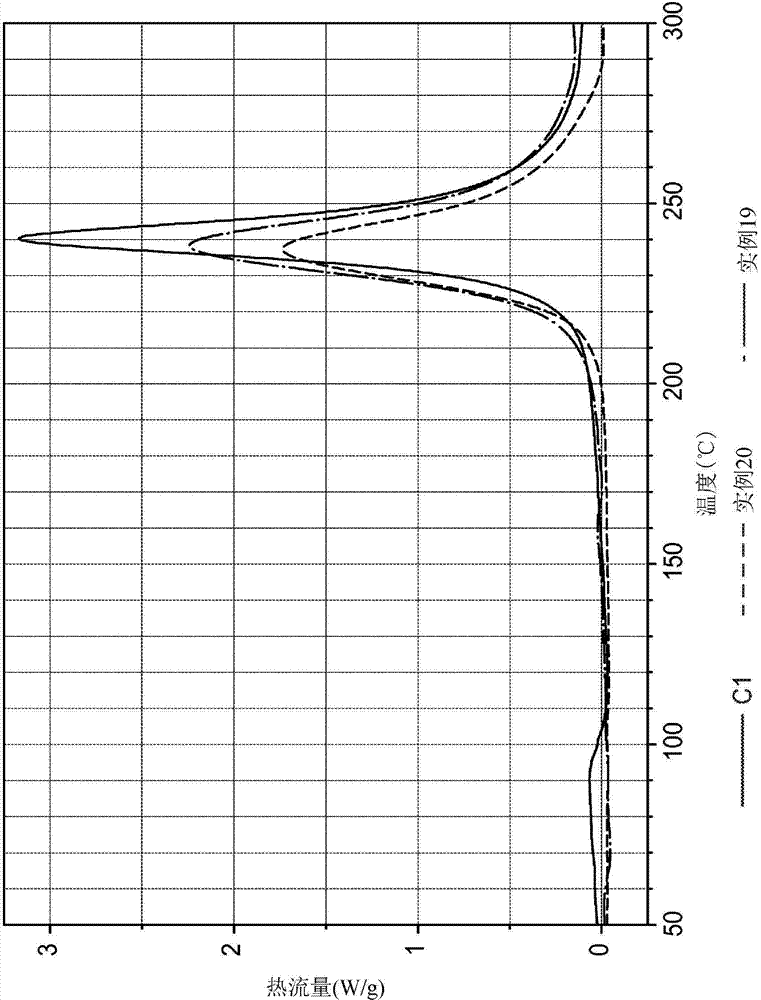
[0218] Comparative Examples C1–C2
[0219] About 4.4 mg of BZ-1 (C1 ) and about 12.0 mg of BZ-2 (C2) were heated to 320° C. in DSC as described in Example 1 . The respective DSC traces of C1 and C2 showed peak exothermic temperatures of 240°C and 246°C, curing onset temperatures of 190°C and 190°C, and energy released during curing of 323 and 113 J / g, respectively.
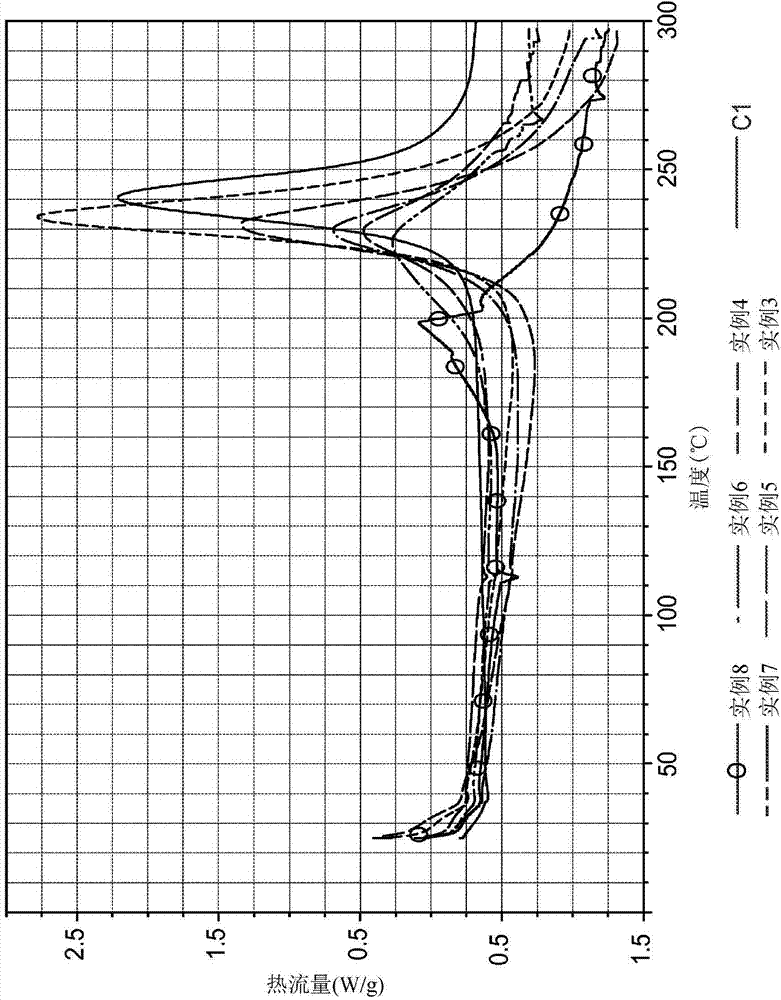
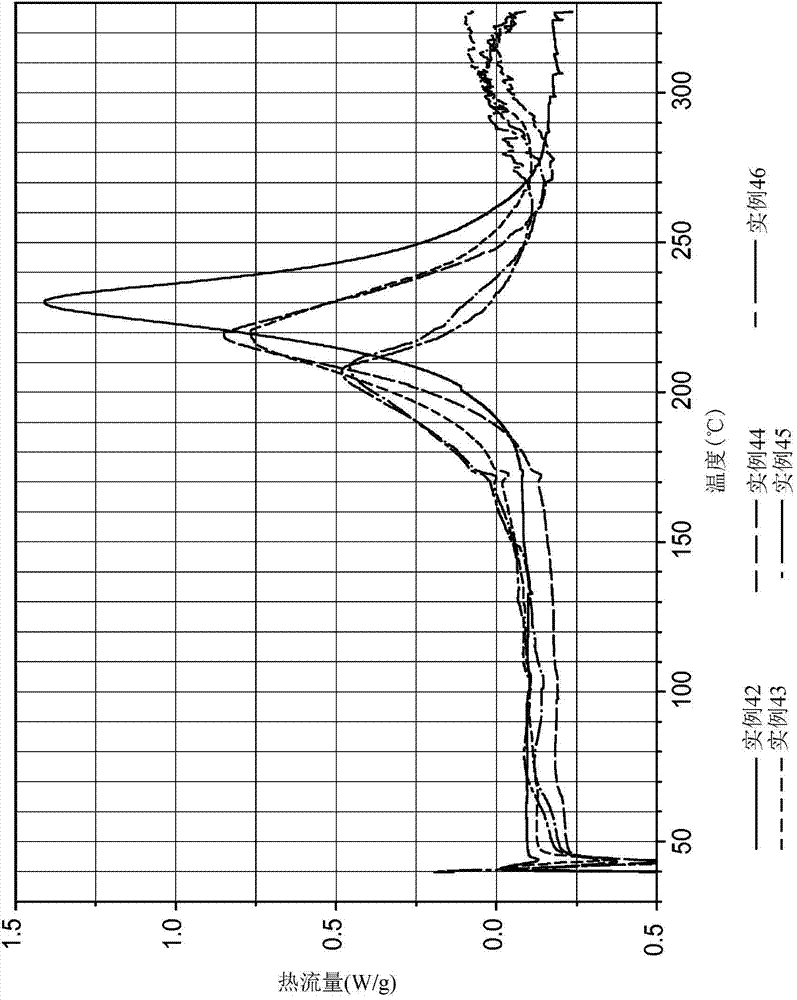
[0220] Examples 3-8, Comparative Example C1A
[0221] Fin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com