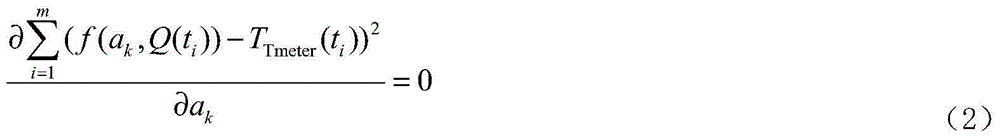Calibration method for pure rotational Roman laser radar system constants
A laser radar and Raman laser technology, applied in radio wave measurement systems, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inconvenience of operation, errors, and difficulties, and achieve the effect of improving convenience, avoiding differences in time domain changes, and improving application popularity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
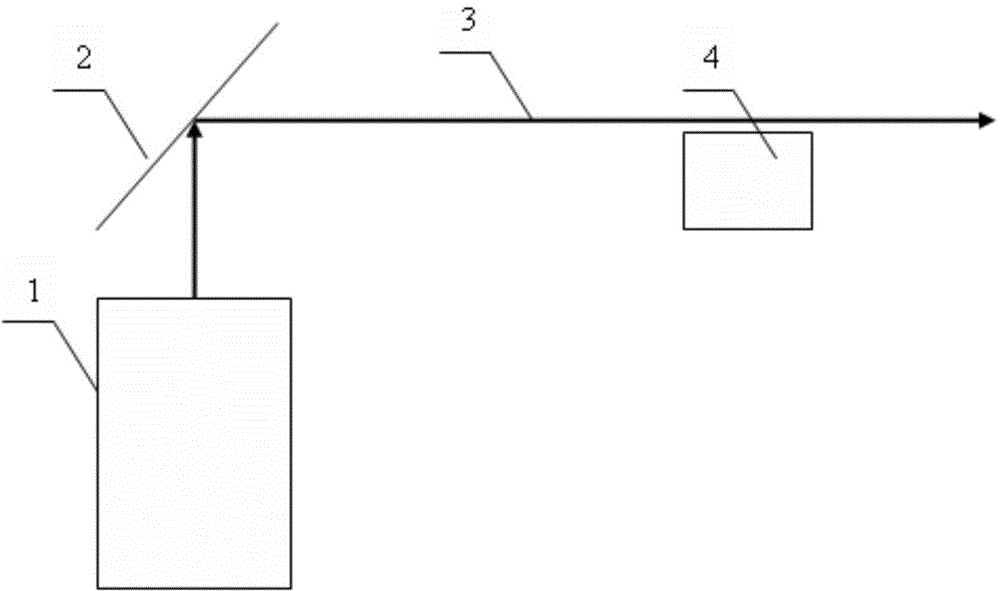
[0020] Such as figure 1 As shown, a calibration method of pure rotational Raman lidar system constants, the steps are as follows:
[0021] Step 1: On a clear and cloudless night when the temperature difference exceeds 5 degrees Celsius, use the laser radar 1 to perform horizontal detection through the scanning system 2 to ensure that there are no obstacles in the transmitting and receiving beams 3;
[0022] Step 2: placing a temperature measuring instrument 4 on the horizontal detection path of the laser radar 1;
[0023] Step 3: After debugging the laser radar 1 signal, measure the laser radar 1 and the temperature measuring instrument 4 at the same time to obtain a series of time series data: P low (t i ), and T Tmeter (t i ), where P low (t i ),, P high (t i ) and T Tmeter (t i ) respectively represent at t i Place the laser radar 1 low-order channel signal, high-order channel signal and temperature data measured by the temperature measuring instrument at the p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com