Radar radiation source identification method based on phase noise unintentional modulation characteristic
A phase noise, unintentional modulation technology, applied in the field of radar radiation source identification, can solve the problem of low recognition rate, achieve the effect of accurate identification model, accurate radar radiation source identification and judgment, and good radar radiation source identification and classification effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0022] Specific embodiment one: a radar radiation source identification method based on phase noise unintentional modulation features, comprising the following steps:
[0023] Step 1: According to the structure of the phase-locked frequency synthesizer in the radar transmitter system, the phase noise model generated by the phase-locked frequency synthesizer is established as follows:
[0024] s ( t ) = sin ( 2 π f c t ) + Σ m ′ Δ φ m ′ 2 sin [ 2 π ( f c + ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0030] Specific implementation mode two: described in this implementation mode
[0031] The phase noise model formula (7) concrete steps that the phase noise model formula (7) that the described setting-up phase-locked frequency synthesizer of step 1 produces are as follows:
[0032] Phase noise can be seen as the phase of the original signal with frequency f m The sine wave modulation of , taking the single frequency signal as an example, let the frequency of the original signal be f c , the signal after adding a single phase noise is expressed as
[0033] s(t)=sin(2πf c t+Δφ(t))=sin(2πf c t+Δφ m sin(2πf m t)) (1)
[0034] Among them, Δφ(t) represents the modulation signal, Δφ m is the phase modulation coefficient, t is the pulse width, f m is the modulation signal frequency;
[0035] Expand the above formula to
[0036] s(t)=sin(2πf c t)cos(Δφ m sin(2πf m t))+cos(2πf c t)sin(Δφ m sin(2πf m t)) (2)
[0037] The expressions of (3) and (4) in the Bessel functio...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0049] Specific implementation mode three: the described in this implementation mode
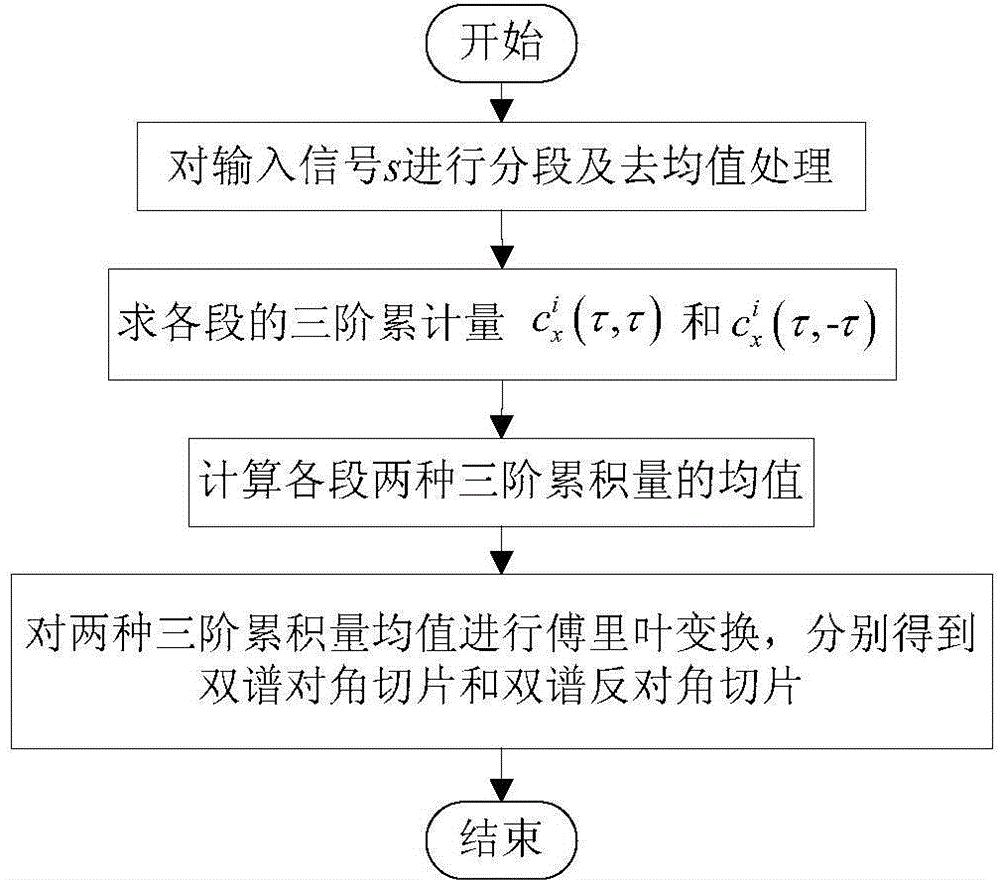
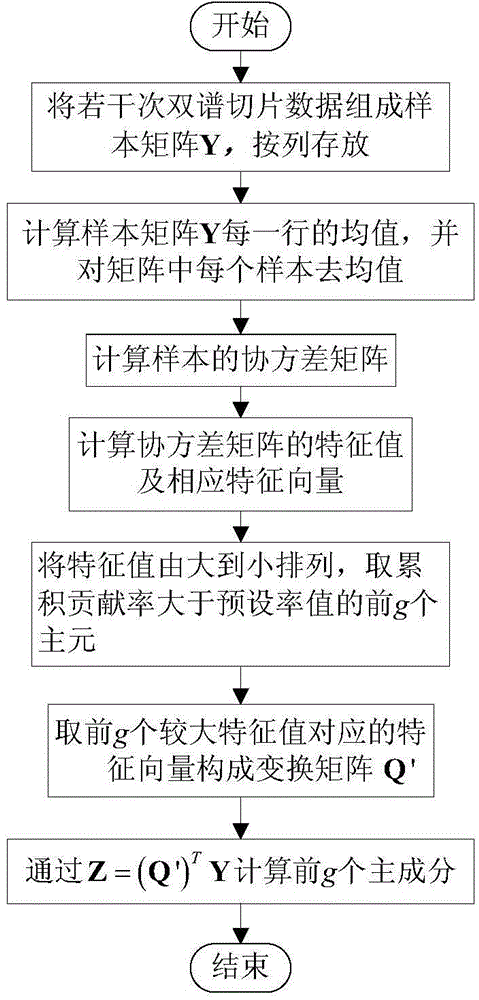
[0050] Calculate the bispectral diagonal slice feature multiple times described in step 2 to obtain the bispectral diagonal slice sample composition matrix A 1 The specific steps are as follows:
[0051] Step 2.1.1: The received signal s(t) is abbreviated as s, and it is segmented and processed. Each segment takes M data, which is divided into P segments, and the data in each segment is de-averaged:
[0052] x i ( n ′ ) = s i ( n ′ ) - 1 M Σ n ′ = 1 M s i ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com