Systems and methods for detecting genetic variation
A technology for genetic variation and sequencing, applied in the field of systems and methods for detecting genetic variation, which can solve the problems of wasted samples, low efficiency, reduced reliability and reproducibility, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0169] Example 1: Sample preparation and sequencing method
[0170] Genomic DNA (gDNA) is extracted in 96-well format, leaving wells A1, G12, and H12 vacant (which will later contain no-template controls, respectively, containing Coriell samples lacking each pathogenic genetic variant tested. NA12878 genomic DNA universal Negative standards, and samples containing one of multiple known pathogenic genetic variants). Transfer 50 μL from each well to the corresponding well of the absorption plate. A Tecan M200 plate reader was used to measure the absorbance at 260nm to calculate the amount of DNA. Transfer 50 μL of gDNA from the absorption plate to the Eppendorf twin.tec plate. Add control samples to their respective positions on the twin.tec board. Fragment gDNA and control in a SonicMan (Matrical, Spokane WA) sonicator at 10°C according to the following protocol: pre-cooling for 180 seconds, cycling 100 times, ultrasound for 3.0 seconds, power 35%, lid cooling for 1.0 second, p...
Embodiment 2
[0177] Example 2: Amplification and sequencing method
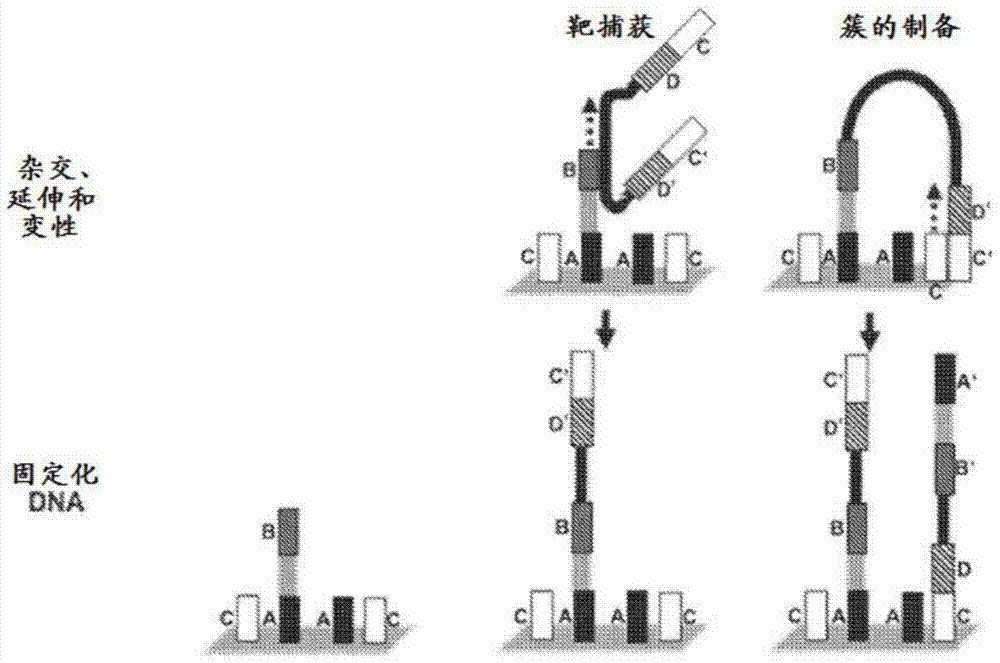
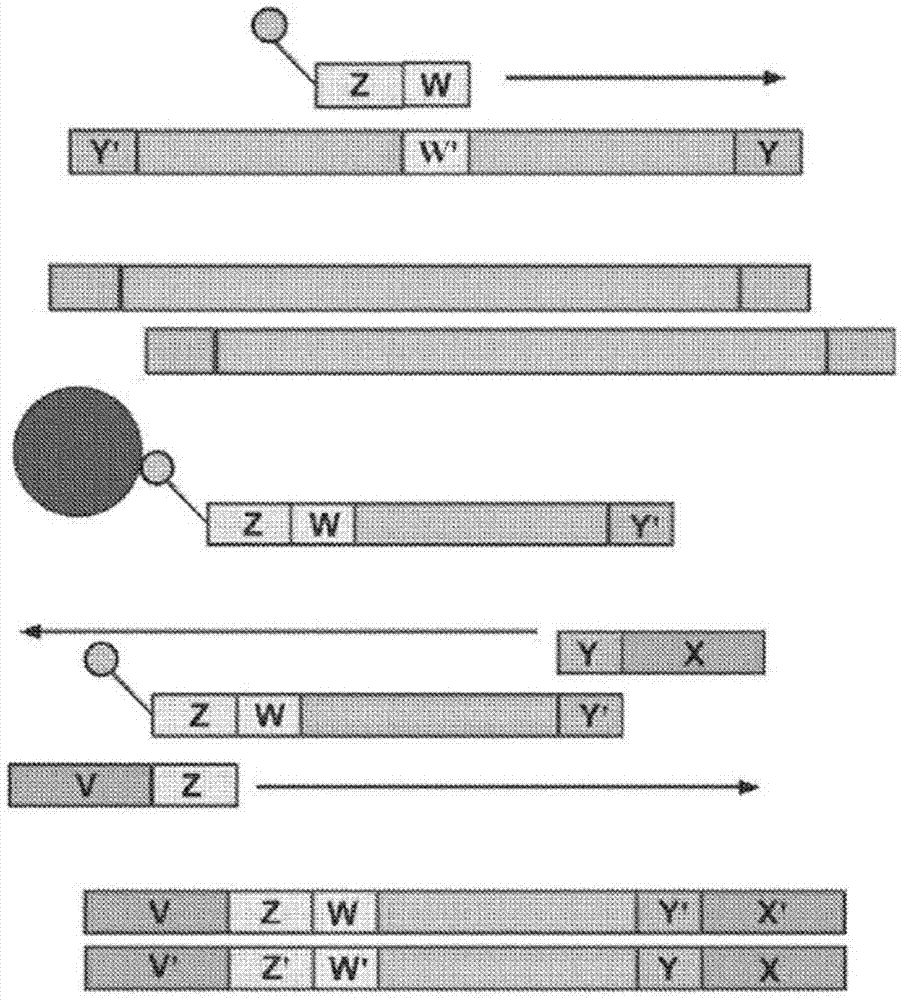
[0178] An exemplary method for the amplification of multiple different target polynucleotides is shown in figure 2 with 5 , The main difference is figure 2 It includes a solid phase purification step. Figure 7 An exemplary amplification method is also illustrated, and figure 2 The main difference in the methods exemplified in is that oligonucleotide primer extension is performed before adaptor coupling rather than after adaptor coupling. Amplification may or may not include a solid phase purification step. Image 6 Exemplified Figure 5 The amplification methods shown in, as well as exemplary bridge amplification and sequencing methods. Can be Image 6 The amplification method exemplified in is used in combination with any bridge amplification method and related sequencing methods.
[0179] First, part of the single-stranded adaptor is ligated to the fragmented polynucleotide. Part of the single-stranded adaptor has a dou...
Embodiment 3
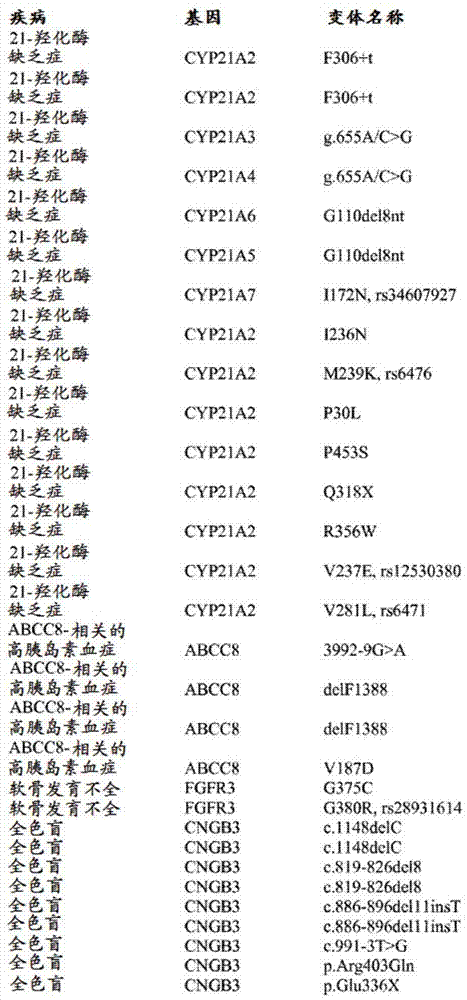
[0181] Example 3: Identification of non-subject sequences
[0182] Using standard methods known in the art, polynucleotides (e.g., DNA and / or RNA) are extracted from samples from subjects suspected of containing virus and / or bacterial polynucleotides. The sample polynucleotide is fragmented, end modified and tailed (for example in Example 1). The adaptor oligonucleotide containing sequence D is then ligated to the sample polynucleotide, and then amplified using amplification primers containing sequence C, sequence D and barcode. The amplified target polynucleotide is hybridized with a plurality of different first oligonucleotides attached to the solid surface. Each first oligonucleotide contains sequence A and sequence B, wherein sequence B is different for each different first oligonucleotide, is located at the 3'end of each first oligonucleotide, and contains The sequence of the non-subject sequence or the sequence within 200 nucleotides of the non-subject sequence is complem...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com