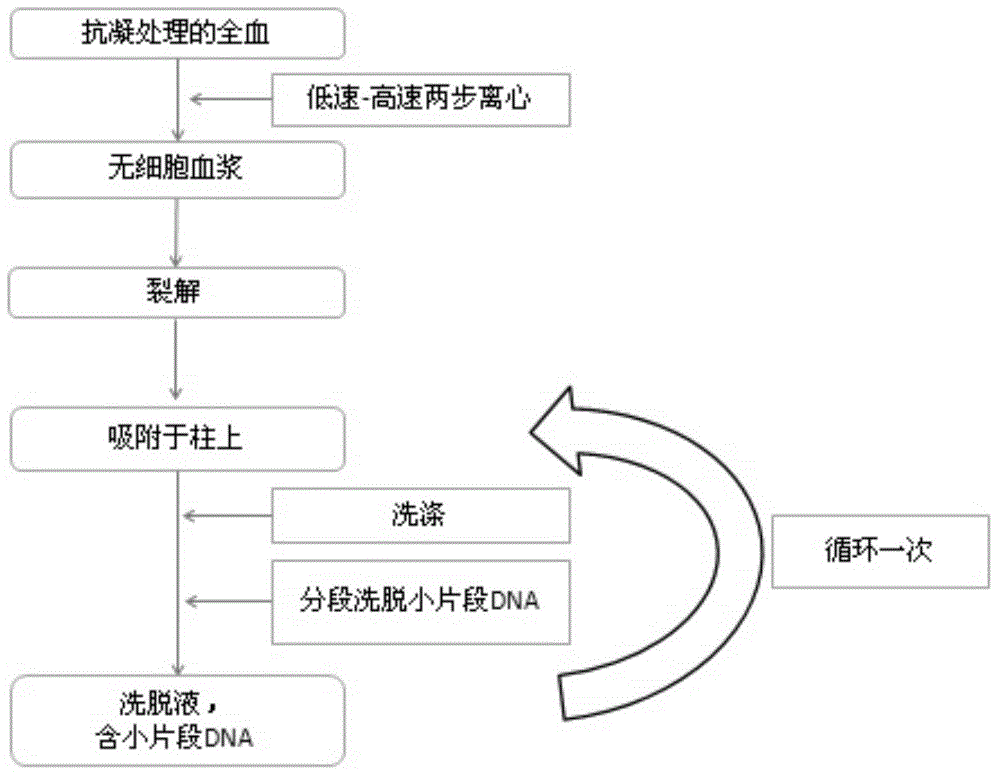
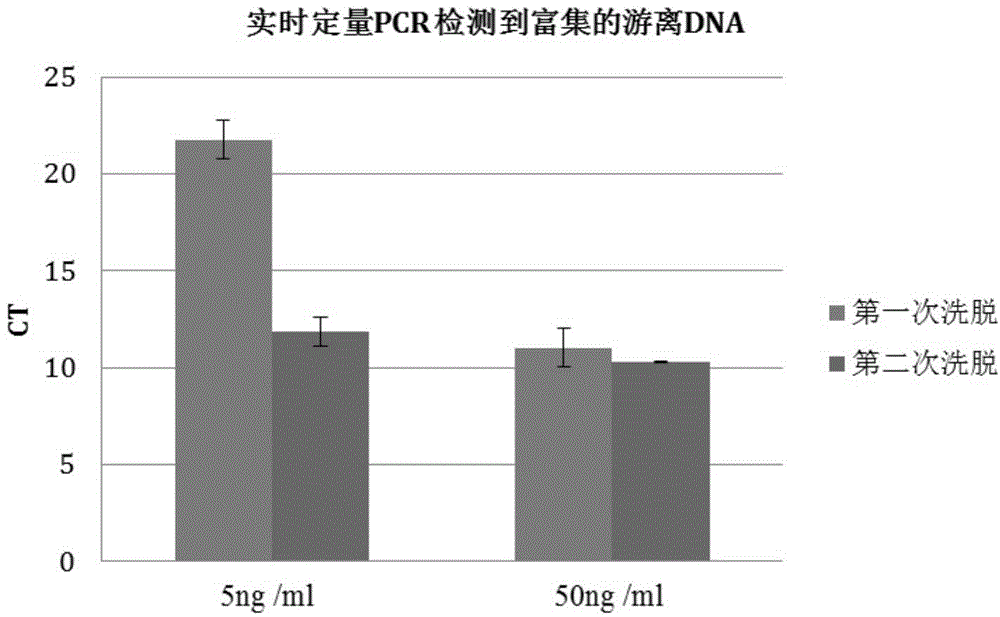
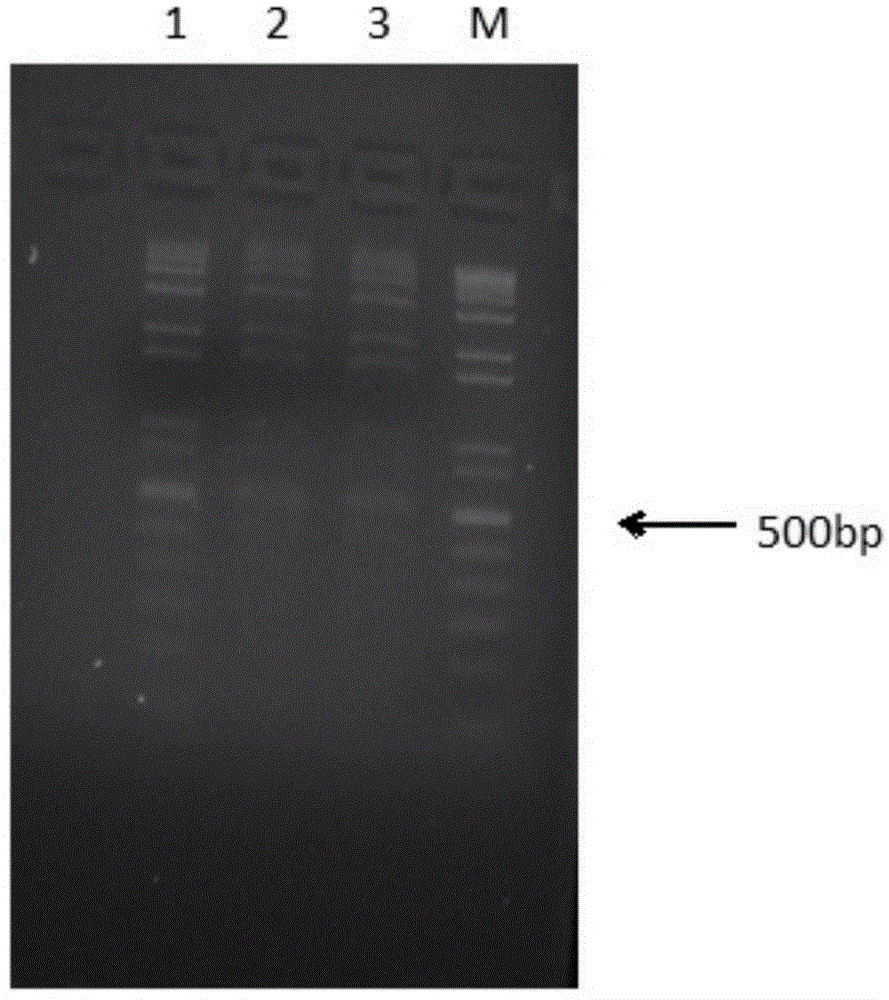
Method for separating and enriching free fetus DNA from maternal blood plasma
A technology for separation, enrichment, and plasma, applied in the field of separation and enrichment of cell-free fetal DNA, can solve the problems of low cffDNA content, low recovery rate, loss of samples, etc., and achieves the effect of removing DNA interference, good application prospects, and simple method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Example 1 Using the method of the present invention to enrich and purify fetal DNA from plasma of pregnant women
[0084] 1. Experimental method
[0085] 4 pregnant women with a gestational age of 12-16 weeks, samples 1-3 are male fetuses, and sample 4 is female fetuses. Take 5ml of venous blood from pregnant women, and centrifuge the freshly obtained BD blood collection tube (EDTA whole blood) at 4°C, 1900×g for 10 minutes; draw the supernatant into a 15ml conical bottom centrifuge tube, and then centrifuge at 4°C, 16000×g After 10 minutes, carefully transfer the supernatant to a new preservation tube, and use the following methods for cell-free fetal DNA extraction:
[0086] 1. Add 100 μl proteinase K to a 15ml centrifuge tube;
[0087] 2. Add 1ml of maternal plasma to the centrifuge tube;
[0088] 3. Add 0.9ml of binding buffer A, vortex for 15-30s, and mix well;
[0089] 4. Incubate at 60°C for 30 minutes;
[0090] 5. Add the lysate to the silica column twice, ...
Embodiment 2
[0125] Example 2 The method of the present invention is used to extract the male-specific SRY gene in plasma
[0126] In this example, the effectiveness of the method of the present invention is verified by adding SRY gene fragments to blank plasma. The SRY gene fragment of the present invention has a length of 194bp and belongs to free fetal DNA.
[0127] 1. Experimental method
[0128] There are Y chromosome-specific sequences in male fetal DNA. Currently, researchers usually use fluorescent quantitative PCR technology to detect specific genes on the Y chromosome, such as SRY gene, DYS14, etc., so as to quantify male free fetal DNA.
[0129] The SRY gene is a male-specific gene. Usually the free DNA content in human plasma is about 1–100ng / ml. Two parts of 600 μl of plasma come from a 75-year-old female, and the nucleotide sequence such as SEQ ID NO.1 is added according to the ratio of the following table 1
[0130](aattgcagtttgcttcccgcagatcccgcttcggtactctgcagcgaagtgcaac...
Embodiment 3
[0138] Embodiment 3 The present invention selects the screening experiment of eluent
[0139] 1. Experimental method
[0140] The operation steps are as follows, and step 7 is processed according to three methods:
[0141] 1. 5ul 1kb plus DNA ladder plus 1ml H 2 In the centrifuge tube of O;
[0142] 2. Add 0.9ml of binding buffer A, vortex for 15-30s, and mix well;
[0143] 4. Incubate at 60°C for 30 minutes;
[0144] 5. Add the lysate to the silica column twice, 1ml each time;
[0145] 6. Centrifuge at 13000rpm for 1min, discard the collection tube, and replace with a new collection tube;
[0146] 7. Treatment 1: Add 750 μl of washing buffer B, centrifuge at 13,000 rpm for 1 min, discard the collection tube, and replace it with a new collection tube, the nucleic acid is still bound to the membrane, and the residual pollutants such as protein and divalent cations are effectively washed away;
[0147] Or treatment 2: Add 750 μl of washing buffer C1 (treatment 2 is selecti...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap