A Material Analysis Method of Space Debris Based on Nonnegative Matrix Factorization
A non-negative matrix decomposition, space debris technology, applied in the direction of testing moving boards, etc., can solve problems such as poor accuracy and inability to apply to deep space environments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
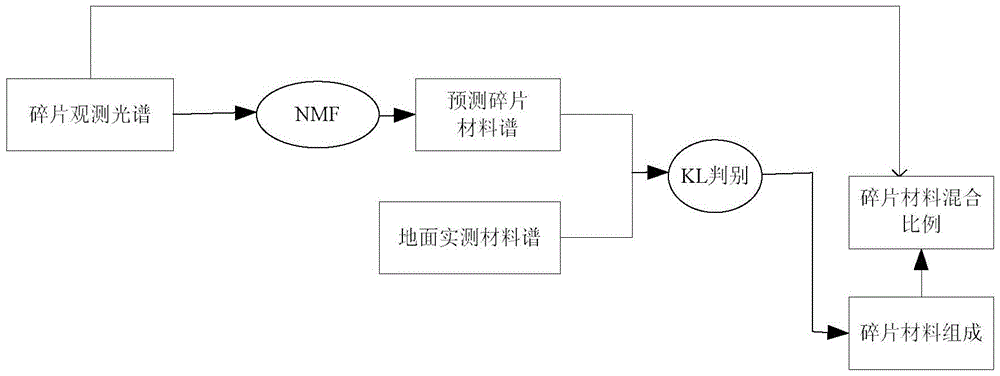
[0067] Example: A space debris material analysis method based on non-negative matrix factorization, the process is as follows:
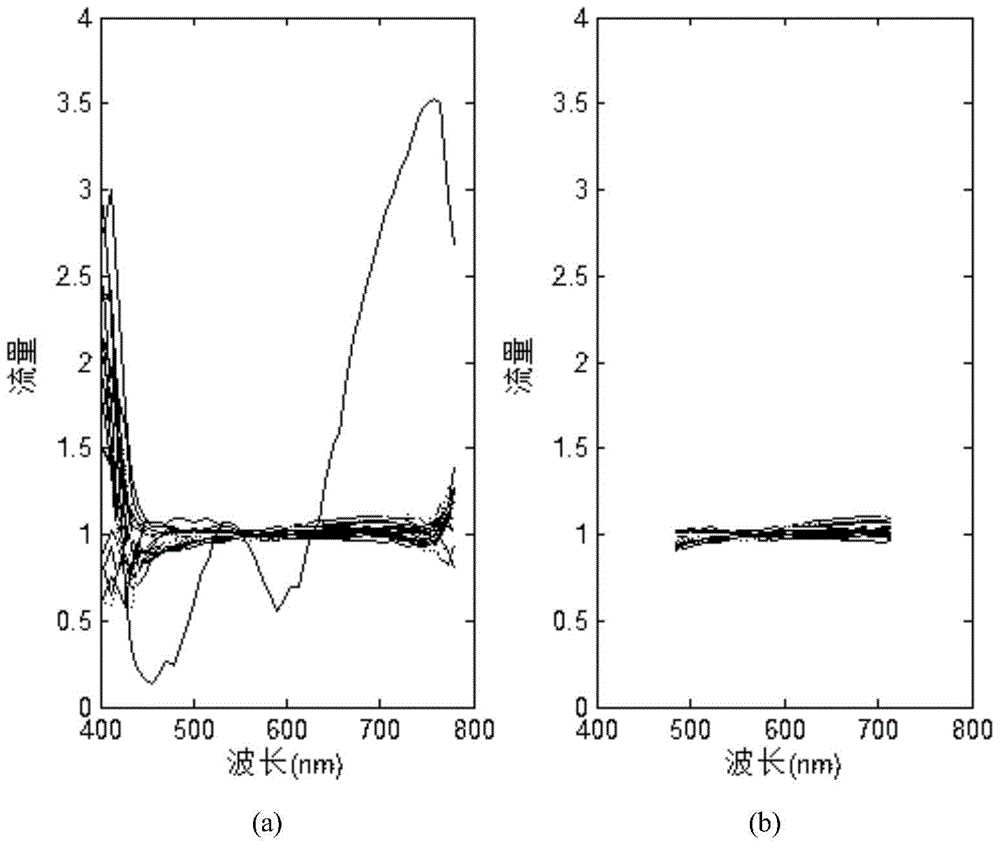
[0068] (1). Data preprocessing, such as figure 2 Shown:
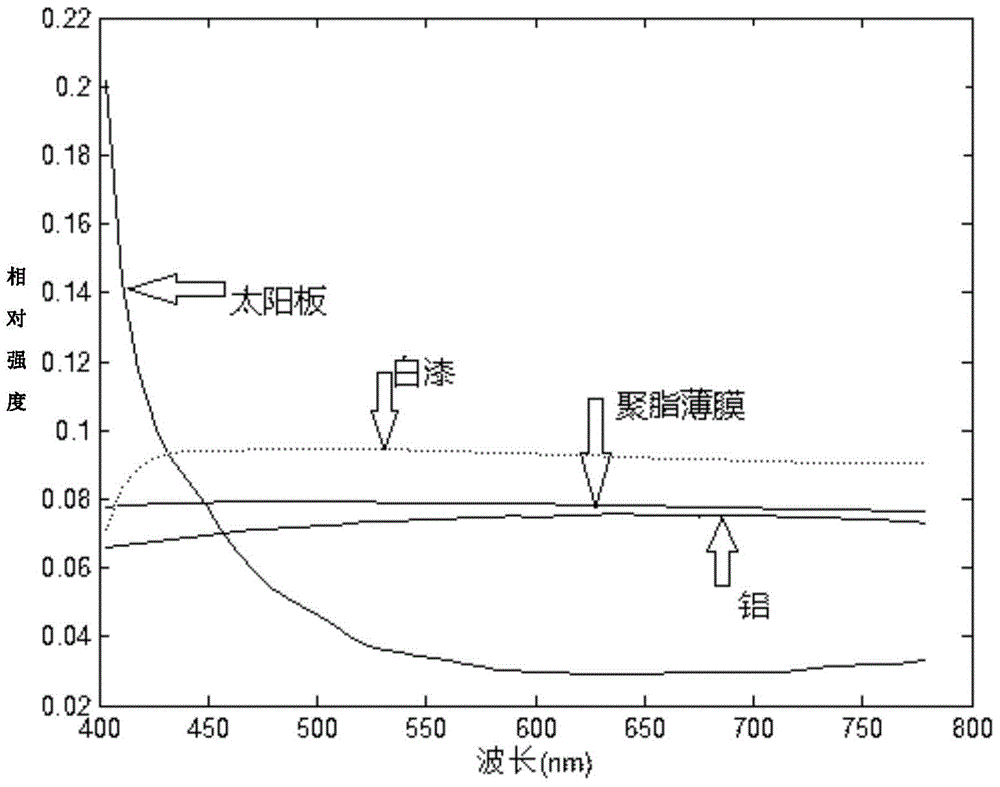
[0069] (2). Collection of ground material spectra, namely aluminum (Aluminum), polyester film (Mylar), solar panel (SolarCell), white paint (White paint), and the image 3 , and its wavelength range is [403--779] nanometers.
[0070] (3).Material spectrum mixing
[0071] Mix 'Aluminum' and 'Mylar' in a certain proportion, add 1% Gaussian noise, take the mixing number 100, and get the mixed spectrum see Figure 4 As shown, the abundance plots of both are shown in Figure 5 .
[0072] (4).NMF decomposition
[0073] For material composition estimated by NMF see Image 6 .
[0074] (5). Composed of least non-negative square calculation materials, the estimated error is given by Figure 7 express. Among them, the average relative error of the abundance of Aluminum is 3.4556%, and the ave...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com