Patents
Literature
82 results about "Human spaceflight" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Human spaceflight (also referred to as crewed spaceflight) is space travel with a crew or passengers aboard the spacecraft. Spacecraft carrying people may be operated directly, by human crew, or it may be either remotely operated from ground stations on Earth or be autonomous, able to carry out a specific mission with no human involvement.
Low-density ablation thermal insulation type composite and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a low-density ablation thermal insulation type composite and a preparation method thereof. The composite adopts phenolic aerogel of the nanometer particle structure as a matrix and adopts a flexible fiber blanket or a fiber weaving body as a reinforcement body, and the composite is obtained through the steps of phenolic resin preparation, phenolic resin solution preparation, thermal treatment of the flexible fiber blanket or the fiber weaving body, steeping of the flexible fiber blanket or the fiber weaving body with the phenolic resin solution, a sol-gel reaction, aging, drying and curing of the composite and the like. Compared with the prior art, the composite is excellent in thermal protective performance, good in mechanical performance, high in designability, simple in preparation technology, low in cost and easy to process and mold, promotes later-period dimensional cutting, meets different thermal protective needs under the medium heat flow and medium and low heat flow environments, and can be applied to manned space flight and deep space detection aircrafts, outer thermal protective layers of various tactic and strategic weapons working for a short time, and inner ablation heat insulation and thermal protective layers of engines, disposable hypersonic vehicles and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Variable Heat Rejection Device
ActiveUS20170160021A1Increase the turndown ratioCosmonautic environmental control arrangementCosmonautic vehiclesWorking fluidControl system
A heat rejection system that employs temperature sensitive shape memory materials to control the heat rejection capacity of a vehicle to maintain a safe vehicle temperature. The technology provides for a wide range of heat rejection rates by varying the shape and thus effective properties of the heat rejection system in response to temperature. When employed as a radiator for crewed spacecraft thermal control this permits the use of higher freezing point, non-toxic thermal working fluids in single-loop thermal control systems for crewed vehicles in space and other extraterrestrial environments.
Owner:COGNATA THOMAS JASPERO +3
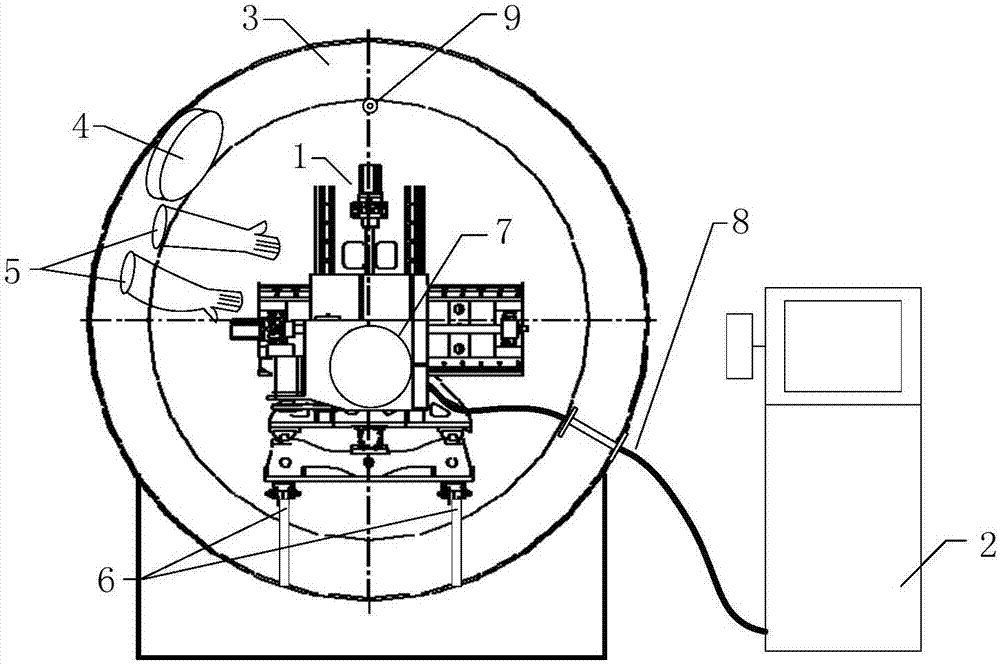
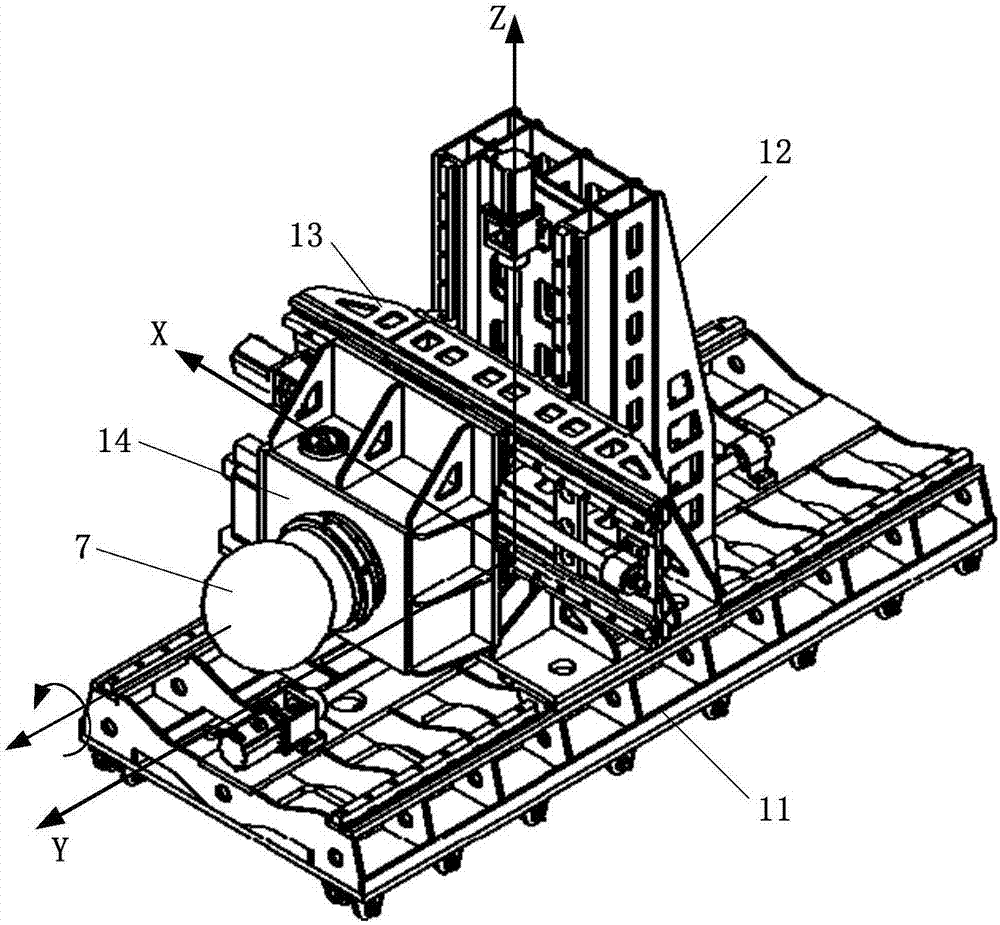
Manned spacecraft extravehicular maintenance ground simulating system
InactiveCN107215487AEnsure consistencyImprove effectivenessCosmonautic condition simulationsSlide plateEngineering
Provided is a manned spacecraft extravehicular maintenance ground simulating system. The system comprises a servo mechanism, a control platform, a vacuum tank, an observation window, spacesuit gloves and a support guide rail. The servo mechanism comprises a base, a stand column, a slide plate and a rotary platform. The base of the servo mechanism is fixed to the support guide rail, and the stand column is installed on the base and can move in the axial direction of the vacuum tank; the slide plate is installed on the stand column and can move in the perpendicular direction; the rotary platform is installed on the slide plate, and can move in the direction vertical to the axial direction of the vacuum tank within a horizontal plane; the rotary platform is internally provided with a motor connected to a rotary disc, the rotary disc is provided with a cross notch which can fix a maintenance equipment imitation part, and the motor rotates to drive the maintenance equipment imitation part to roll; the observation window and the spacesuit gloves are arranged on the vacuum tank. Through the manned spacecraft extravehicular maintenance ground simulating system, the maintenance equipment imitation part can be placed in the vacuum tank, and when the internal and external pressure difference of the spacesuit gloves is simulated, it is simulated that in-orbit extravehicular maintenance experiments are supported for a manned spacecraft when the relative position of the experiment personnel and the maintenance equipment imitation part are arbitrary.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
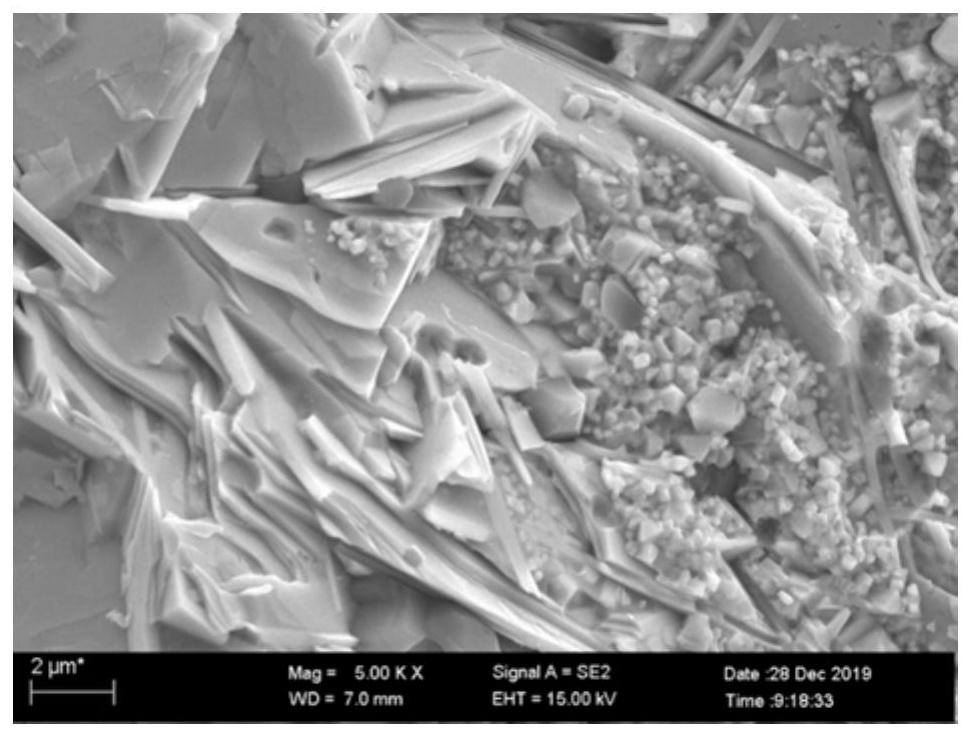
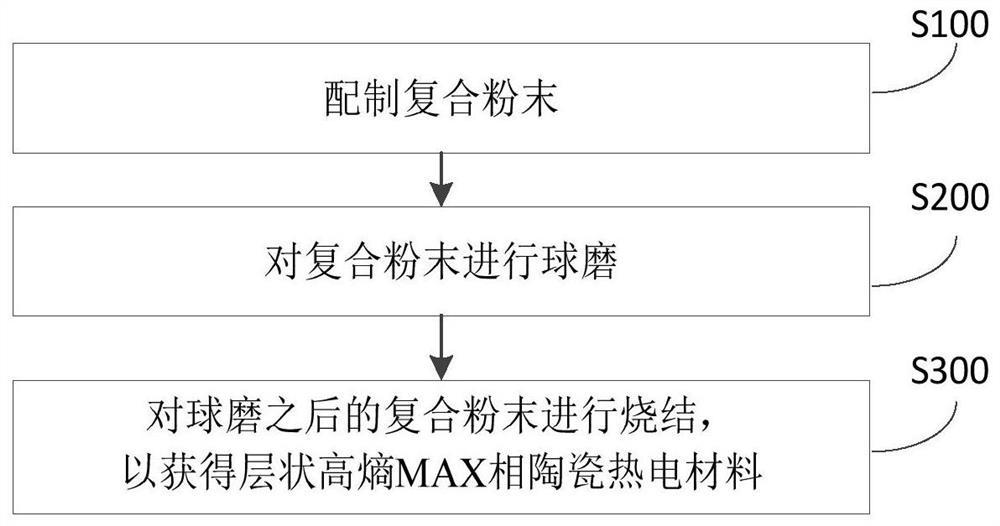
Layered high-entropy MAX-phase ceramic thermoelectric material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111725380AHigh thermoelectric figure of meritSimple processThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsThermoelectric materialsHexagonal crystal system
The invention provides a layered high-entropy MAX phase ceramic thermoelectric material and a preparation method thereof. A molecular formula of the layered high-entropy MAX phase ceramic thermoelectric material is Mn+1AXn, M is at least three elements selected from IIIB, IVB, VB and VIB group elements, A is at least one element selected from IIIA, IVA, VA and VIA group elements, X is a carbon element, and n is 1, 2 or 3. The layered high-entropy MAX phase ceramic thermoelectric material is advantaged in that an element ratio in the same position can be regulated and controlled according to actual requirements, the material has a hexagonal crystal system structure, the space group is P63 / mmc, a crystal cell is formed by alternately stacking Mn+1Xn units and A-layer atoms in the c direction, and the high-entropy alloy is formed through the design of the combination of more than three M elements so that the high-entropy MAX-phase ceramic thermoelectric material has very wide applicationprospects in the fields of manned spaceflight, national defense war industry, automobile manufacturing, micro-nano electronics and the like, particularly in the fields of thermoelectric power generation, thermoelectric refrigeration and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
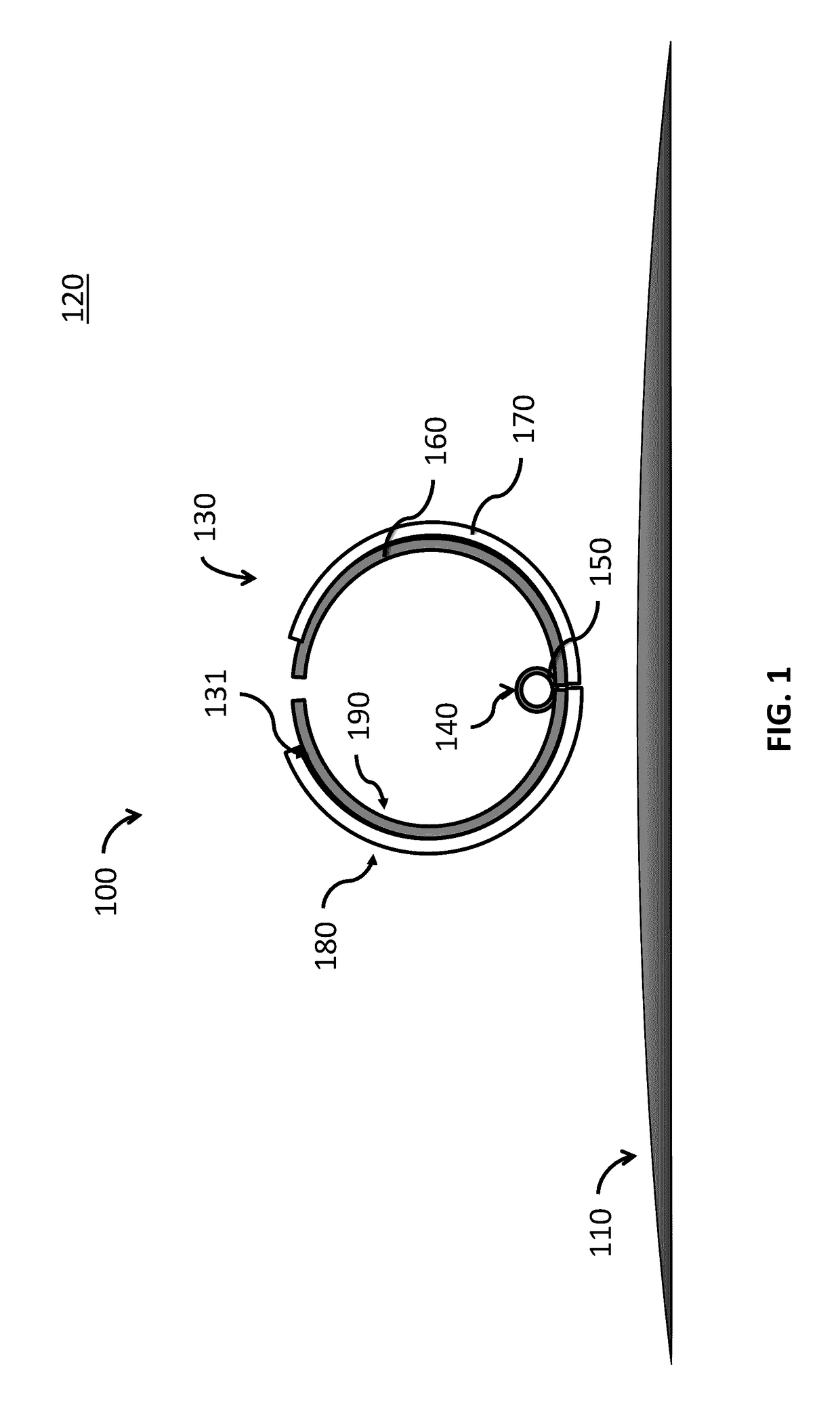
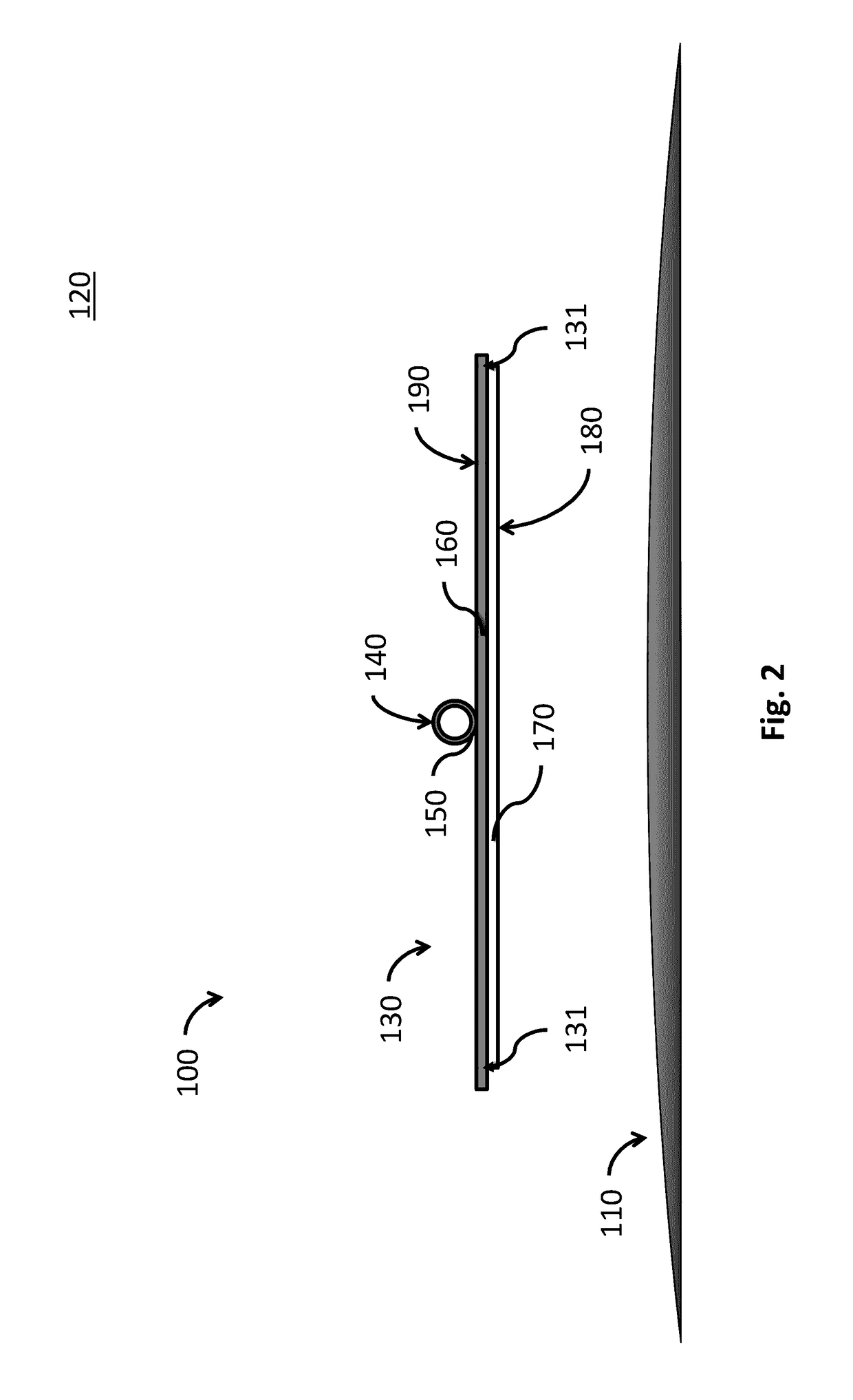
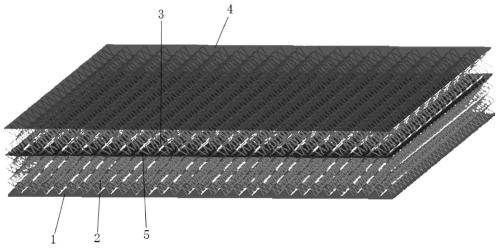
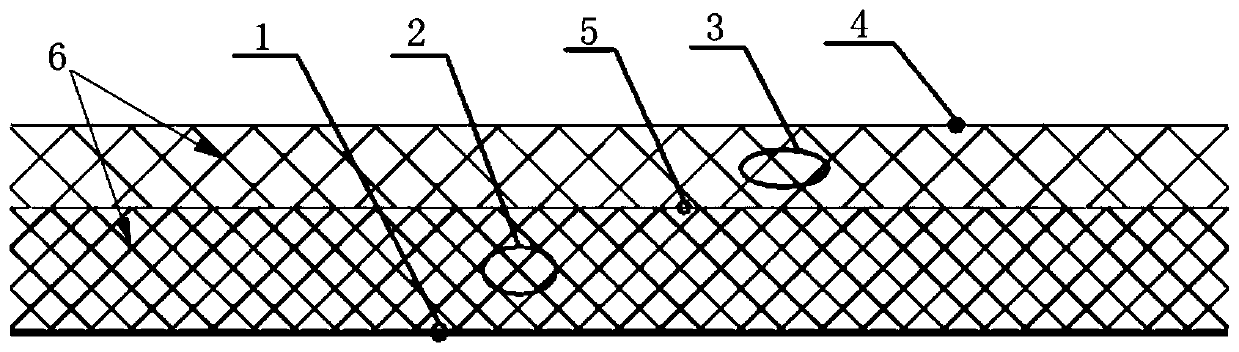
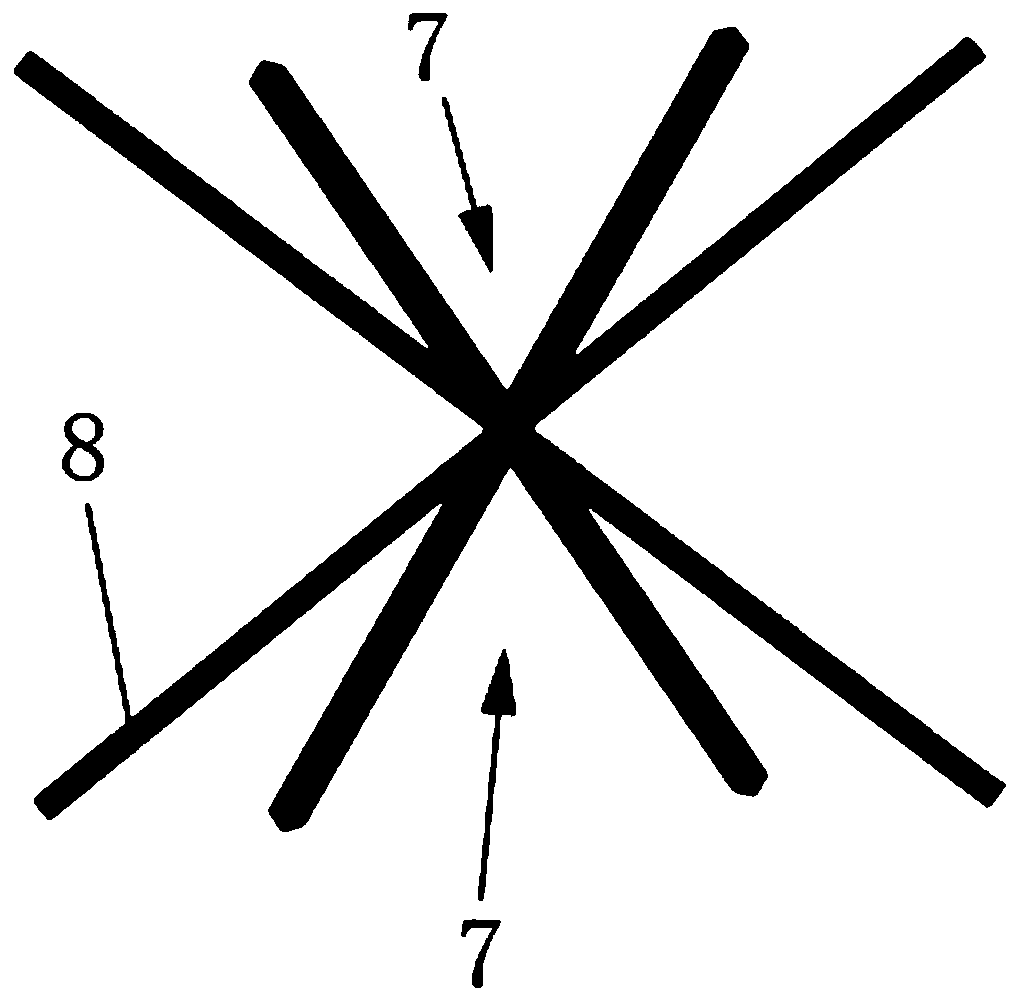
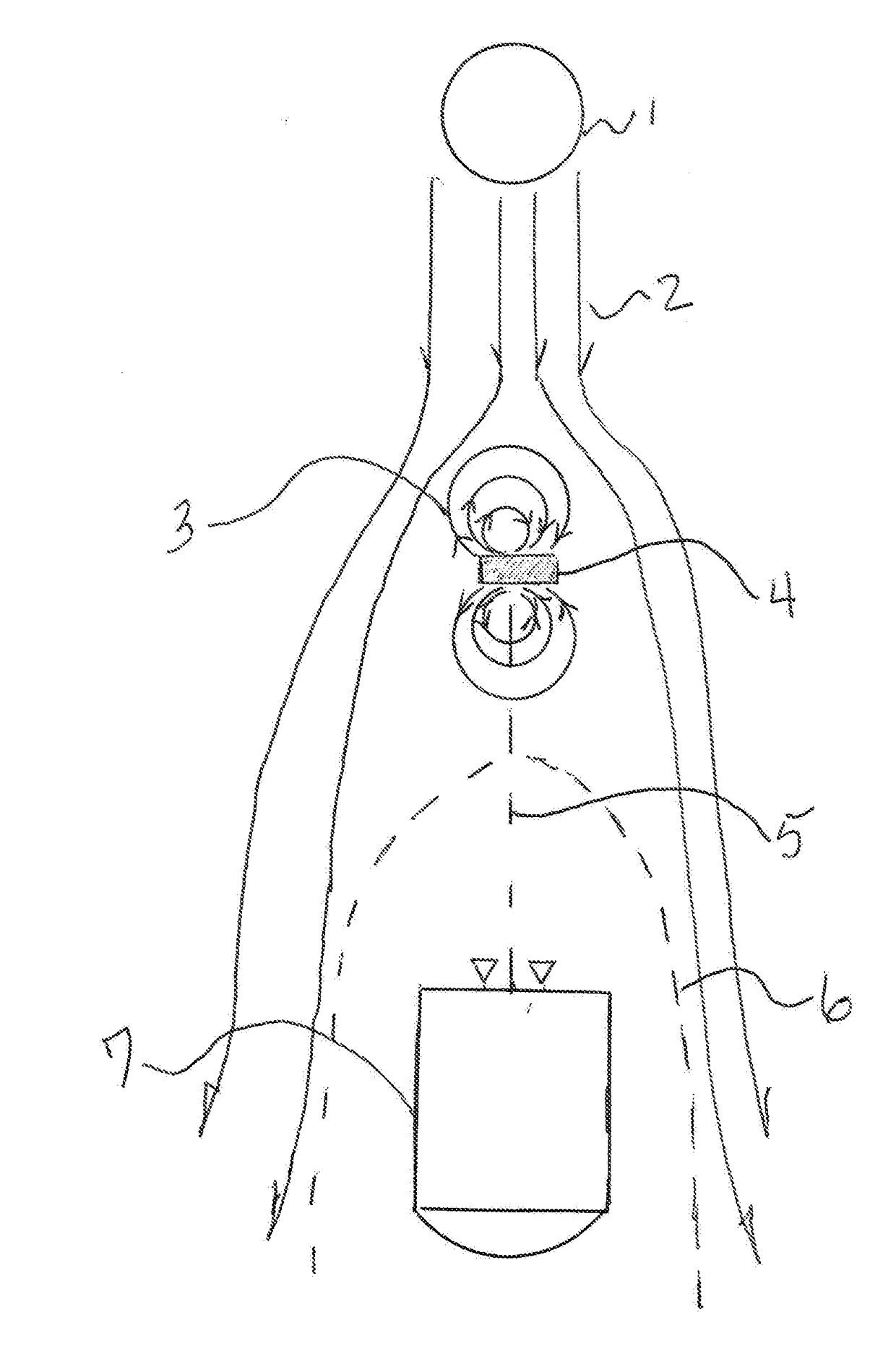
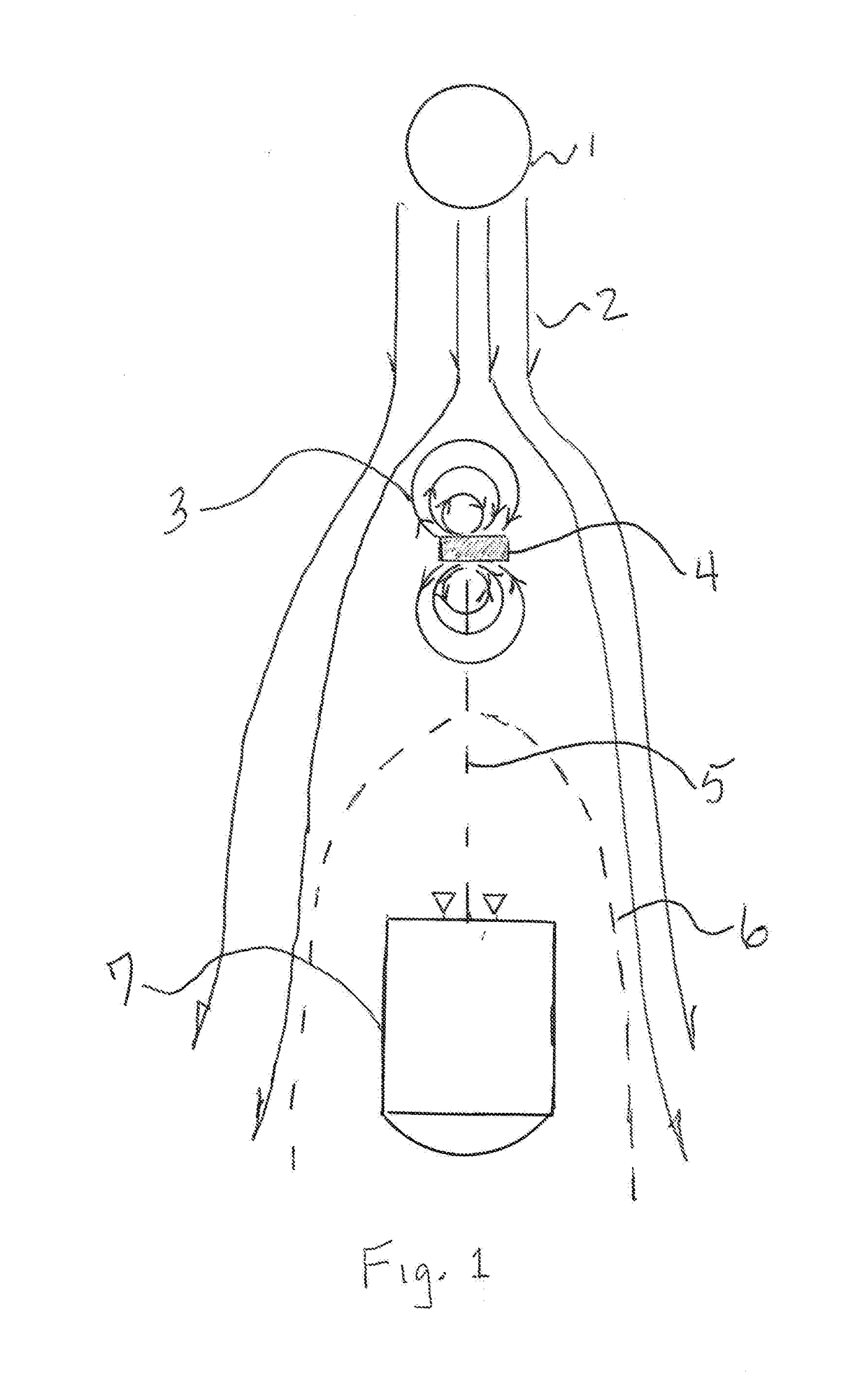
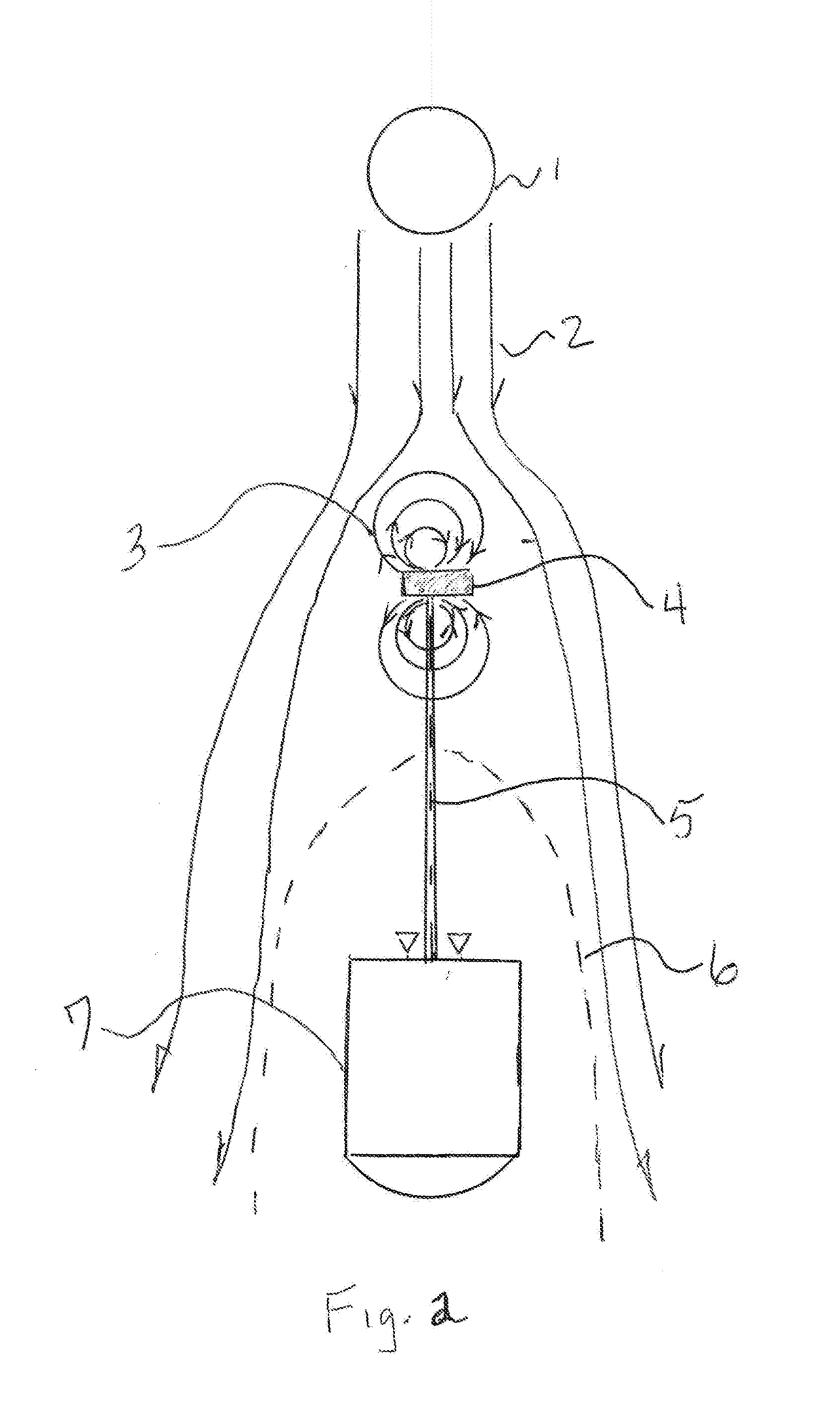
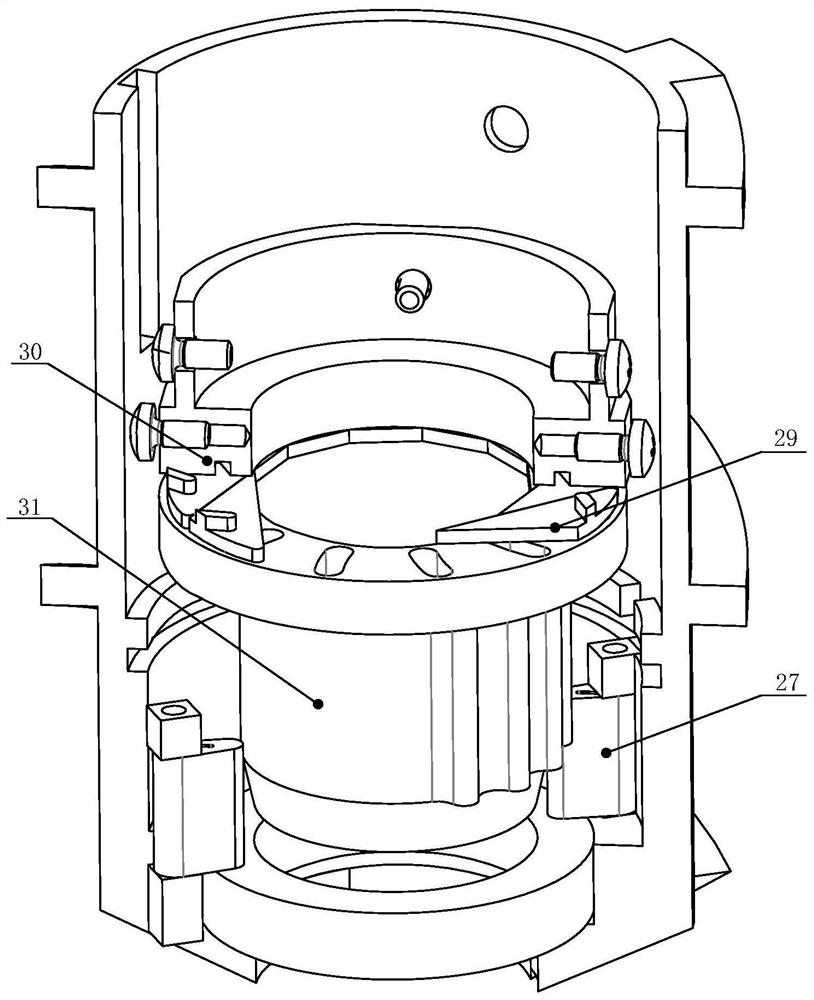
Sealed cabin wall structure of manned spacecraft
The invention relates to a sealed cabin wall structure of a manned spacecraft. The sealed cabin wall structure comprises a first partition plate (1), a first dot matrix layer (2), a second dot matrixlayer (3) and a third partition plate (4) which are sequentially arranged; the first dot matrix layer (2) and the second dot matrix layer (3) are both composed of tightly arranged cell structures (6);the sealed cabin wall structure further comprises a second separation plate (5), and the second partition plate (5) is positioned between the first dot matrix layer (2) and the second dot matrix layer (3); the size of a single cell structure (6) forming the first dot matrix layer (2) is smaller than that of a single cell structure (6) forming the second dot matrix layer (3); and the thickness ofthe first dot matrix layer (2) is larger than that of the second dot matrix layer (3). The cabin wall structure integrates multiple functions, and the requirements for weight reduction and efficiencyimprovement of spacecraft design are met.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
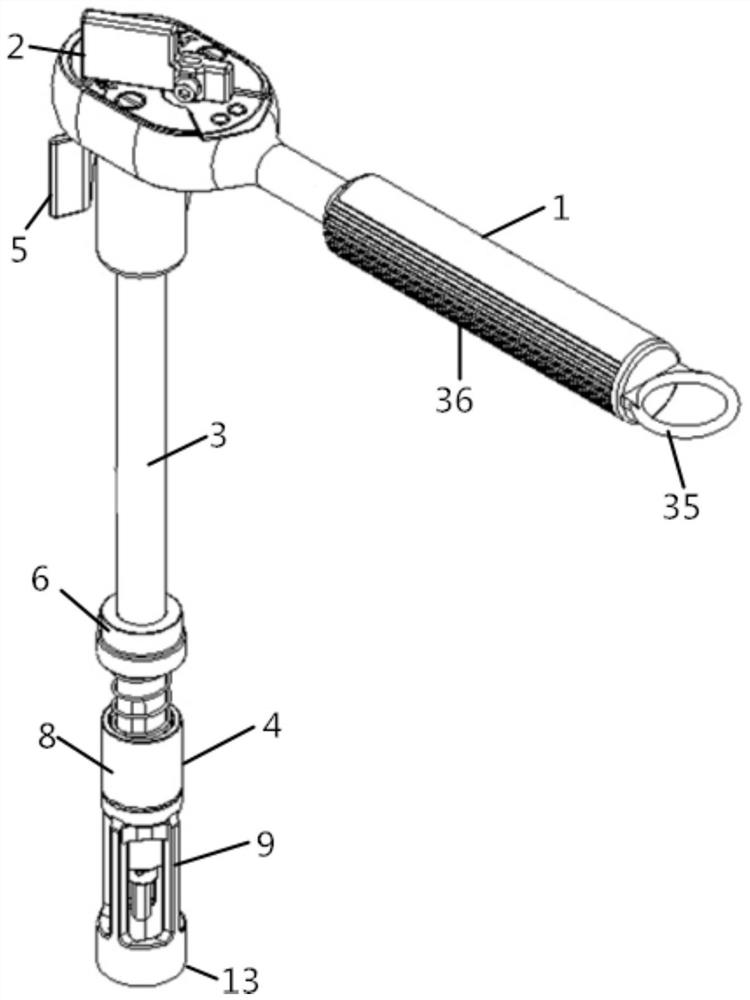
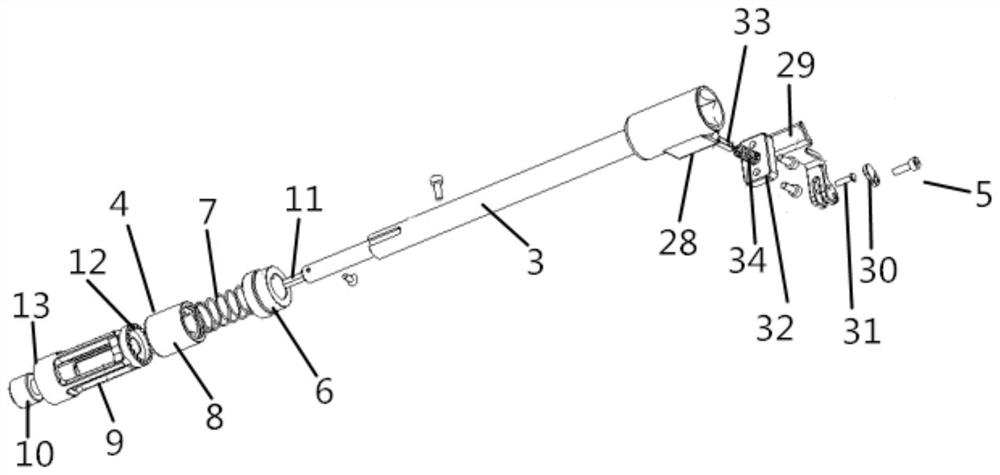
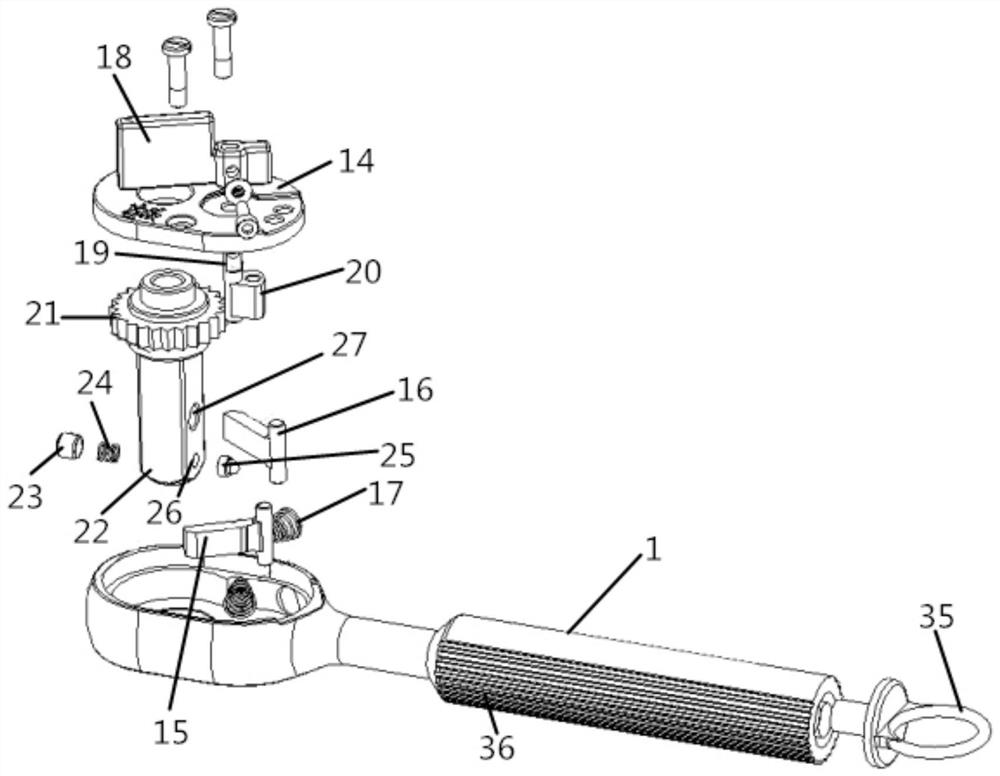
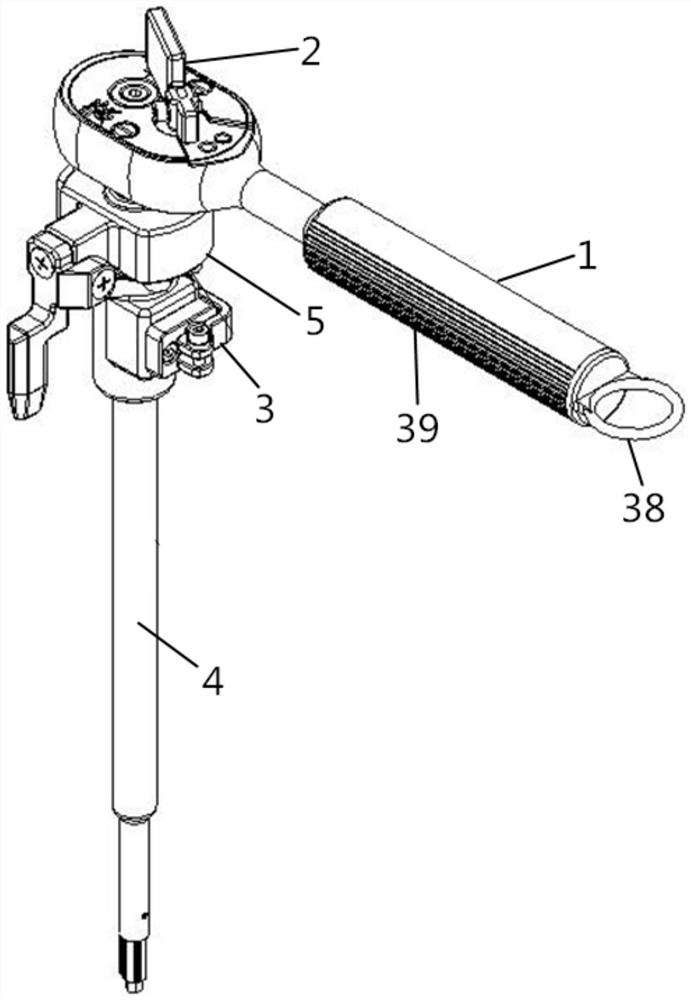
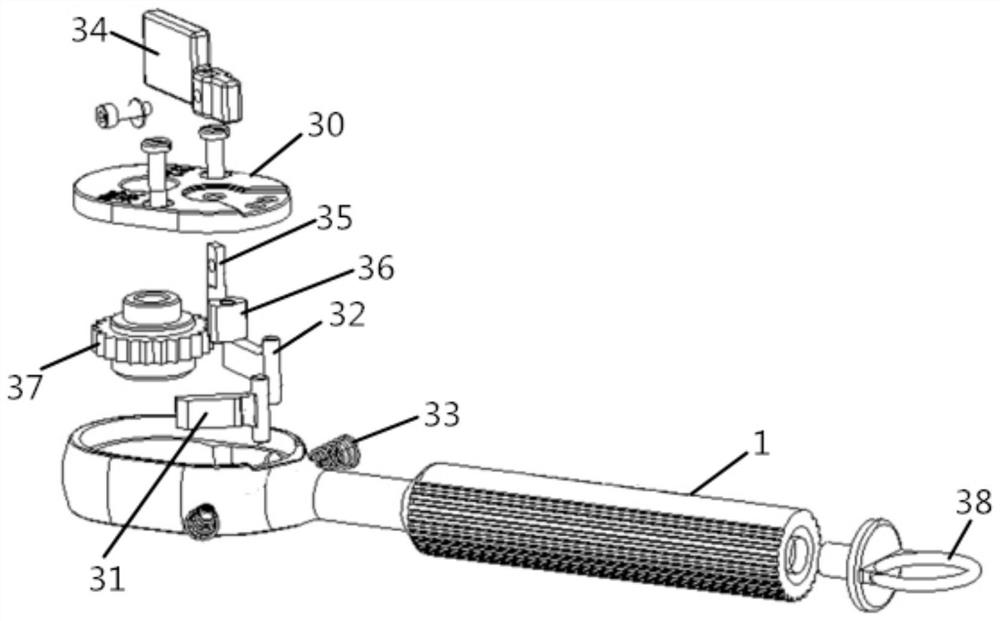
Spaceflight ratchet wrench capable of being used by one hand
The invention relates to the technical field of manned spaceflight, in particular to a spaceflight ratchet wrench capable of being used by one hand, which comprises a handle shell, a ratchet device and an extension bar, and further comprises a screwdriver head guide device and a locking mechanism, wherein the ratchet device is arranged on the handle shell; the the screwdriver head guide device and the locking mechanism are arranged at the head end and the tail end of the extension bar respectively, and the extension bar is connected with the ratchet device through the locking mechanism. According to the spaceflight ratchet wrench capable of being used by one hand disclosed in the invention, the screwdriver head guide device and the locking mechanism are respectively arranged at the front end and the tail end of the extension bar; the locking mechanism can be quickly locked with the ratchet device, and the screwdriver head guide device for realizing the ratchet wrench at the front end of the extension bar can realize the wheel returning operation of the ratchet device, so that the space station astronaut can be ensured to mount and dismount the screw by a single hand outside a cabin.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
In-orbit operation labor-saving device for load supporting frame in space station cabin
PendingCN112520069ASmall transports take up resourcesCompact structureCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsControl theorySpace requirements
The invention belongs to the field of manned aerospace engineering space station systems, and particularly relates to an in-orbit operation labor-saving device for a load supporting frame in a space station cabin. The device comprises an in-cabin load supporting frame, a fixed adapter, a labor-saving mechanism, non-disengagement screws and corner fittings, the corner fittings are arranged at the bottom and the top of the in-cabin load supporting frame, and all the corner fittings are connected with a standard interface of a space station cabin section through the non-disengagement screws; andthe labor-saving mechanism is arranged on the fixed adapter, the fixed adapter is connected with the in-cabin load supporting frame, so that the labor-saving mechanism corresponds to the non-disengagement screws on the corner pieces, and the labor-saving mechanism tightens or loosens the non-disengagement screws through torque multiplication, thereby assembly and disassembly of the in-cabin load supporting frame are achieved. Efficient torque and rotating motion transmission can be achieved, the beneficial effects of single input and two-way output are achieved, and the requirements of astronauts for on-orbit operation capacity and torque and operation space needed by screw disassembling and assembling are met.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Deployed electromagnetic radiation deflector shield (DERDS) which creates a zone of minimum radiation and magnetic/plasma effects for spacecraft and extra-planetary base station protection
ActiveUS20180281995A1Precise positioningIncrease field strengthCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic radiation protectionNatural satellitePlasma effect
A deployable electromagnetic radiation deflector shield (DERDS) is disclosed. It is used in protecting manned spacecraft or robotic spacecraft flying outside of the Earth's protective magnetic field as well as manned extra-planetary base stations. This DERDS is deployed from the spacecraft during flight and positioned to be between the Sun and the protected spacecraft (or in the case of Jupiter / Saturn missions, transitioning to be between that planet and the spacecraft). It remains in the proper position from the spacecraft by its own sensors and computer controlled gaseous or ion thrusters. It is deployed away from the spacecraft to better deflect incoming solar radiation (or Jovian radiation and the like), and not have its magnetic field affect the protected spacecraft or extra-planetary base station's equipment and astronauts (as in prior art). Its deployment will also prevent any captured radiation in its generated magnetic torus (like Earth's Van Allen radiation belts) from affecting the protected spacecraft or extra-planetary base station. The DERDS has a self-contained superconducting electromagnet that creates a magnetic field to deflect incoming solar radiation, including CMEs (coronal mass ejections) and repositioned for x-ray and gamma ray bursts from distant supernovae. It utilizes a tethered umbilical cord to transmit electrical power and back up commands from the spacecraft or satellite. Another variant or embodiment would be to mount the DERDS on a telescopic / extendable solid mount and remove the need for thrusters within the DERDS as it would move as an attachment to the spacecraft. The source of electrical power in this embodiment is the protected spacecraft's solar arrays, RTG (radioisotope thermal generator), fuel cells, and or batteries. In addition, it can be constructed with these power supplies mounted within the DERDS, as in a self-contained deployed spacecraft / satellite. Another embodiment of the DERDS would be mounted on an ecliptic track wherein the DERDS moves along the track to protect the manned base station.
Owner:NASA
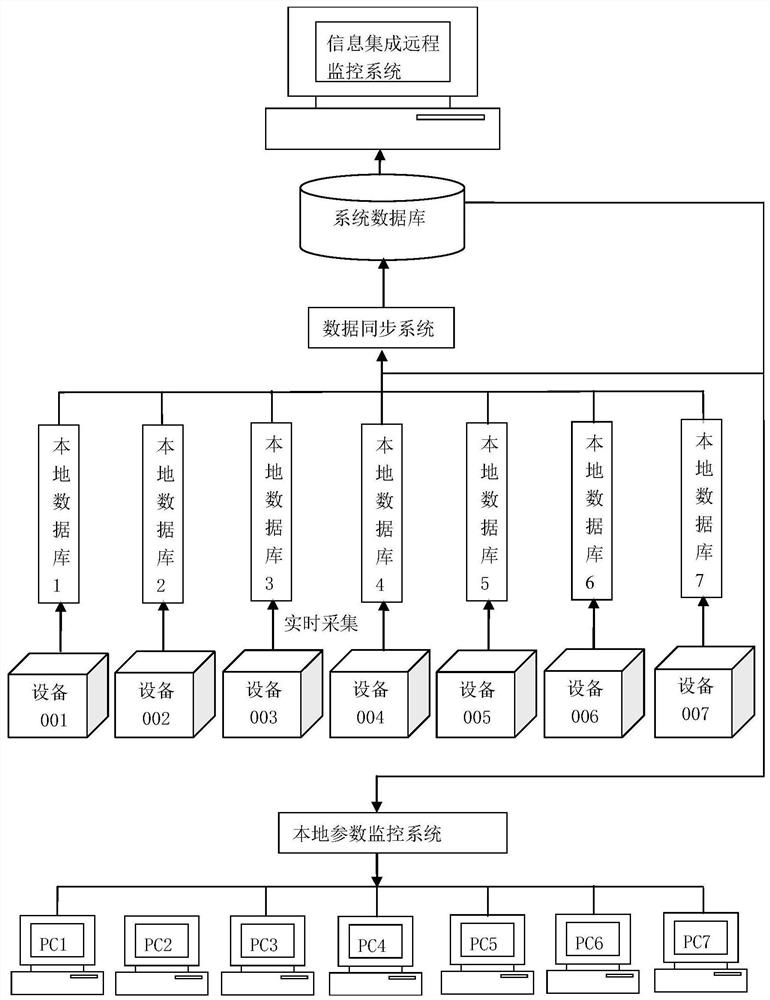
Intelligent remote parameter monitoring system for manned spacecraft manufacturing equipment production line
InactiveCN111624960AEasy to understandEasy for statistical analysisProgramme total factory controlData synchronizationData acquisition
The invention discloses an intelligent remote parameter monitoring system for a manned spacecraft manufacturing equipment production line. The intelligent remote parameter monitoring system comprisesa plurality of data acquisition systems, a plurality of local computers and a database server, wherein the plurality of data acquisition systems are correspondingly connected with the plurality of local computers, the plurality of local computers are connected with the database server, and each data acquisition system comprises a field controller, a camera, a card reader and a scanning gun; and each local computer is provided with an OPC client, a local database and a local parameter monitoring system. The database server is provided with a data synchronization system, a system database and aninformation integration remote monitoring system. According to the invention, local monitoring and remote monitoring of a plurality of equipment parameters are realized on a manned spacecraft manufacturing equipment production line. According to the invention, the production state and production data of each device can be remotely checked in real time by connecting with the Internet in a conference room large screen or an office terminal, and remote monitoring and management of field devices and task completion conditions are realized.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF AUTOMATION FOR MACHINERY IND
Pressure protection device for sealed cabin of manned spacecraft under emergency pressure loss condition
ActiveCN110963088AImprove securityImprove reliabilityCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic safety/emergency devicesPressure suitClassical mechanics
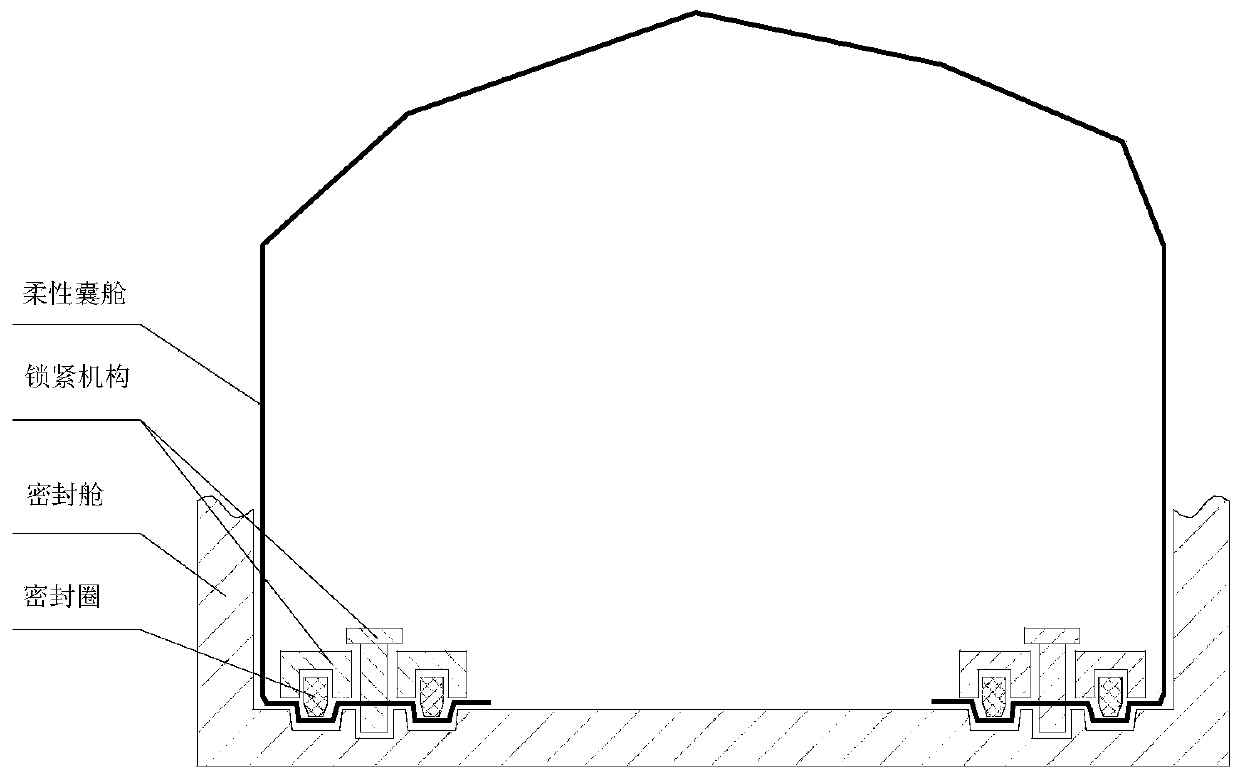
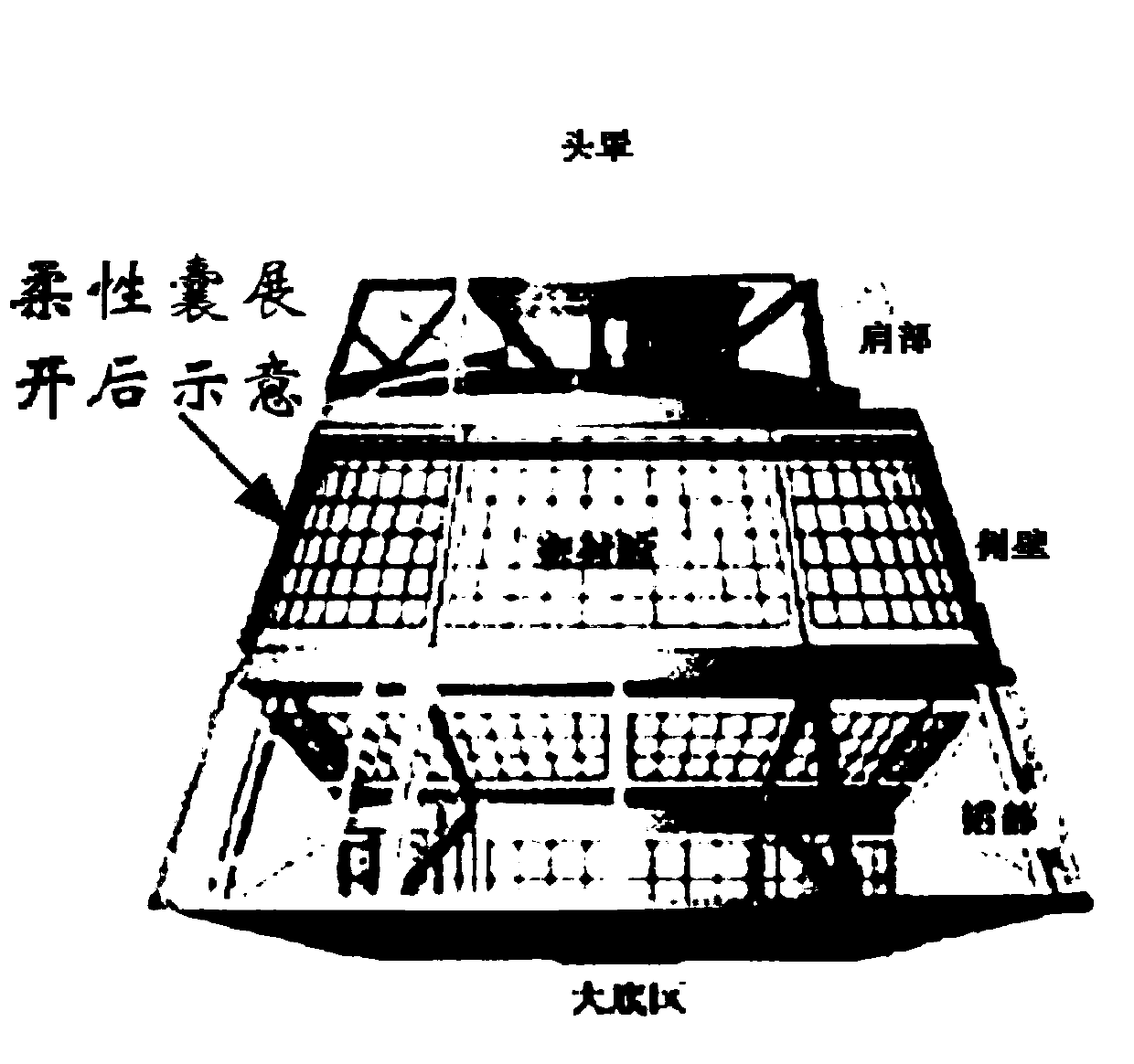
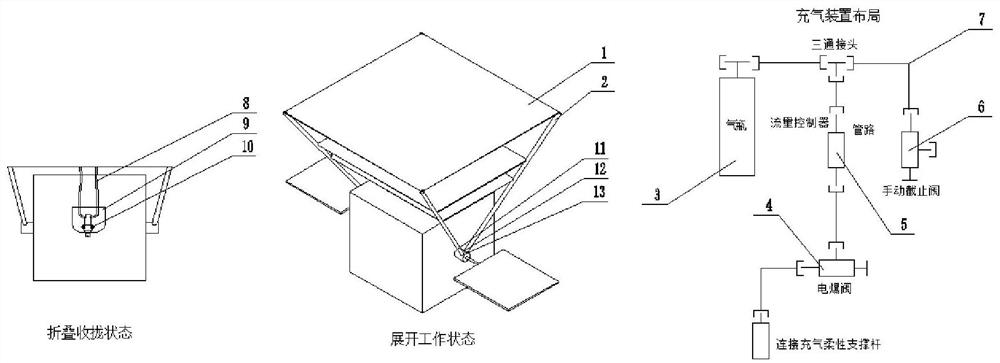
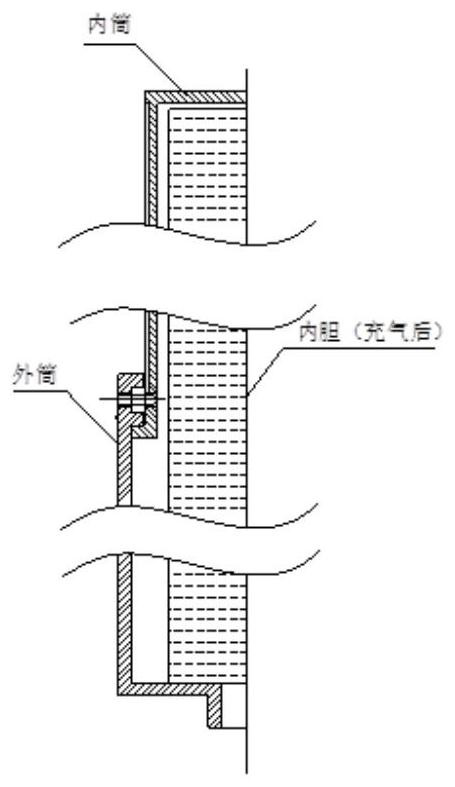
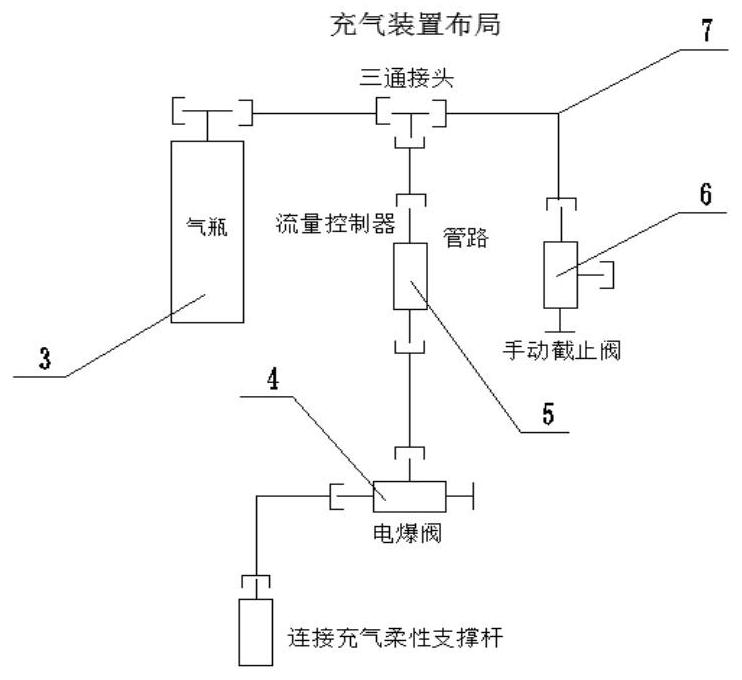
The invention relates to a pressure protection device used under the pressure loss condition of a sealed cabin of a re-entry capsule of a manned spacecraft. A flexible cabin inner bag is arranged in aconnecting area of the side wall of the re-entry capsule and an outsole; the side wall is shaped after unfolding; when the sealed cabin of the re-entry capsule loses pressure, by starting the flexible cabin inner bag installed in the re-entry capsule in advance, the flexible cabin inner bag is rapidly unfolded, fixed, inflated and sealed, so that a new sealed environment is created, and resourcessuch as a life support system, cabin pressure clothes and communication which are originally arranged on the spaceship are used for jointly guaranteeing that astronauts fly emergently on orbit for seven days until the astronauts return safely.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Flexible deployable active defense device
ActiveCN112498749AImplement proactive protectionLight in massCosmonautic thermal protectionProtection against meteoritesFlight vehicleStructural engineering
The invention relates to a flexible deployable active defense device which comprises a protection device, an inflation device, a locking device and a rotation control device. The protection device comprises an expandable protection screen and an inflatable supporting rod, the expandable protection screen can be divided into at least two functional layers according to the protection type, and one functional layer is a thermal shock protection screen and used for preventing attacks of laser weapons; the other one is a kinetic energy impact protection screen which respectively undertakes the functions of differentiating energy distribution and attenuating and arresting kinetic energy; the functional layers can be adjusted according to actual requirements; the inflatable supporting rod is composed of a telescopic rod and an inner container. The method has a wide application prospect in the field of spacecraft protection and safety, can be particularly used for high-value satellite protection, manned spacecraft protection and the like, and can further realize product serialization and industrialization.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
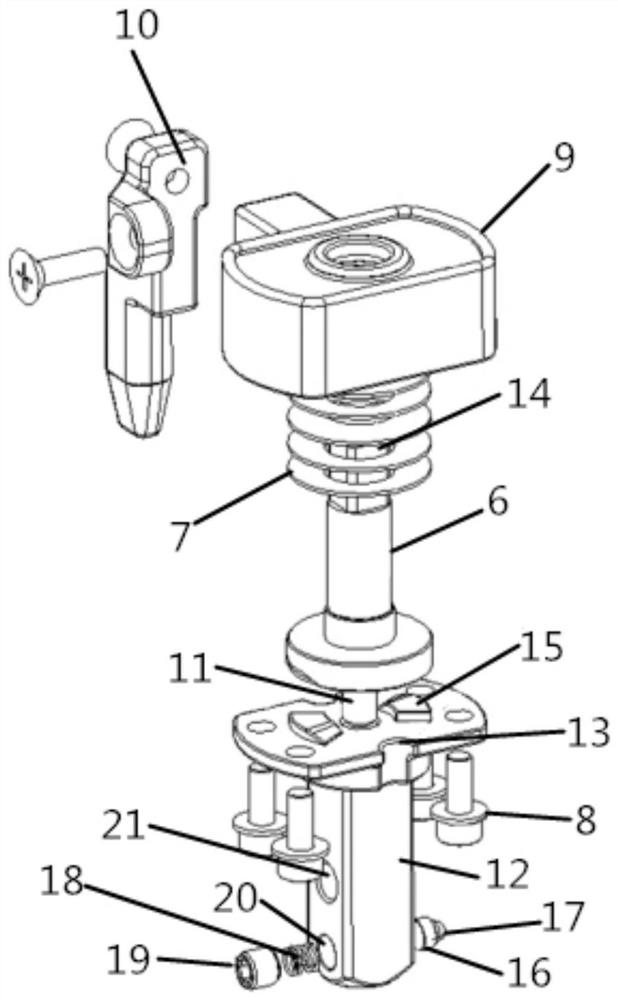
Constant-force wrench used by astronaut in zero-gravity environment
The invention relates to the technical field of manned spaceflight, in particular to a constant-force wrench used by an astronaut in a zero-gravity environment. The constant-force wrench comprises a handle shell, a ratchet device, a locking mechanism, an extension bar and a force measuring assembly, wherein the ratchet device is arranged on the handle shell; the force measuring assembly and the ratchet device are arranged in a matched mode to control input torque; and the extension bar is connected with the force measuring assembly through the locking mechanism. According to the constant-force wrench used by the astronaut in the zero-gravity environment, through the arrangement of the force measuring assembly, the force measuring assembly can measure and fix force in the screw tightening process; on the premise that the astronaut cannot accurately sense the magnitude of applied force, force fixing operation needs to be completed on a non-disengaging fastening device in the screwing process, and the torque is controlled within a certain range; and in addition, through the arrangement of the ratchet device and the locking mechanism, alignment operation and vertical force application operation can be rapidly conducted on the extension bar, so that the astronaut can screw nails through the wrench more conveniently and rapidly.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
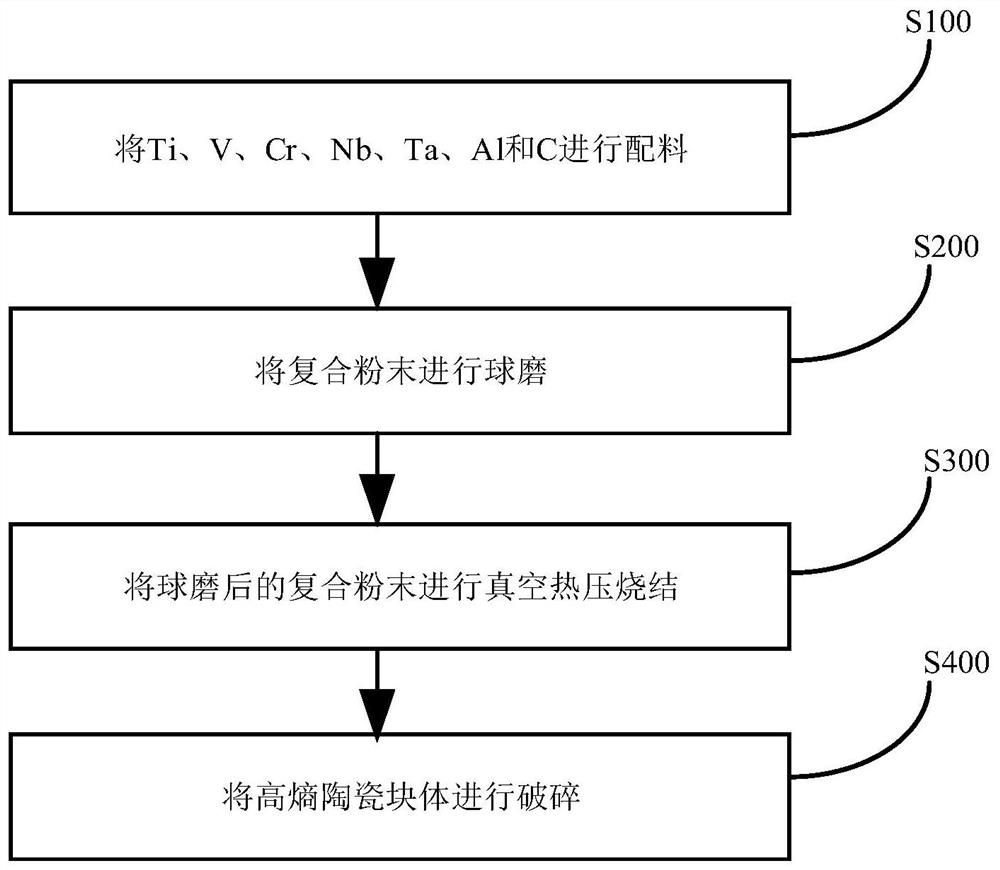
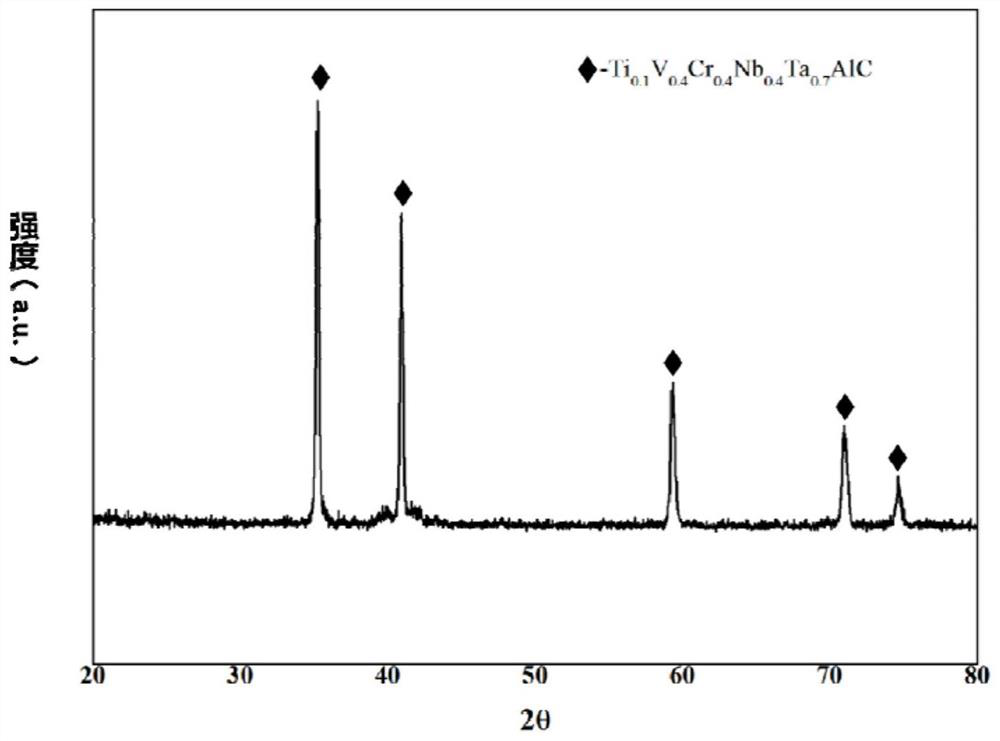
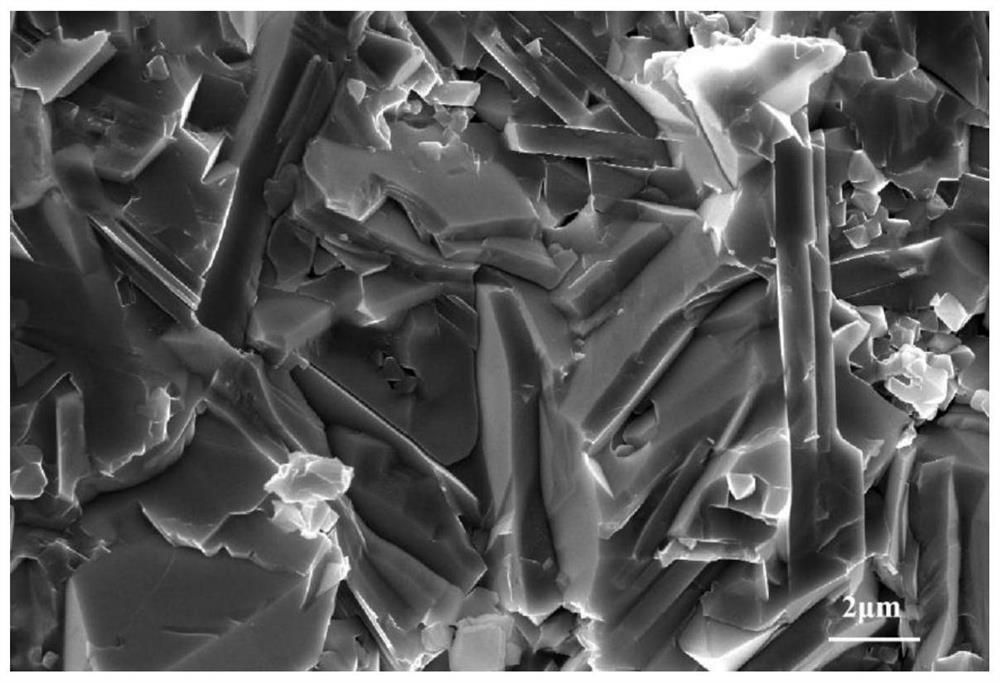
High-entropy ceramic material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-entropy ceramic material and a preparation method thereof. The chemical formula of the high-entropy ceramic material is TiaVbCrcNbdTaeAlC, wherein a + b + c + d + e = 2, and the values of a, b, c, d and e are not completely the same. Therefore, the high-entropy ceramic material has the advantages of high strength, high hardness, strong oxidation resistance, good thermal stability and the like, and has a very wide application prospect in the fields of manned spaceflight, national defense war industry, automobile manufacturing, micro-nano electronics and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
On-orbit service and maintenance verification method and system
ActiveCN112158360ATimely assessmentUnderstand clearlyLaunch systemsCosmonautic partsSimulationSpaceflight
The invention relates to a manned spacecraft on-orbit service and maintenance verification method. The method comprises the following steps of a building a test environment, transporting materials required by on-orbit verification to an extraterrestrial space station, and quickly building the test environment by utilizing the existing resources of a manned aerospace system and the flexible controlcapability of an astronaut; b assembling materials in a cubesat module form in a space station cabin, and carrying out on-orbit comprehensive detection on the materials; and c releasing the target inthe materials out of the space station cabin, and performing an approaching observation test and a net capturing test on the target. Verification is carried out on the manned spacecraft on-orbit service and maintenance technology, and compared with other technical verification methods, the method has the advantages of being good in technical basis, high in supporting capacity, small in task risk,large in number of guarantee resources, low in test cost, high in efficiency, comprehensive in verification and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
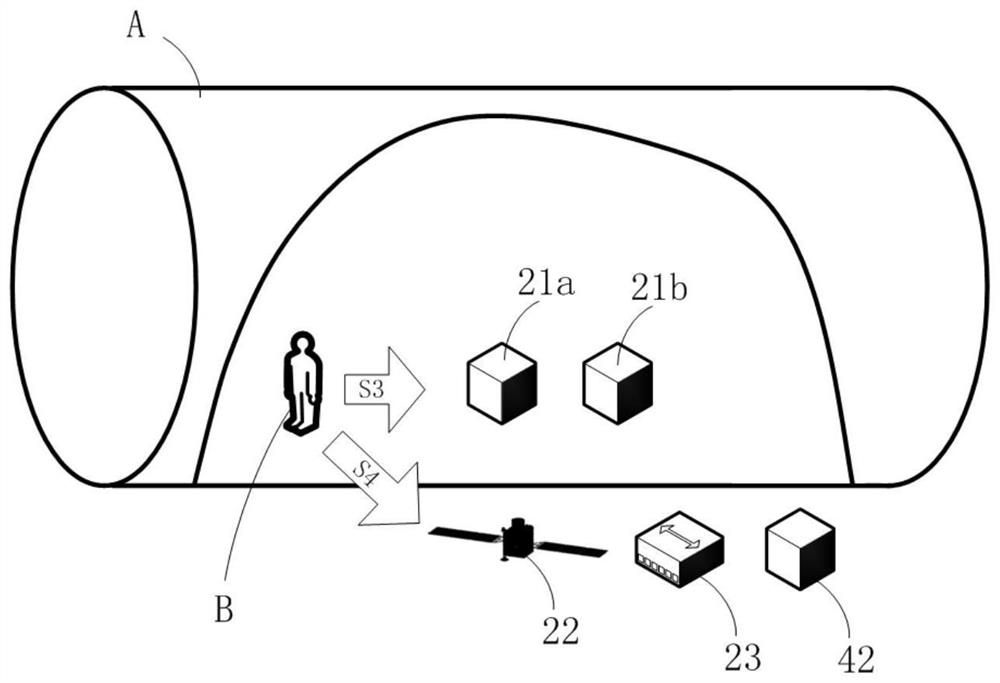
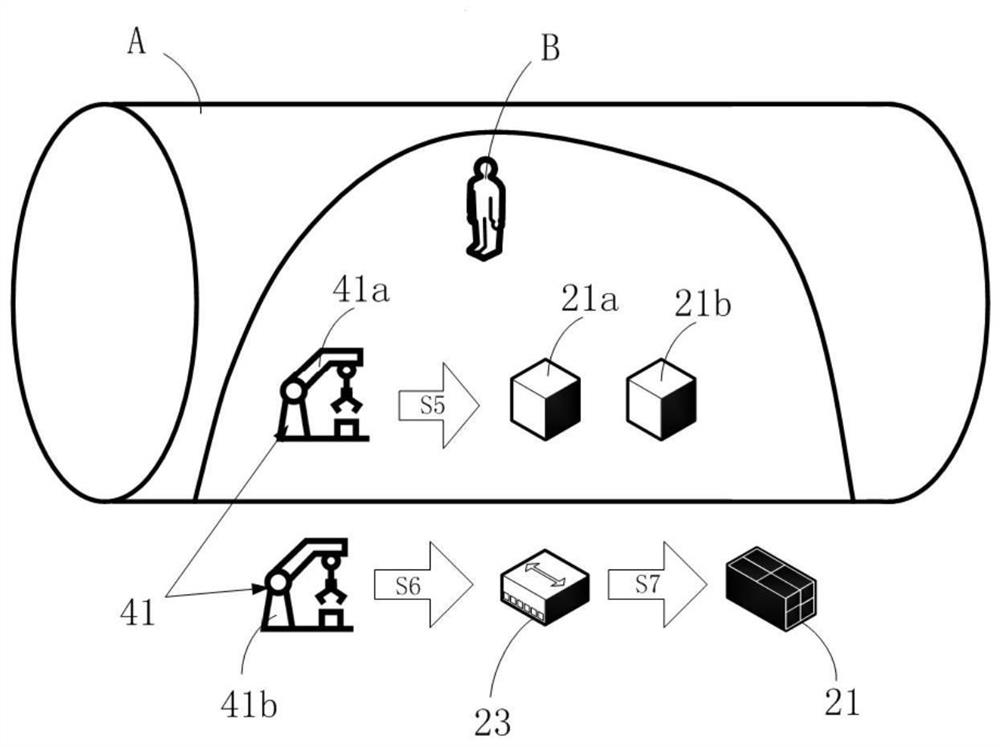
Manned spacecraft on-orbit replaceable unit identification method
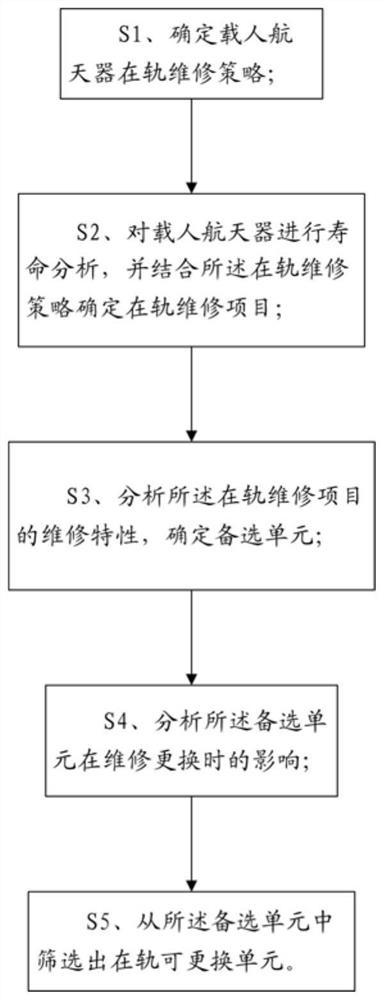
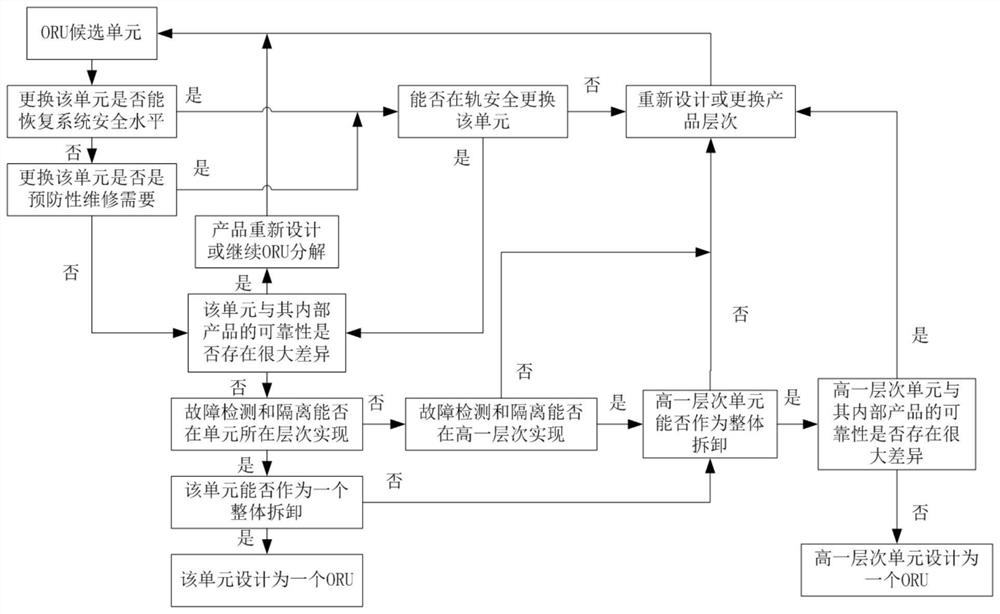
ActiveCN112722328AEasy to replaceEnsure safetyCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsMaintenance strategySystem safety
The invention relates to a manned spacecraft on-orbit replaceable unit identification method. The method comprises the following steps of S1, determining a manned spacecraft on-orbit maintenance strategy; S2, performing life analysis on the manned spacecraft, and determining an on-orbit maintenance project in combination with the on-orbit maintenance strategy; S3, analyzing the maintenance characteristics of the on-orbit maintenance project, and determining alternative units; S4, analyzing the influence of the alternative units during maintenance and replacement; and S5, screening out an on-orbit replaceable unit from the alternative units. Requirements and influences of the on-orbit maintenance unit on the aspects of safety, reliability, maintainability, testability, supportability and the like are comprehensively considered, so that the purposes of quickly and conveniently replacing the unit and reducing maintenance and guarantee resources on the basis of guaranteeing system safety are achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
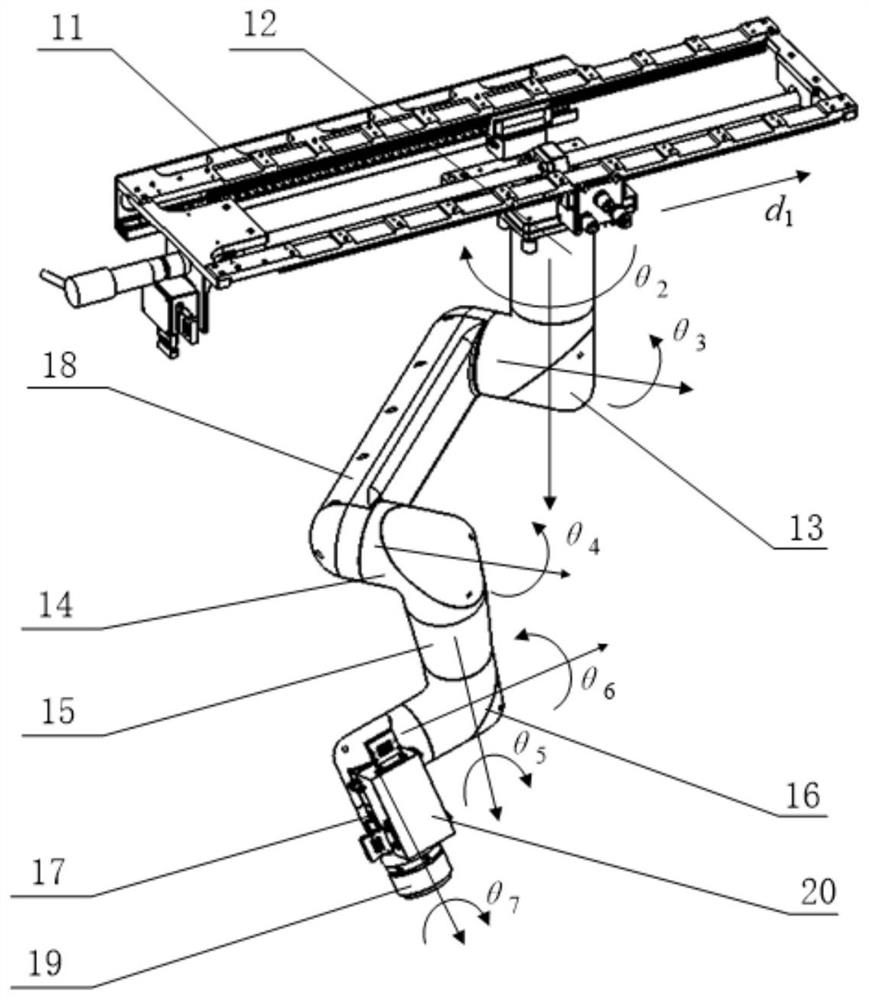
Mechanical arm used for space station load on-orbit maintenance
The invention relates to manned aerospace space station scientific experiment operation equipment, in particular to a mechanical arm used for space station load on-orbit maintenance. The mechanical arm comprises a maintenance box and a load maintenance mechanical arm body hung upside down in the maintenance box. The load maintenance mechanical arm body has seven degrees of freedom, a quick locking mechanism and a camera module are arranged at the execution tail end, the quick locking mechanism is used for being connected with a maintenance tool, and the camera module is used for collecting image information of to-be-maintained loads. According to the mechanical arm, the minimization design of the size, weight and energy consumption can be realized, the functional requirement of carrying out load maintenance on a space station is met, and an astronaut autonomously completes or is assisted in completing load on-orbit in-place maintenance.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
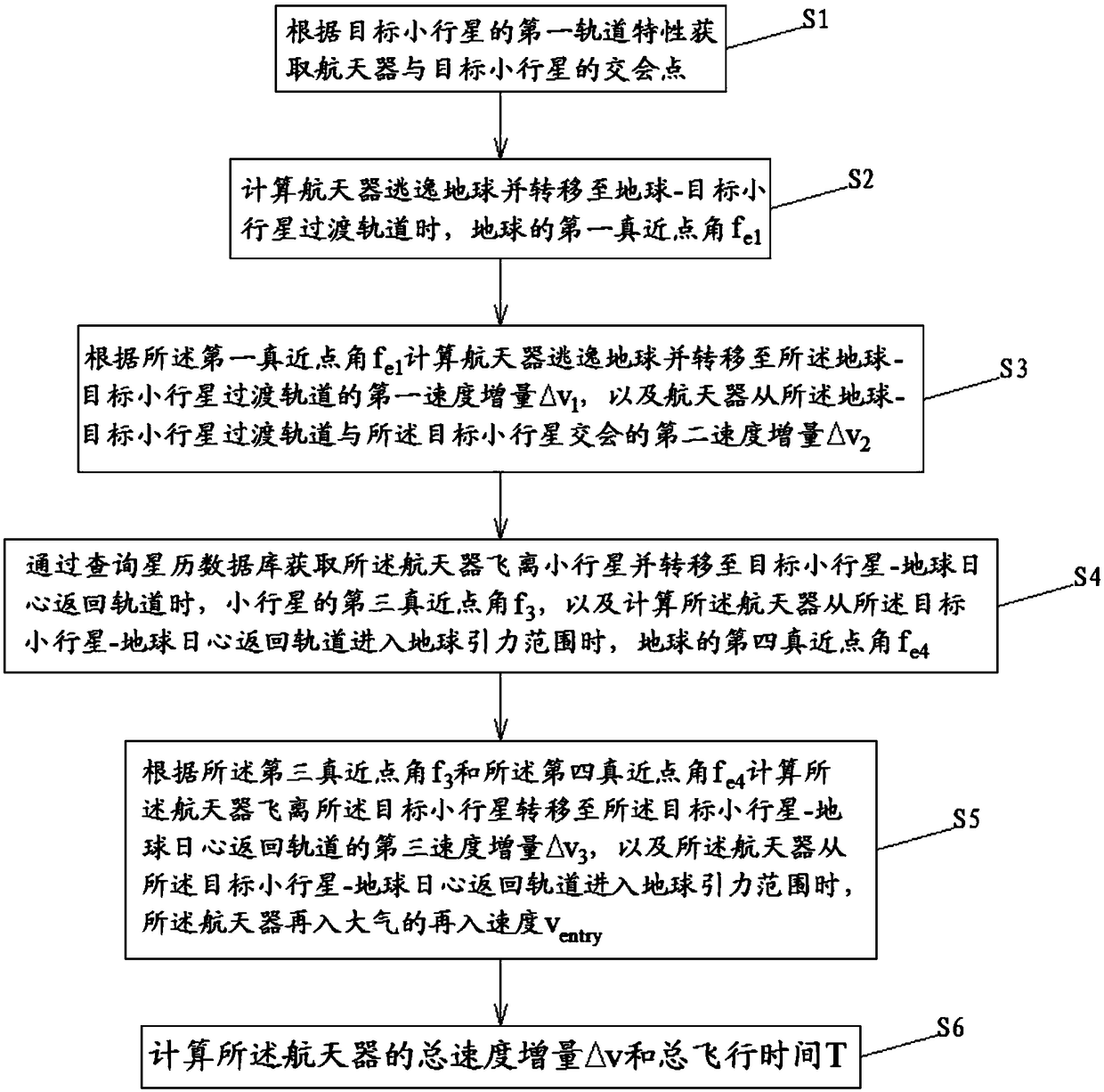
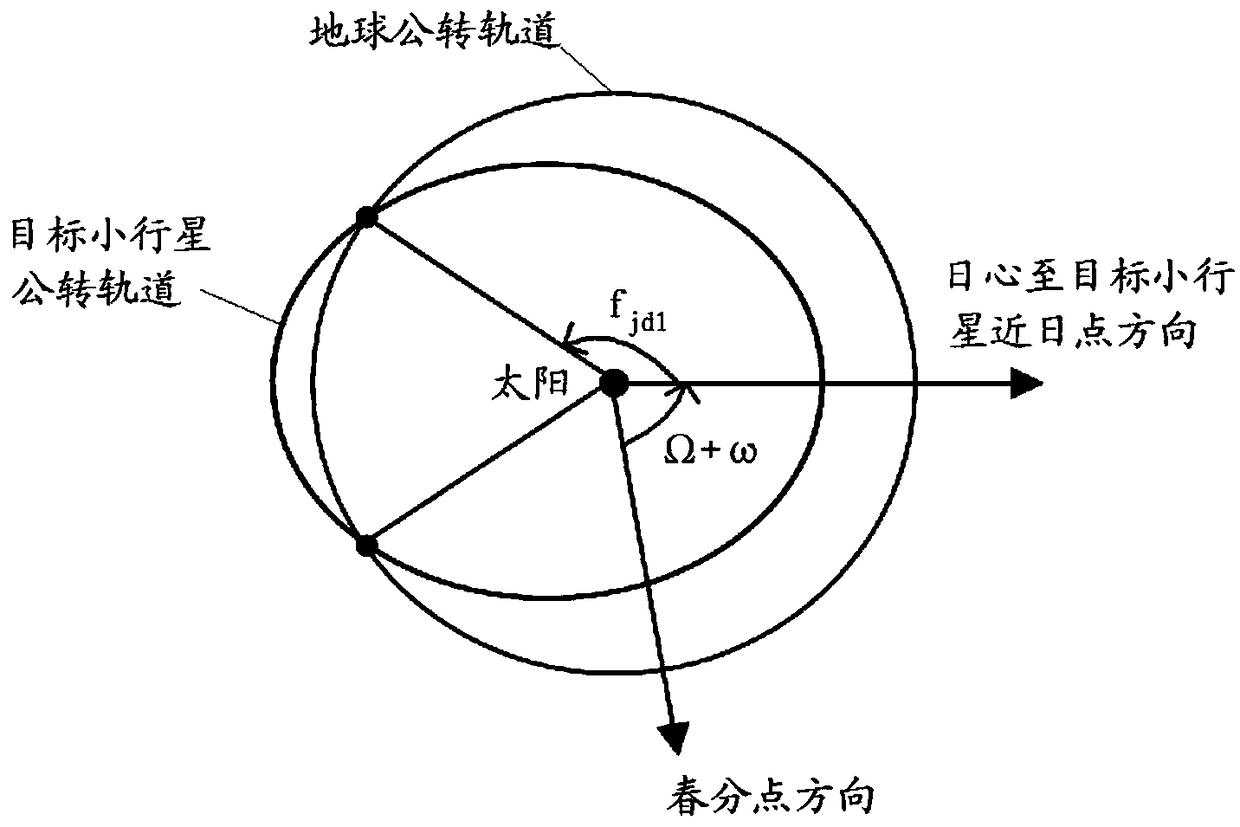
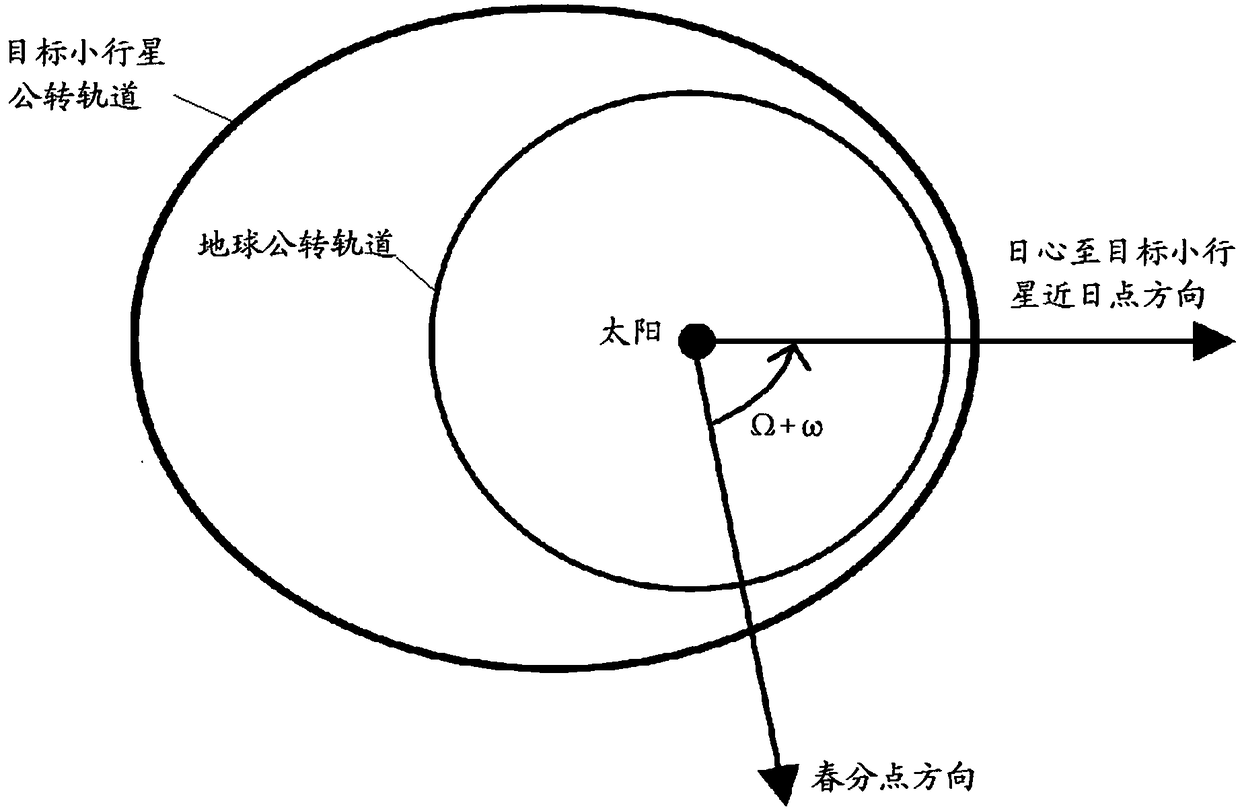
Orbit design methods for the detection and return of near-Earth asteroids by manned spacecraft
ActiveCN109117543ATotal speed increment for small orbital changesReduce weightDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTrue anomalyTime of flight
The invention relates to an orbit design method for detecting and returning a near-earth asteroid by a manned spacecraft, comprising the following steps: S1, acquiring an intersection point of the spacecraft and the target asteroid according to the first orbit characteristic of the target asteroid; S2, calculating the first true proximal angle of the Earth when the spacecraft escapes from the Earth and transfers to the transition orbit; S3. calculating a first velocity increment for the spacecraft to escape from the Earth and transfer to the transition orbit, and a second velocity increment for the spacecraft to rendezvous with the target asteroid from the transition orbit; S4. acquiring a third true proximity angle of the asteroid when the spacecraft flies away from the asteroid and transfers to the return orbit, and calculating a fourth true proximity angle of the Earth when the spacecraft enters the Earth's gravitational range from the return orbit; S5, calculating a third velocityincrement for the transfer of the spacecraft from the target asteroid to the return orbit and the reentry velocity of the spacecraft into the atmosphere when the spacecraft enters the Earth's gravitational range from the return orbit; S6. calculating the total velocity increment and the total time of flight of the spacecraft.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
Cryogenic hydrogen radiation shield for human spaceflight
InactiveUS20170073090A1Cosmonautic environmental control arrangementCosmonautic vehiclesNuclear engineeringSpaceflight
Owner:NASA
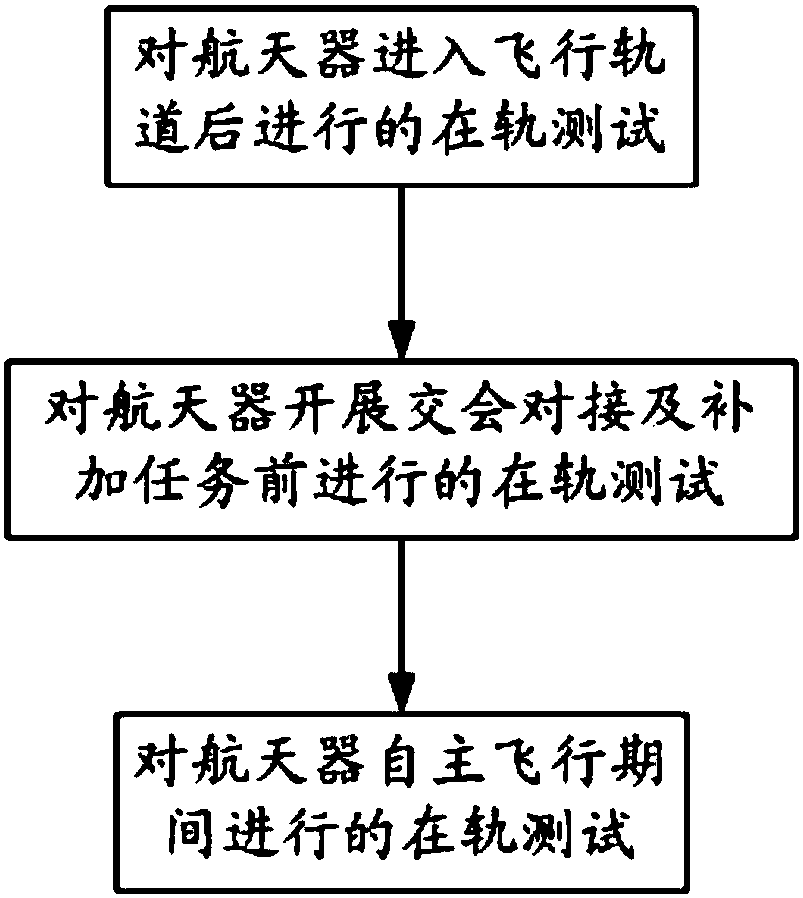
In-orbit test method for low earth orbit long-life manned spacecraft
ActiveCN108408087AMeet the needs of on-orbit testingSmooth goingMeasurement devicesCosmonautic vehicle trackingLow earth orbitOrbit
The invention relates to an in-orbit test method for a low earth orbit long-life manned spacecraft. The in-orbit test method for the low earth orbit long-life manned spacecraft comprises the followingsteps of a, in-orbit test carried out after the spacecraft goes into a light orbit; b, in-orbit test carried out before the spacecraft develops a docking and adding mission; and c, in-orbit test carried out during the autonomous flight period of the spacecraft. The in-orbit test method for the low earth orbit long-life manned spacecraft can make targeted test projects and carry out multiple in-orbit tests for different flight stages and the executions of different missions.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
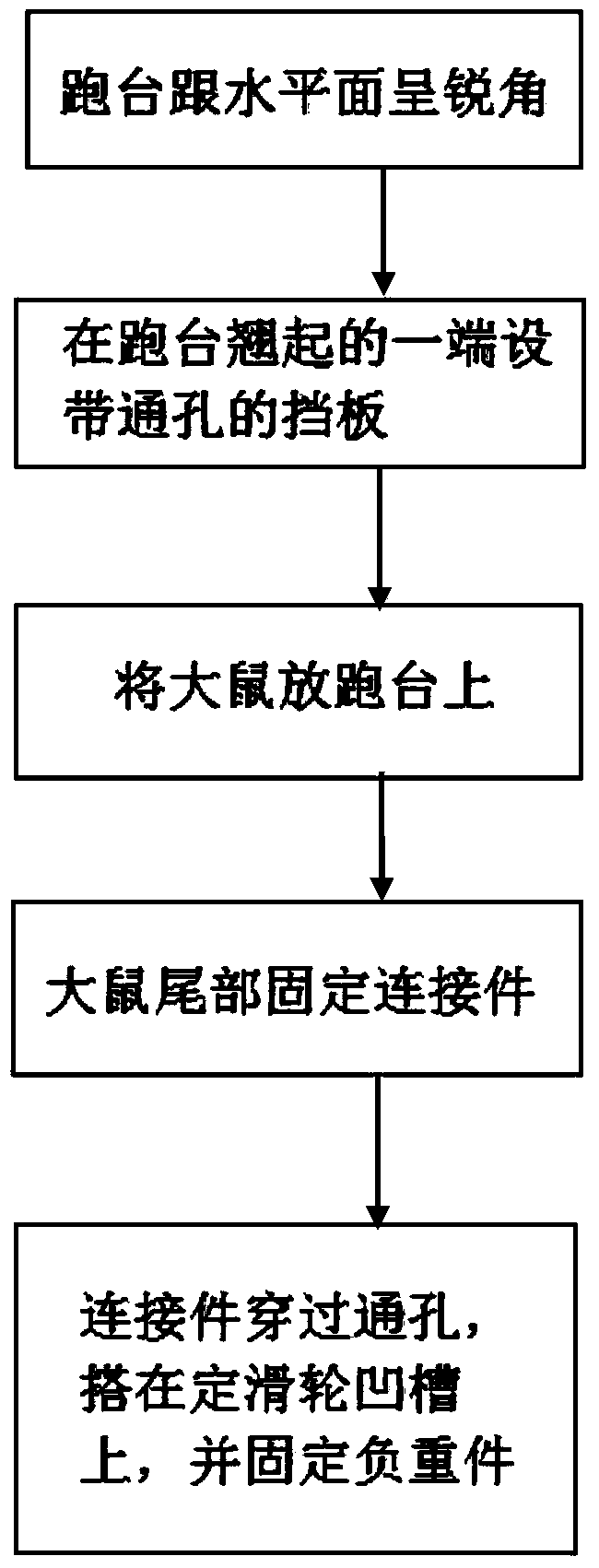
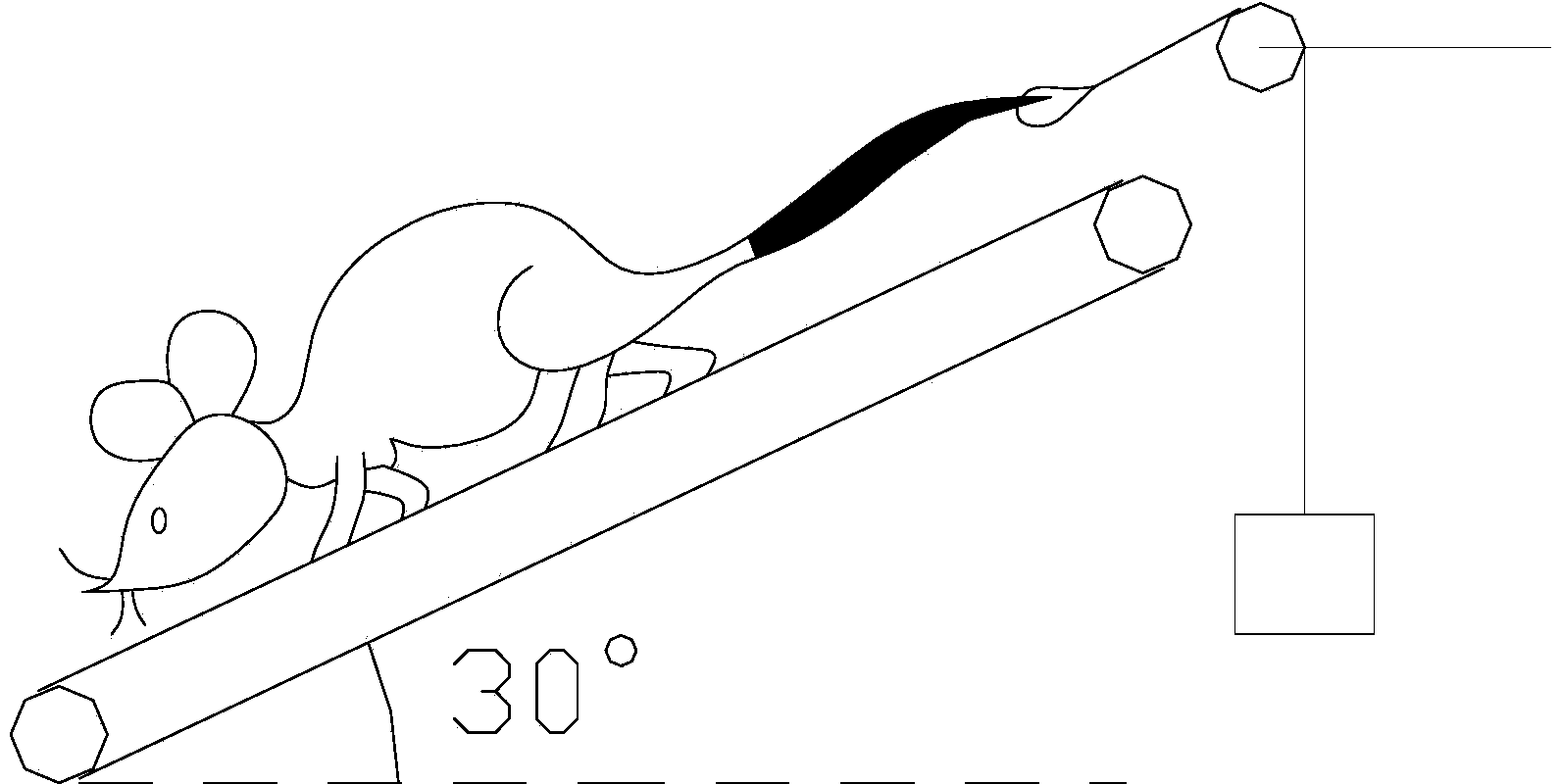
Rat simulation weightless treadmill training method and rat simulation weightless treadmill
ActiveCN103999794AQuality improvementDecreased orthostatic enduranceTaming and training devicesAcute angleSimulation
The invention relates to a rat simulation weightless treadmill training method and a rat simulation weightless treadmill. The rat simulation weightless treadmill training method comprises steps of setting a rat treadmill and enabling an acute angle to be formed between the treadmill and the horizontal plane; arranging a baffle board at one turnup end of the treadmill and enabling the baffle board to extend out of a fixed pulley support; remaining a through hole in the baffle board; placing the rat on the treadmill with the tail orienting to one end of the baffle board, fixing one end of an insulated connection part to the tail of the rat and enabling a load bearing part to be fixed at the other end of the insulated connection part after the other end penetrating the through hole of the baffle board and straddling on a groove of a fixed pulley. The rat simulation weightless treadmill training method can satisfy manned space flight special scientific research requirements and enables the space zero gravity environment to be simulated in the ground.
Owner:SCI RES TRAINING CENT FOR CHINESE ASTRONAUTS
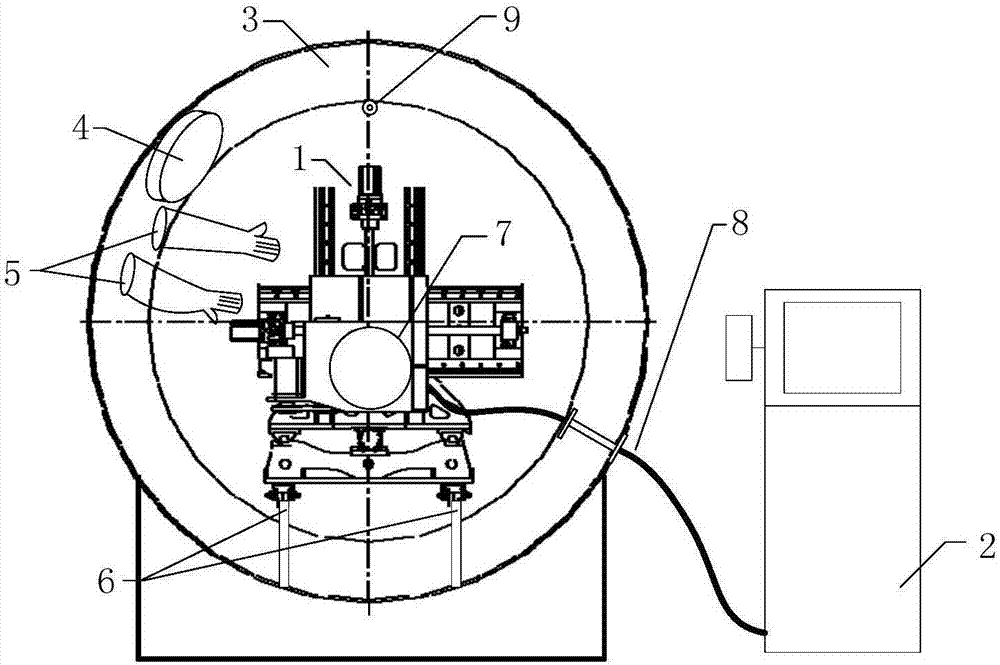
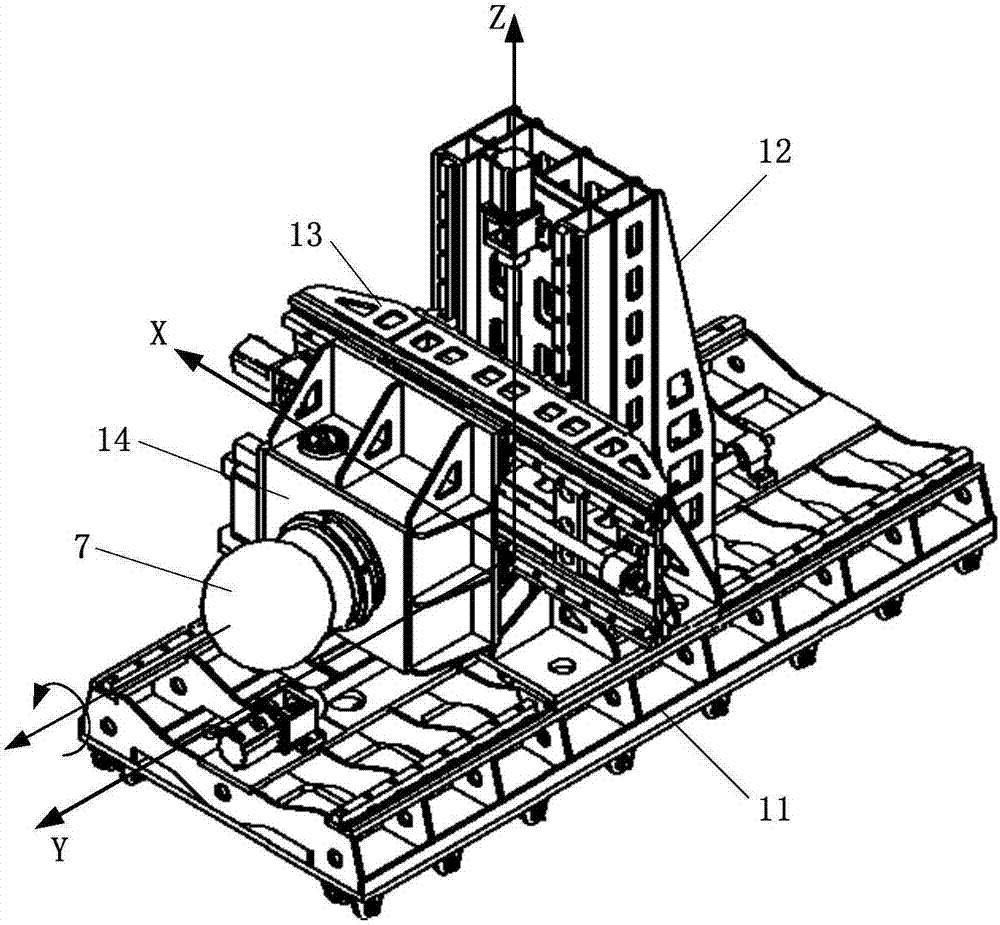
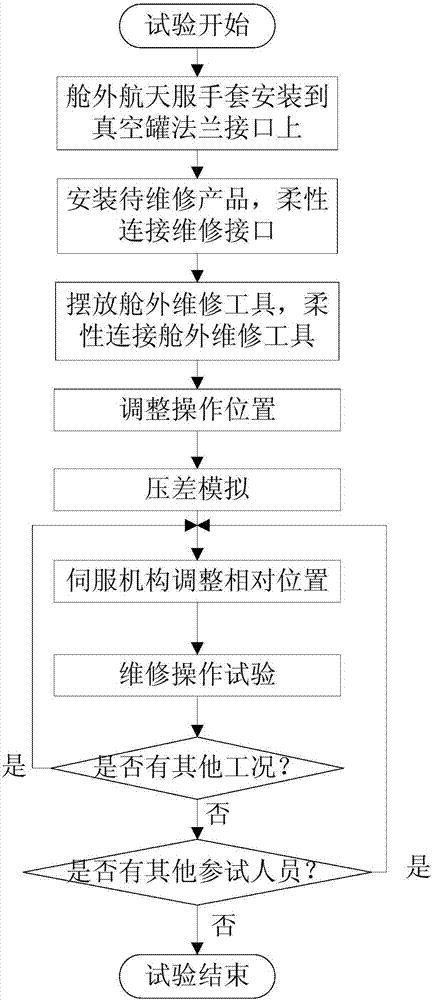
Outboard maintenance tool testing method
ActiveCN107215489ASatisfy the requirements of relative positionImprove effectivenessCosmonautic condition simulationsDifferential pressureGround testing
An outboard maintenance tool testing method comprises the following steps that 1, a pair of outboard space suit gloves is installed on a vacuum tank flange; 2, a simulated maintenance device sample is installed, and a maintenance interface of the simulated maintenance device sample is flexibly connected; 3, an outboard maintenance tool to be tested is put in a vacuum tank and is flexibly connected with the top of the vacuum tank; 4, a servo mechanism is controlled to move, and the simulated maintenance device sample is prevented from damaging the outboard space suit gloves in the pressure extraction process; 5, a cabin door of the vacuum tank is closed, and differential pressure simulation is performed; 6, the relative positions of the simulated maintenance device sample and the outboard space suit gloves are adjusted; 7, the maintenance interface is operated and experimented. The maintenance tool and the maintenance interface can be flexibly connected into the vacuum tank and are prevented from slipping off and damaging a testing device in the maintenance operation process, meanwhile the internal-external pressure difference of the vacuum tank and the relative positions of the maintenance device and a tester can be simulated, and the method supports ground testing of outboard maintenance tools of manned spacecrafts.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
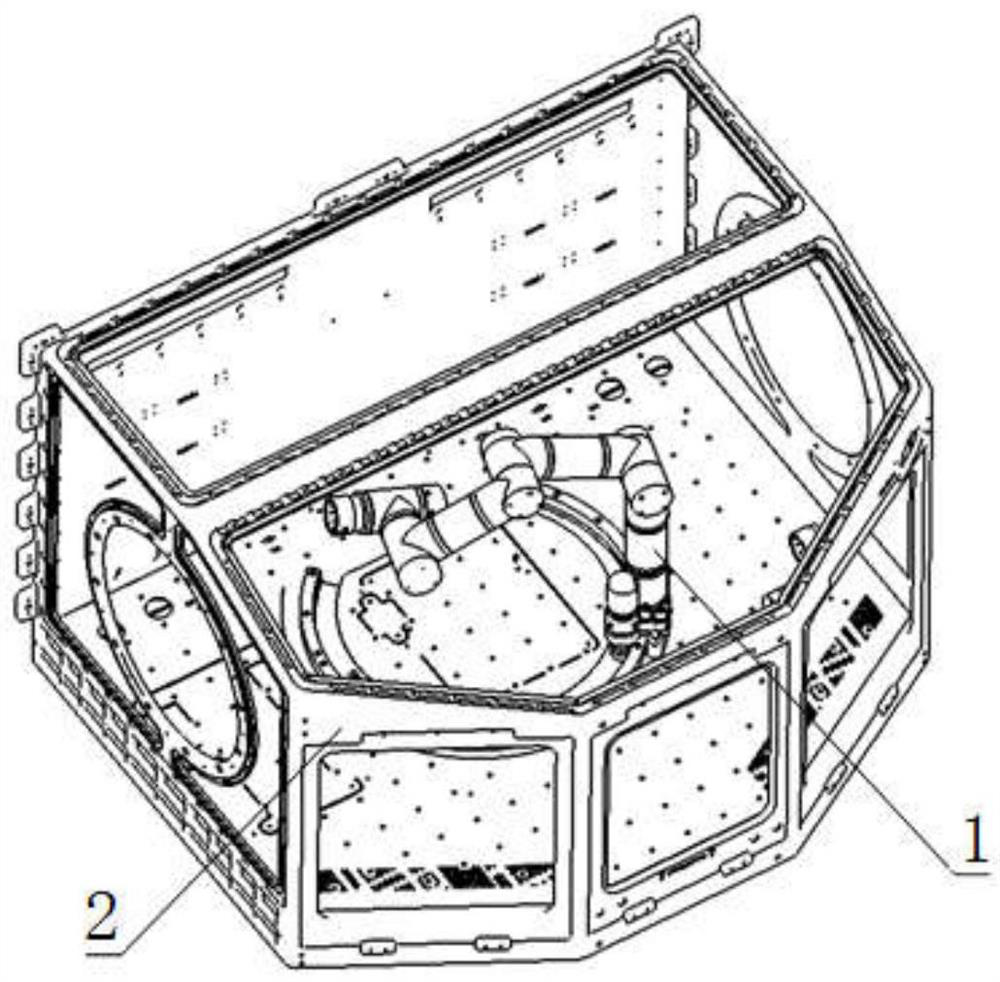
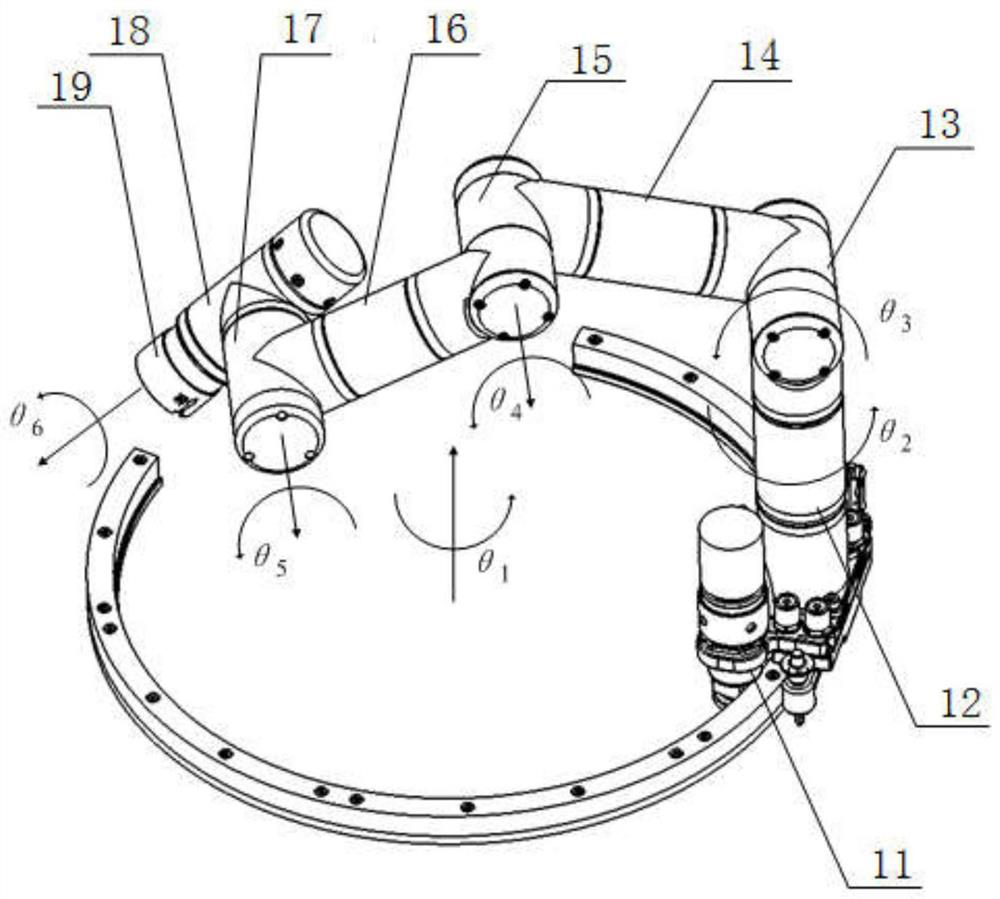
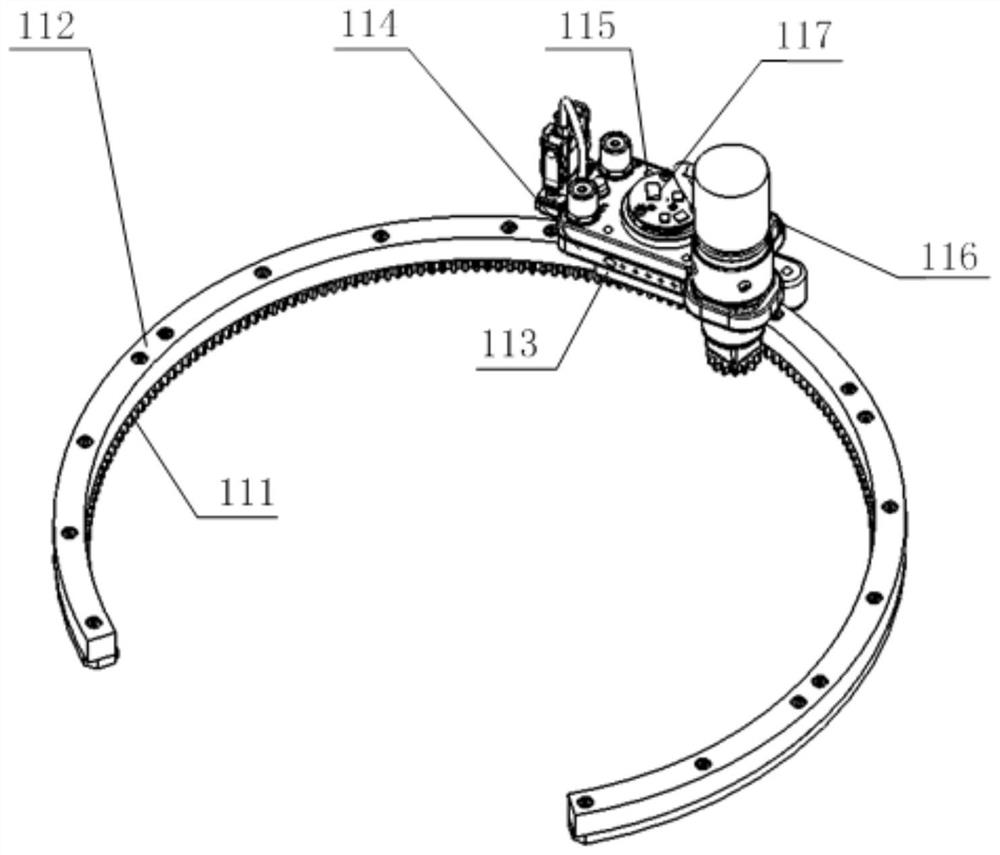
Scientific glove box mechanical arm for space station
PendingCN113103282AMaximize useful workspaceEasy to replaceProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringSpaceflight
The invention relates to manned spaceflight space station scientific experiment equipment, in particular to a scientific glove box mechanical arm for a space station. The mechanical arm is arranged in the scientific glove box for the space station and comprises six joints connected in sequence and a tail end rapid connector connected with a tail end joint, the six joints are all rotating joints, and a first joint is connected with the bottom of the scientific glove box for the space station and can rotate along an arc track. According to the mechanical arm, six-degree-of-freedom operation tasks can be achieved so as to assist astronauts in completing fine operations or autonomously completing the fine operations, the labor intensity of the astronauts in operating the fine tasks in orbit can be greatly reduced, and the task success rate of the astronauts can be improved.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
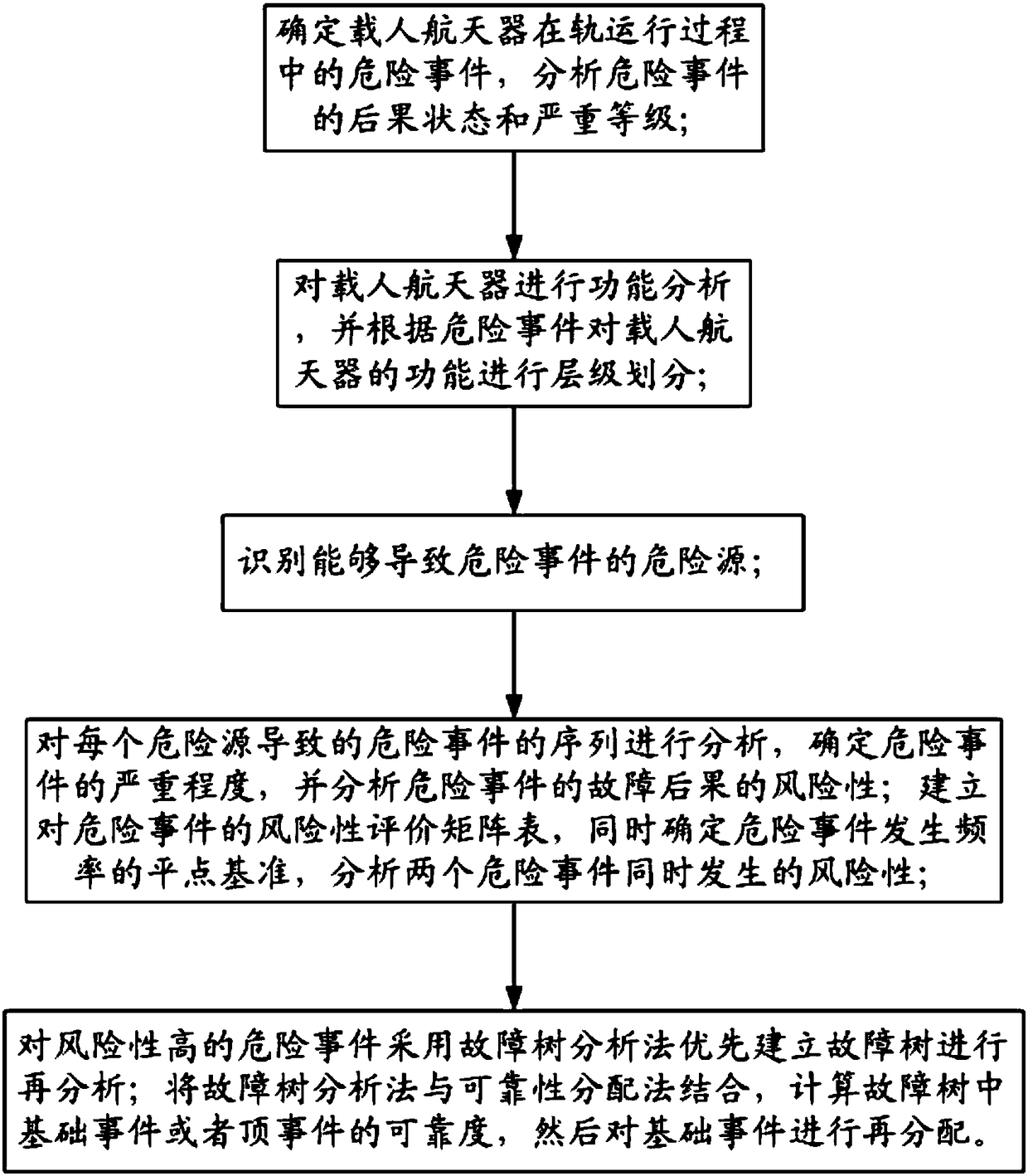
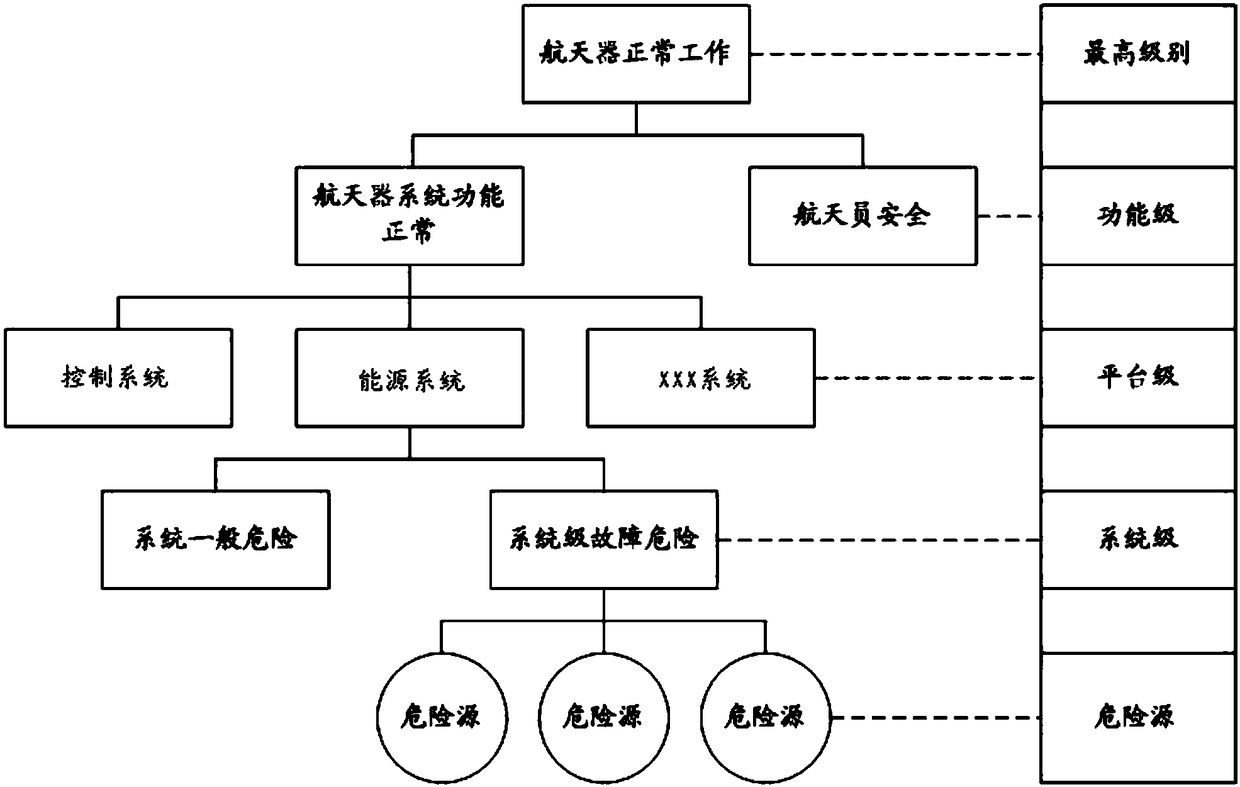
Long-term on-orbit danger event analysis method of manned spacecraft and danger analysis system
ActiveCN108491587ALow resource costEasy to operateGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsSeverity levelSafety control
The invention relates to a long-term on-orbit danger event analysis method of a manned spacecraft and a danger analysis system. The analysis method comprises the following steps: a, determining dangerevents in an on-orbit process of the manned spacecraft, and analyzing consequence status and severity levels of the danger events; b, carrying out function analysis on the manned spacecraft, and carrying out hierarchical division on functions of the manned spacecraft according to the danger events; c, identifying sources of danger that can lead to danger events; d, analyzing a sequence of dangerevents caused by each danger source, determining severity degrees of the danger events, and analyzing risk of fault consequences of the danger events; and e, for high-risk danger events, using fault tree analysis to fault trees in a prioritized manner for reanalysis. According to the analysis method of the invention, serious dangers which may occur in the on-orbit running process are identified, system resource cost minimization of safety control measures is ensured, and maximum efficiency is realized.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
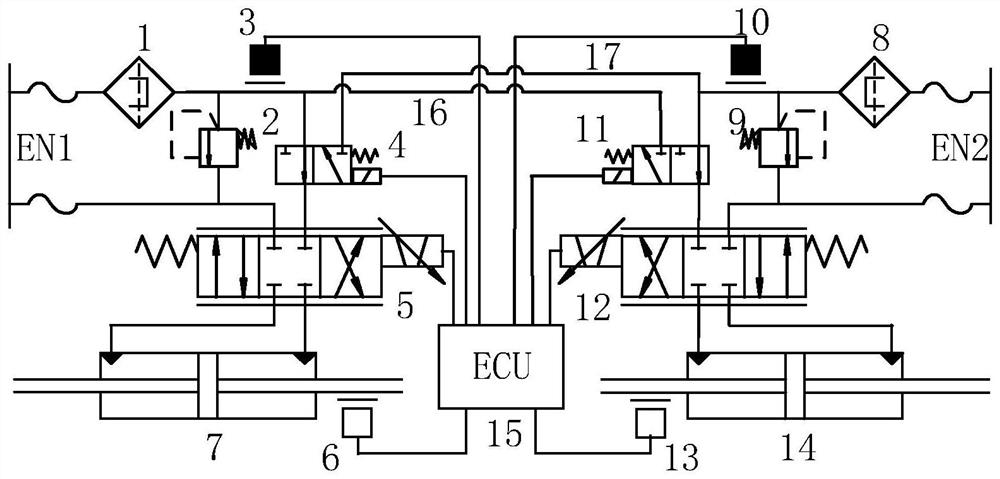
Energy dual-redundancy system and control method thereof
ActiveCN112283207ASolve frequent switchingSolve the phenomenon of miscuttingServomotor componentsServometer circuitsHydraulic cylinderControl system
The invention provides an energy dual-redundancy system and a control method thereof. The energy dual-redundancy system comprises a controller, a main oil way and an auxiliary oil way. Each of the main oil way and the auxiliary oil way comprises a fine oil filter, an overflow valve, a servo valve, a hydraulic cylinder and a displacement sensor, and further comprises a pressure sensor, an energy selection valve, a high-pressure hose, a controller and a double-threshold logic control strategy. Automatic switching and fault isolation between the main oil way and the auxiliary oil way of an energypart are implemented, the structure is simple, the weight is light, and switching responding is fast. Because the double-threshold logic control strategy is applied, false switching between the mainoil way and the auxiliary oil way is avoided, the reliability of a servo system can be improved by one order of magnitude relative to a product in service, and the requirement for high reliability ofmanned aerospace lunar landing in China is met. The energy dual-redundancy system and the control method thereof belong to the field of electro-hydraulic servo systems.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
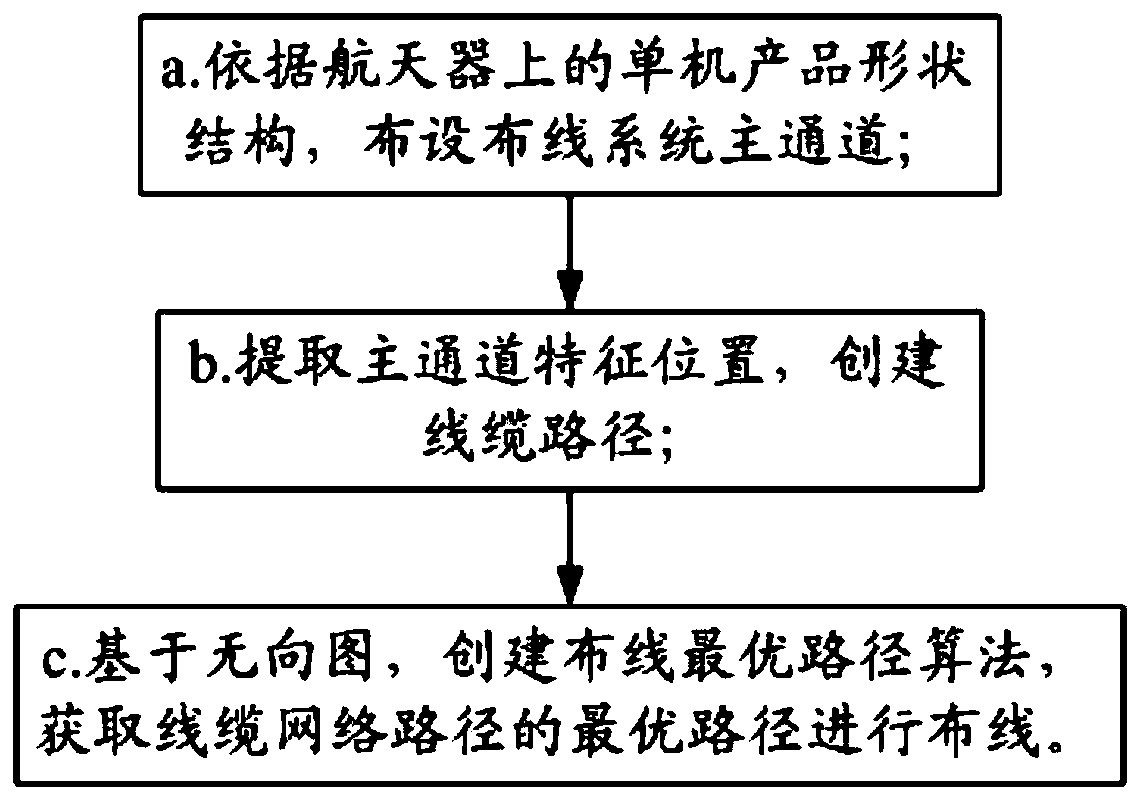
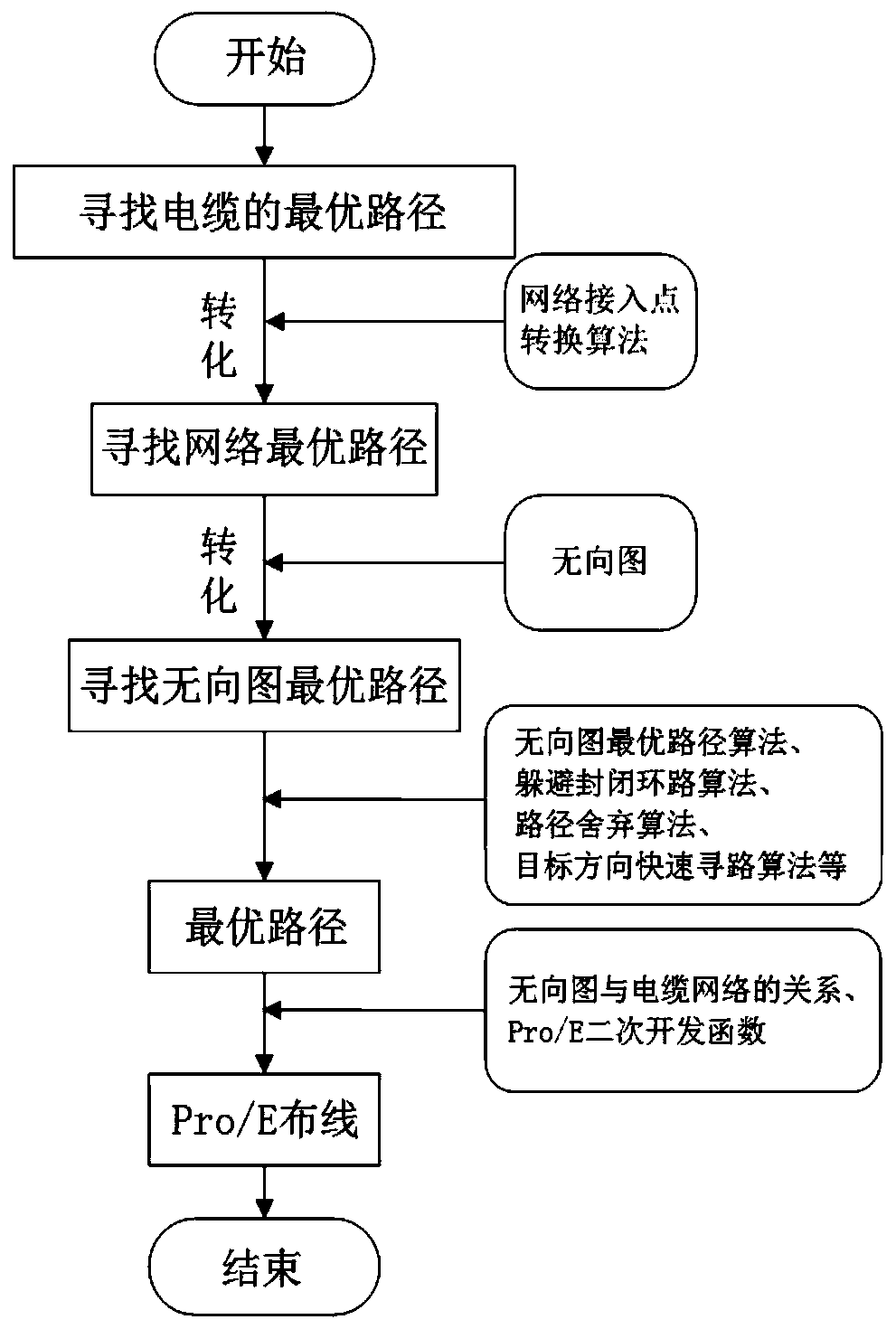
Spacecraft cable three-dimensional wiring method
ActiveCN111046488AReduce weightImprove design efficiencyGeometric CADForecastingUndirected graphCable net
The invention relates to a spacecraft cable three-dimensional wiring method, which comprises the following steps of: a, laying a main channel of a wiring system according to the shape structure of a single-machine product on a spacecraft; b, extracting a main channel feature position, and creating a cable path; and c, based on the undirected graph, creating a wiring optimal path algorithm, and obtaining an optimal path of the cable network path for wiring. According to the spacecraft cable three-dimensional wiring method, cable wiring of the shortest path can be achieved, the design efficiencyis improved, and meanwhile the weight of the spacecraft cable is reduced. Aiming at key links influencing design quality and efficiency in a cable network wiring design process, a set of manned spacecraft cable network three-dimensional wiring design new method based on an intelligent algorithm is formed.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
Micro-operation robot system for space station in-orbit life science experiment
The invention relates to manned spaceflight space station scientific experiment equipment, in particular to a micro-operation robot system for a space station in-orbit life science experiment. The micro-operation robot system comprises a space station scientific glove box and a micro-operation robot system arranged in the space station scientific glove box. The micro-operation robot system comprises a three-dimensional objective table, a microscopic vision system, an operating mechanism, a clamping mechanism and an adsorption and injection mechanism, and the three-dimensional objective table has X-axis, Y-axis and Z-axis movement functions; the microscopic vision system is arranged on the three-dimensional objective table and is used for performing microscopic observation on a space biological experiment sample and outputting image data in real time; the operating mechanism is used for operating the space biological experiment sample; the clamping mechanism is used for clamping and moving the space biological experiment sample; and the adsorption and injection mechanism is connected with the operating mechanism and the clamping mechanism and is used for providing positive pressure aerodynamic force and negative pressure aerodynamic force. The micro-operation robot system for the space station in-orbit life science experiment has the function of performing on-orbit flexible and fine multi-degree-of-freedom autonomous operation, so that the purpose of performing life science experiments in a space station is achieved.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
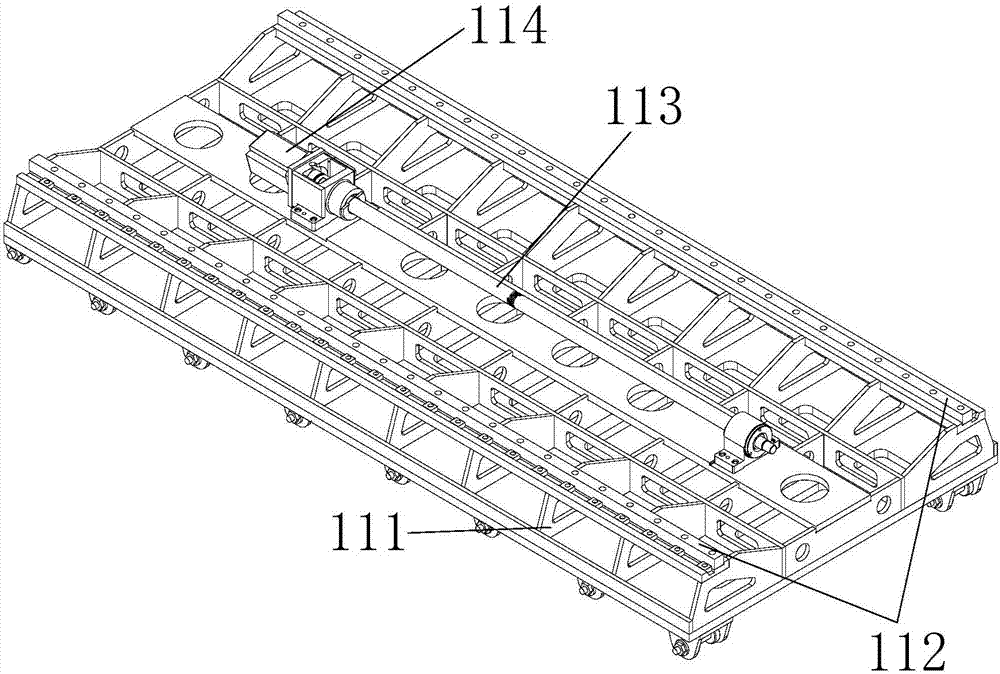
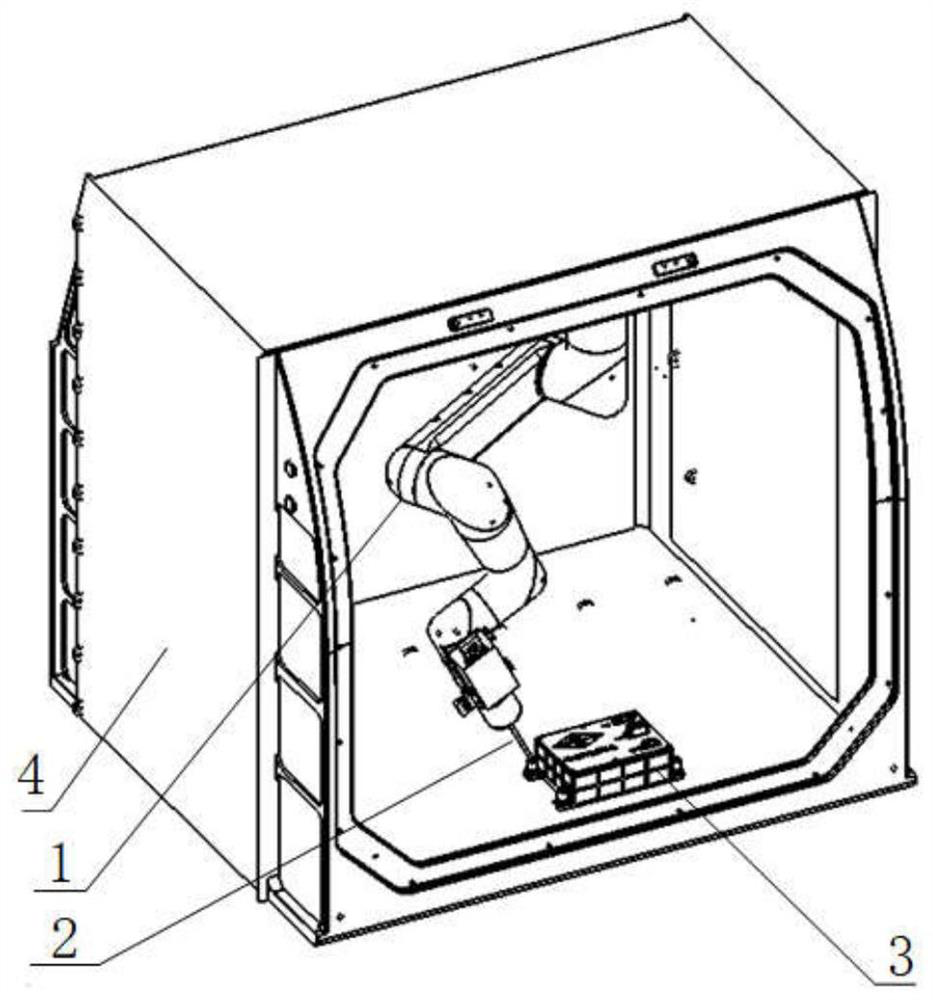
On-orbit dragging-off tool for case in manned spaceflight cabin
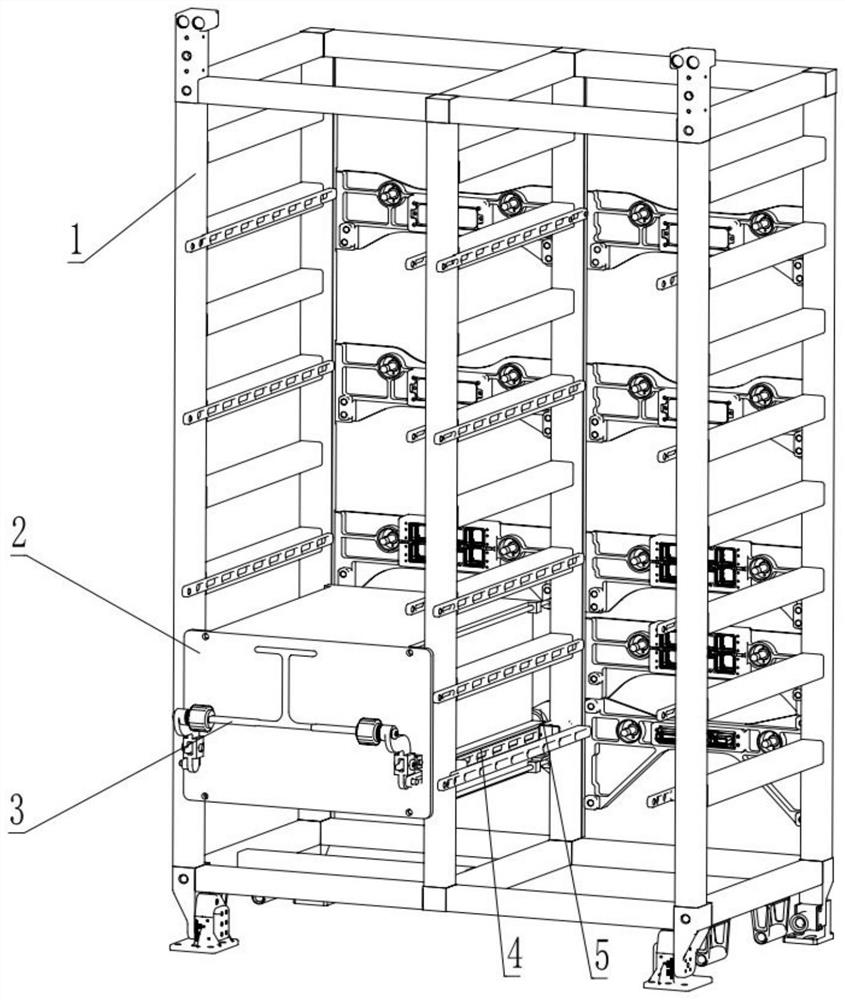
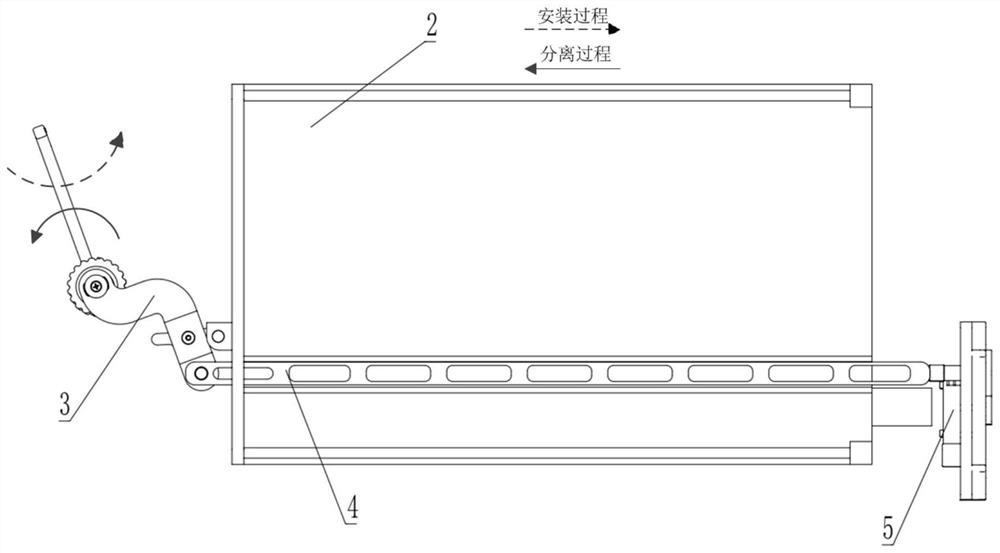
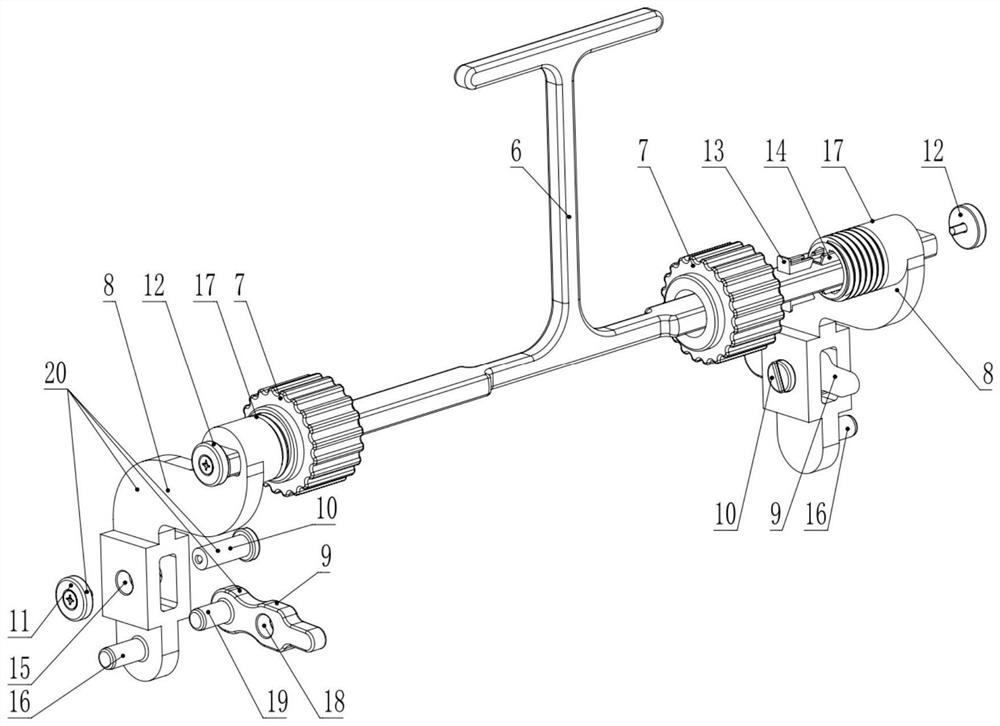
ActiveCN114044175AEasy to operateSimple structureCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsLinear motionEngineering
The invention discloses an on-orbit dragging-off tool for a case in a manned spaceflight cabin, and belongs to the field of manned spaceflight systems. According to the technical scheme, a spaceflight electronic case is installed on the lower portion of a step frame of the spaceflight cabinet and linearly moves through a guide rail; a crank connecting rod precession device is rotationally connected to the guide rail through a crank connecting rod hinge device hinged to a hinge base of a front panel of the case, the rotating motion of the crank connecting rod precession device is converted into linear motion of the spaceflight electronic case along the guide rail, and the crank connecting rod precession device rotates clockwise or anticlockwise. And the spaceflight electronic case is linked to linearly move forwards and backwards along the guide rail, so that on-orbit dragging of the spaceflight electronic case and a back plate is quickly realized. In-orbit dragging of the case and the back plate is achieved through a lever mechanism and a crank sliding block mechanism, operation is convenient, operation force and physical output of astronauts can be effectively reduced, the manned spaceflight operation condition can be adapted, and the in-orbit operation capacity of the astronauts and the pulling force needed for disassembling and assembling the case are met.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Re-entry capsule device
InactiveCN114044171AEnsure safetyAvoid damageSystems for re-entry to earthCosmonautic landing devicesStructural engineeringHeat shield
The invention relates to the technical field of manned spacecrafts, in particular to a re-entry capsule device. The re-entry capsule capsule device comprises a capsule body, wherein an installation blind hole is formed in the bottom face of the capsule body, a containing blind hole is formed in the side wall of the installation blind hole, a first sliding groove is formed in the side wall of the installation blind hole, and a second sliding groove is formed in the side wall of the containing blind hole; an anti-impact column body inserted into the installation blind hole, wherein the lower end of the anti-impact column body abuts against an anti-heat insulation cover, the side wall of the upper end of the anti-impact column body is provided with a first protruding block, and the lower end of the first sliding groove is provided with a first limiting block; a blocking column body inserted into the containing blind hole, a spring is pressed between one end of the blocking column body and the end wall of the containing blind hole, a second convex block is arranged on the side wall of the end, and a second limiting block suitable for blocking the second convex block is arranged at the end of the second sliding groove. According to the re-entry capsule device provided by the invention, the anti-impact column body can resist the impact force borne by the anti-impact column body under the blocking force of the blocking column body, so that the damage caused by direct collision between the capsule body and the ground is avoided, and the safety of astronauts and precise instruments is ensured.
Owner:浙江东握科技有限公司
Vibration penetrating lunar soil coring device with spiral assisted submersion
The invention discloses a spiral assisted dive vibratory penetration type lunar soil coring device and belongs to the technical field of manual lunar surface sampling of manned space flight. The invention aims to solve the problems that the conventional lunar soil sampling device simultaneously realizes external spiral assisted dive and internal vibratory coring by virtue of a coring tube and thesampling capacity is low. The spiral assisted dive vibratory penetration type lunar soil coring device comprises a supporting mechanism, a vibratory coring mechanism, a spiral soil discharge mechanismand a sealing mechanism, wherein the supporting mechanism is used for providing a support frame for the vibratory coring mechanism and the spiral soil discharge mechanism; an electromagnetic exciteroutputs linear vibration, and the vibration is directly transferred to the coring tube by virtue of a vibratory ejector rod; an offset rotary drive motor transfers a rotary motion to a drill rod by virtue of a pair of gears, and the rotary motion path is positioned at the periphery of the vibration path; and the vibratory ejector rod, the coring tube and other vibratory coring parts penetrate through central axes of a low-speed shaft, the drill rod and other spiral soil discharge mechanisms, and the rotary motion path does not have reference to the vibration path. The device disclosed by the invention is used for collecting lunar soil samples.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
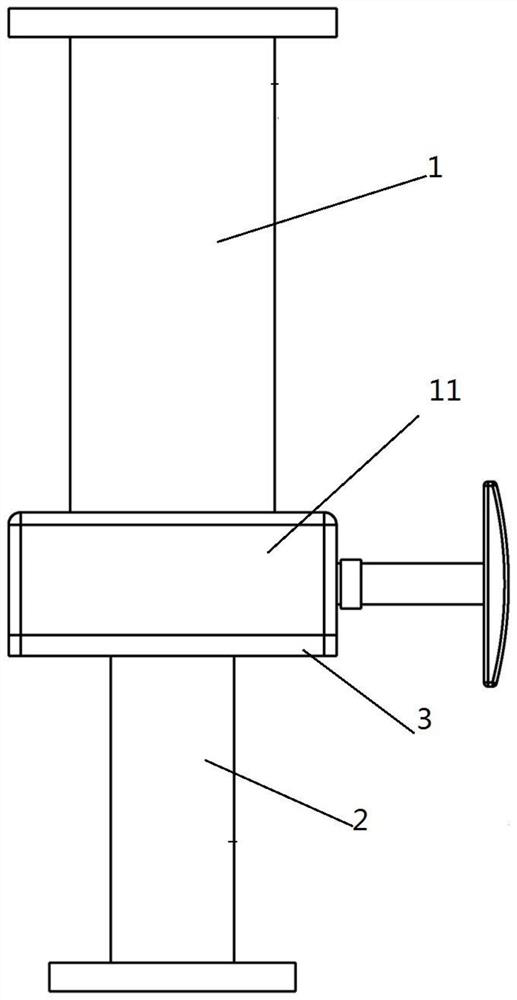
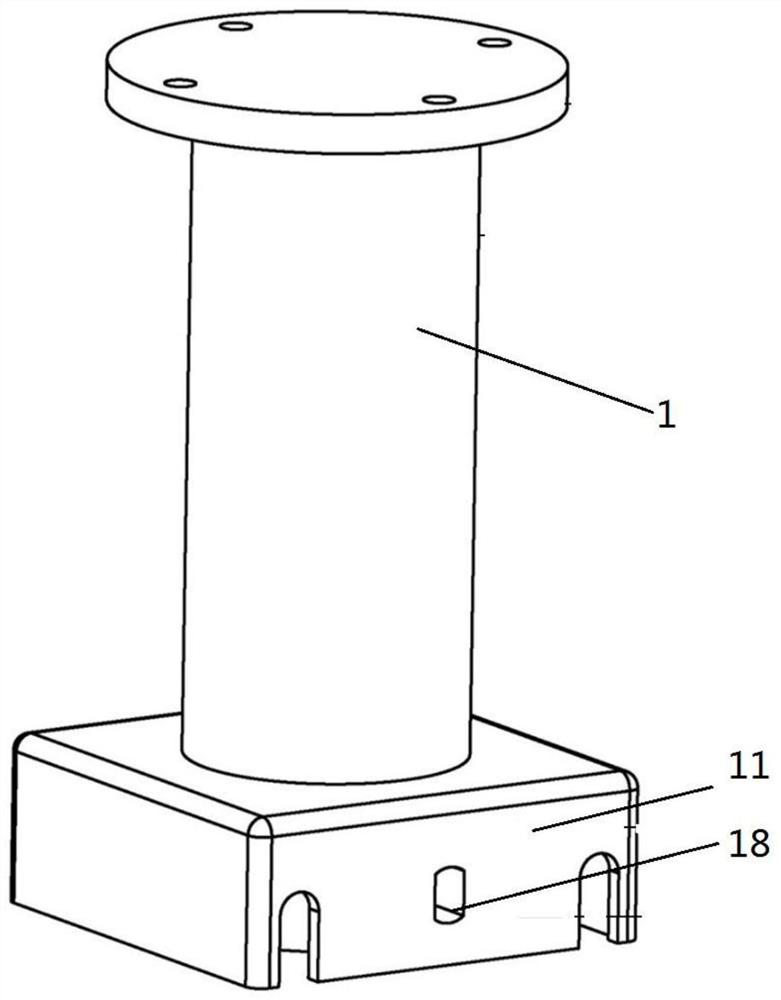
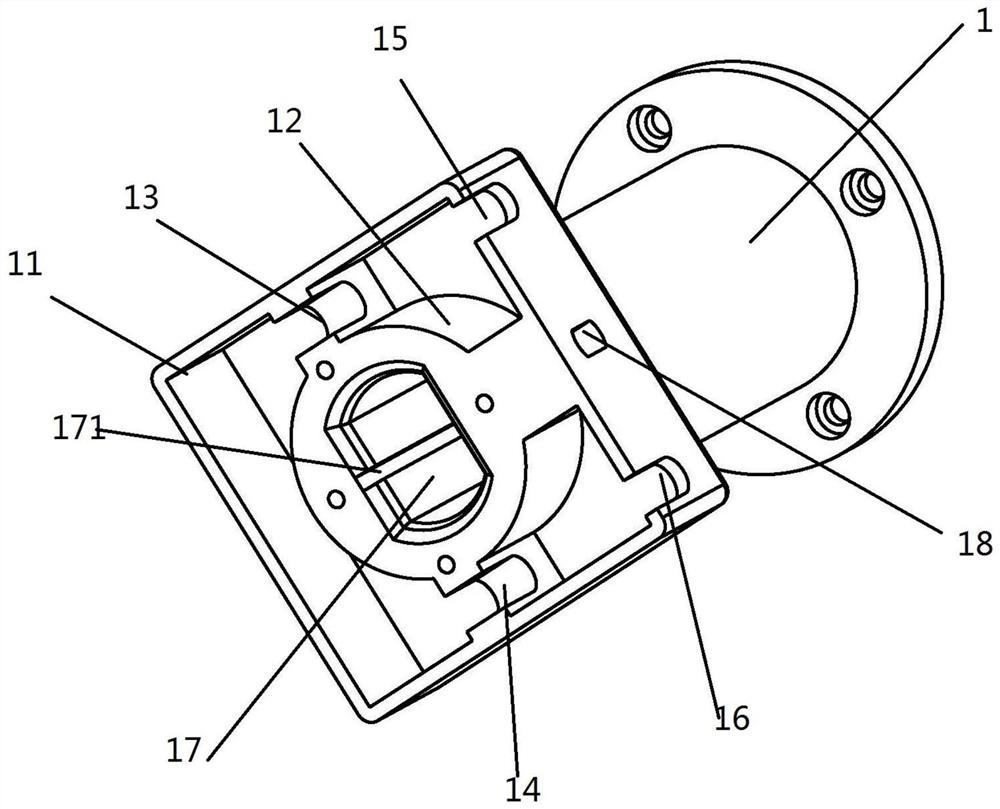
A docking device for neutral buoyancy simulation test of spacecraft
ActiveCN111959833BRealize butt installationSimple structureCosmonautic condition simulationsClassical mechanicsStructural engineering
The invention provides a docking device for a spacecraft neutral buoyancy simulation test, which is characterized in that it includes a guide column, a guide pin and a locking assembly, one end of the guide column is provided with an active flange, and the other end of the guide column is provided with a locking seat , one end of the guide pin is plugged into the guide column through the locking assembly, and the other end of the guide pin is provided with a passive flange. Fixed connection between guide pins. The invention solves the problem of fast and convenient replacement of old and new stand-alone equipment in neutral buoyancy tests of manned spacecraft.
Owner:TIANJIN AEROSPACE ELECTROMECHANICAL EQUIP RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com