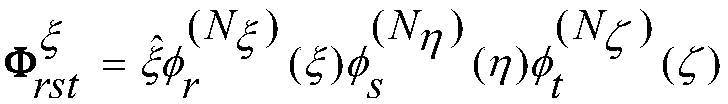Unconditional Stable and Conditionally Stable Hybrid Time-Domain Spectral Element Electromagnetic Analysis Method
A time-domain spectral element, electromagnetic analysis technology, applied in electrical digital data processing, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve problems such as slow solution time, long time spent in inversion, and many time iteration steps, etc., to speed up the solution speed. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The present invention is based on an unconditionally stable and conditionally stable mixed time-domain spectral element electromagnetic analysis method, the steps are as follows:
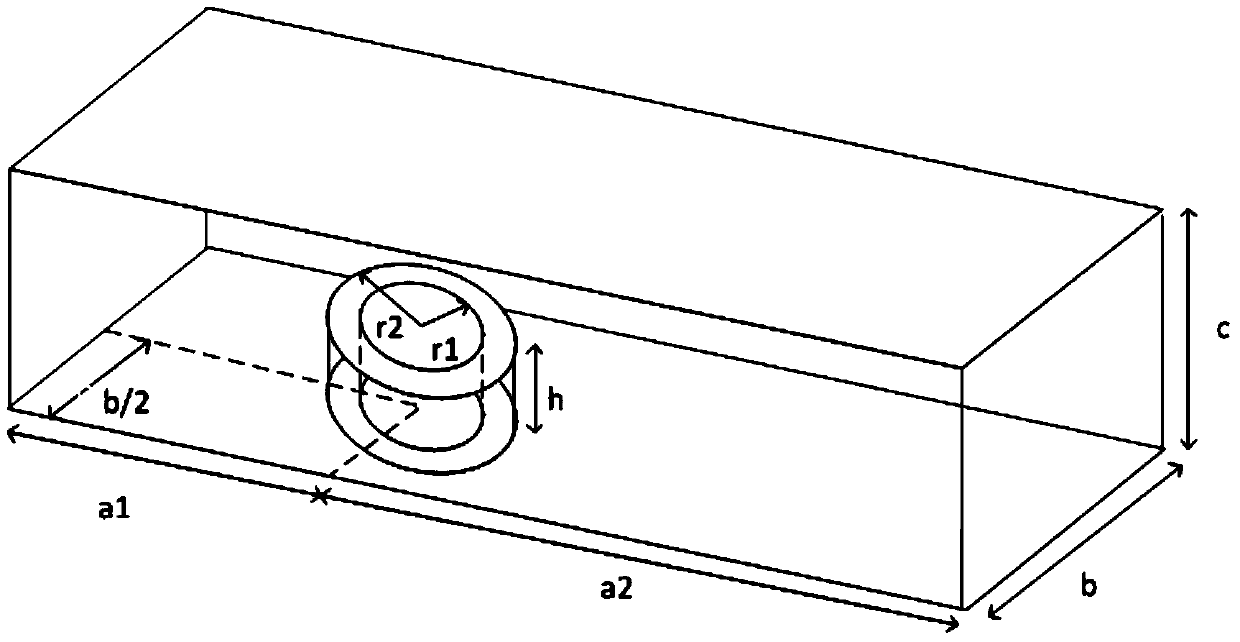
[0035] The first step is the model subdivision, and the model is uniformly subdivided using curved hexahedral meshes.
[0036] The second step is to adaptively find out the hexahedron whose size is smaller than the set value in the grid, and mark it out.
[0037] The third step is to expand the electric field with the basis function, substitute it into the vector wave equation, and use the Galerkin test.
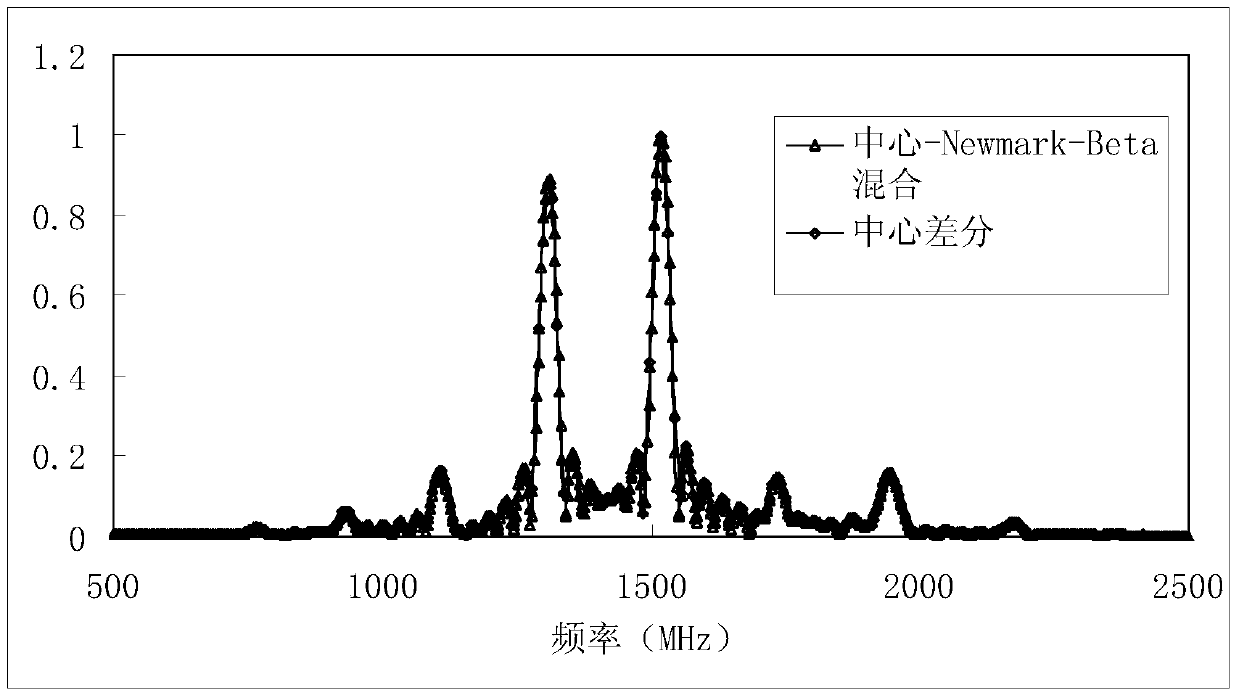
[0038] The fourth step is to solve the matrix equation, expand the time item by time difference, use the Newmark-β difference scheme with unconditional stability in the small-sized area, and use the central difference in other areas, first solve the Newmark-β area, and then perform the center Solving for difference regions.
[0039] The present invention will be further described below in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com