A thermosetting laser-induced metallized thermally conductive composite with stable high dielectric constant
A heat-conducting composite material, laser-induced technology, applied in the field of composite materials, to achieve good high dielectric constant stability, good laser-induced metallization, good linear expansion coefficient effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0025] The preparation method of material of the present invention is:
[0026] (1) Pour high-dielectric ceramic fillers, laser-induced additives, and high-thermal conductivity fillers into a high-speed mixer, and stir at high speed for 3-5 minutes;
[0027] (2) Slowly add the surfactant to the high-speed mixer, and continue high-speed mixing and stirring for 10-20 minutes;
[0028] (3) Add the thermosetting matrix resin, initiator, thickener, low shrinkage additive and the powder mixed in the above step (2) into a kneader and stir for 15-20 minutes to prepare a composite material.
Embodiment 1
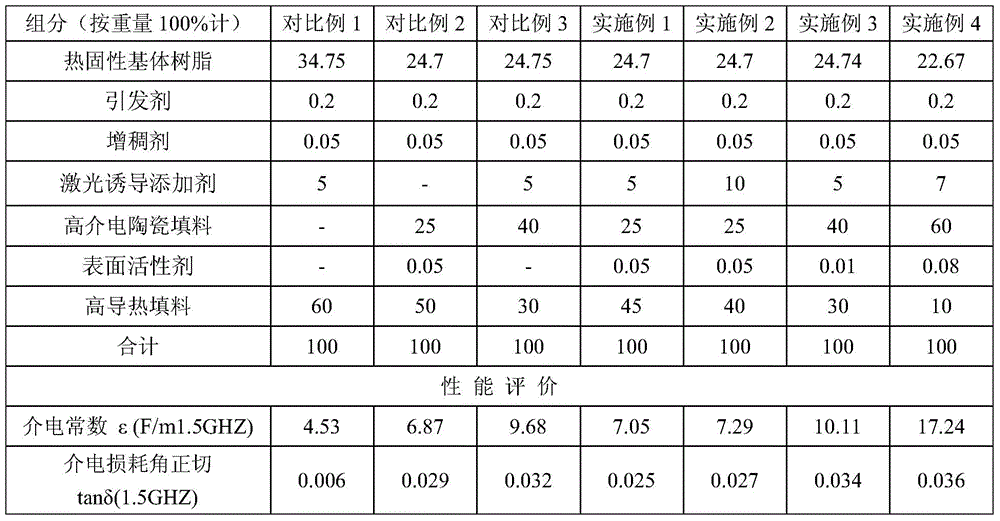
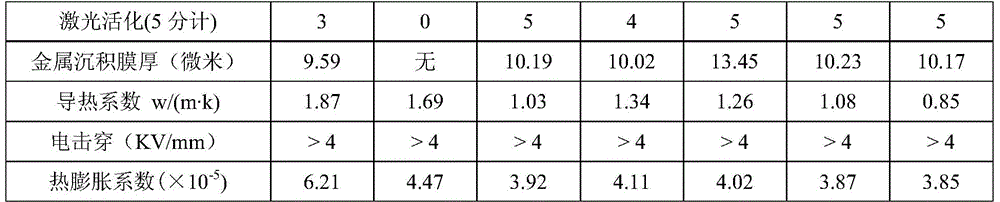
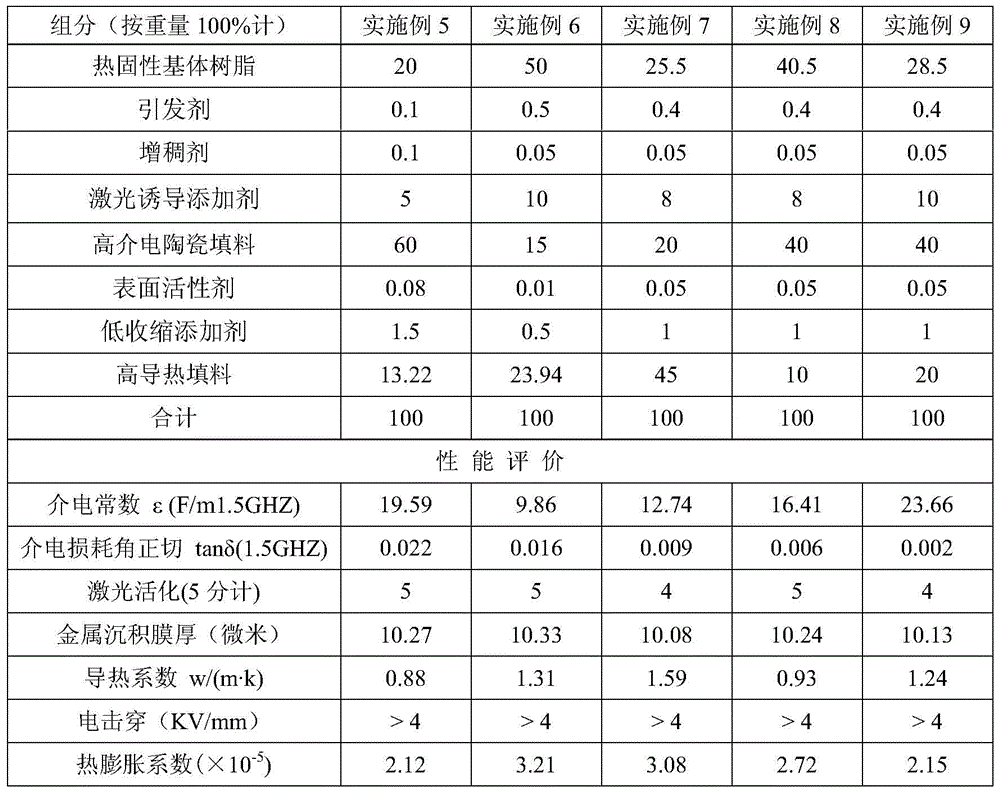
[0030] A thermosetting laser-induced metallization heat-conducting composite material with stable high dielectric constant, made by mixing the following components: thermosetting matrix resin (epoxy resin, commercially available), initiator (1,2-cyclohexanediamine) , thickener (magnesium oxide), laser-induced additives, high dielectric ceramic filler (barium titanate, particle size 1-3 microns), surfactant (silane coupling agent KH560), high thermal conductivity filler (spherical alumina, 10 microns, commercially available). The material was then injection molded for corresponding testing.
[0031] The laser-induced additive is a composition of a micron-scale tin-containing compound (tin dioxide) and a nano-scale tin-containing compound (tin dioxide), and the weight ratio of the micron-scale tin-containing compound to the nanoscale tin-containing compound is 4:1; The particle size of the micron-scale tin-containing compound is 0.5-30 μm, and the particle size of the nano-scal...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The composition of this example is the same as that of Example 1, except that the weight ratio of the micron-scale tin-containing compound to the nano-scale tin-containing compound is 9:1.
[0035] The specific proportioning and material performance test of the components in this embodiment are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com