Intrahepatic duct cell cancer related gene mutation targets and application thereof
A technology for inner bile duct and cell carcinoma, which is applied in the field of biotechnology and medical diagnosis, can solve the problems such as the characteristics of gene mutations are not clear, and achieve a targeted and targeted treatment that is helpful for selection and evaluation, good therapeutic effect, and Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
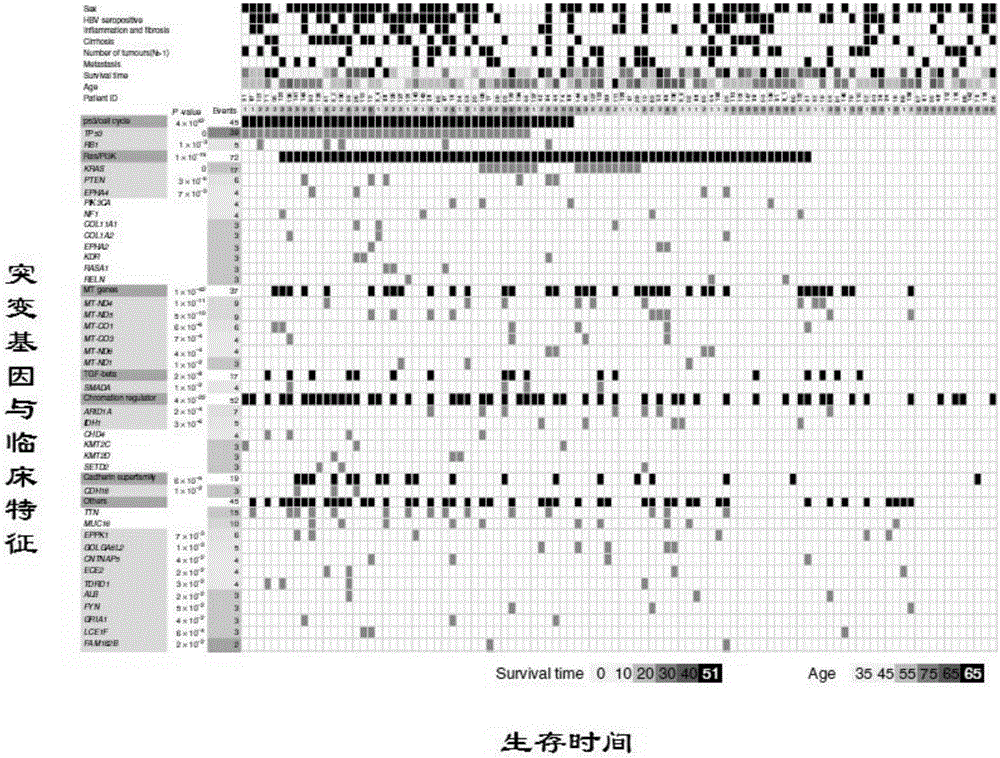
[0036] Shanghai WuXi AppTec New Drug Development Co., Ltd. was entrusted to use IlluminaHiSeq2000 to analyze the whole tissue samples of 103 patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma confirmed by histopathology and their control tissues (distal tissues of cancer tissues) from Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital of Second Military Medical University. The genome exomes were sequenced, and one patient was excluded because the number of somatic gene mutations was significantly different from other patients. The remaining 102 patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma were summarized in Table 1 for the overall exome sequencing results of the above specimens. Bioinformatics analyzed the sequencing results and found that there were significant mutations in 25 genes, including 8 genes, namely TP53 (p=0.0001), KRAS (p=0.004), IDH1 (p=0.00019), PTEN (p=0.0078) ), ARID1A (p=0.00449), EPPK1 (p=0.00486), ECE2 (p=0.0357) and FYN (p=0.00258) may be the driver genes (see Table 2).
...
Embodiment 2
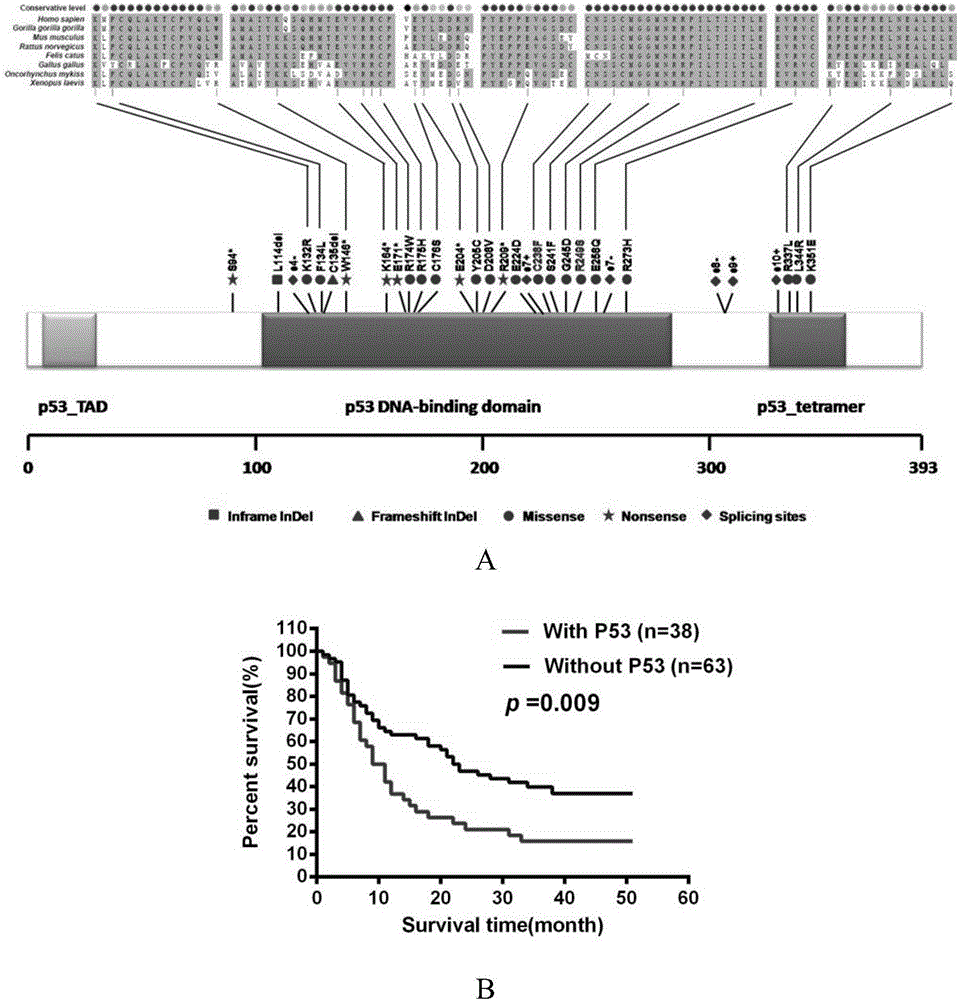
[0046] The whole genome exomes of 102 patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and their control tissues were sequenced and analyzed, and it was found that P53 gene mutation mainly occurred in serum HBsAg-positive intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (61.54%) (see Table 3). .
[0047] Table 3: Correlation analysis of P53 mutation and clinicopathological features of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
[0048] (ComparisonofclinicopathologicalfeaturesofICCpatientsaccordingtop53mutation)
[0049]
[0050]
[0051] *:numberofavailabledata;ICC:intrahepaticcholangiocarcinoma;HBV:hepatitisBvirus;M:male;F:female;TBIL:totalbilirubin;ALT:alanineaminotransferase;AST:aspartateaminotransferase;andAFP:Alpha-fetoprotein;ALP:alkalinephosphatase;r-GT:r-glutamyltransferase; CA19-9:carbohydrateantigen19-9;CK:cytokeratin.
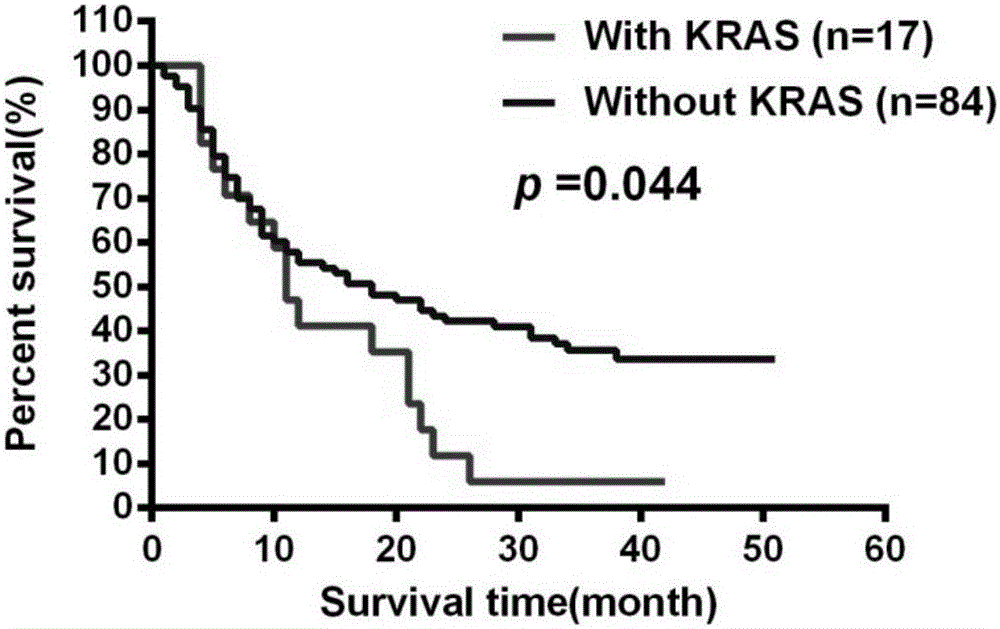
[0052] KRAS gene mutation is basically the only one found in serum HBsAg-negative intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma rate (29.6%) (see Table 4).
[0053] Table 4: Correlatio...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Bioinformatics analysis of the sequencing results found that three signal transduction pathways, namely Ras / PI3K signaling pathway, p53 / cellcycle signaling pathway and TGF-b / SMAD signaling pathway, are very likely to be related to the occurrence and development of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma ( Figure 4 a is the relationship between Ras / PI3K signaling pathway and the occurrence and development of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; Figure 4 b is the relationship between p53 / cellcycle signaling pathway and the occurrence and development of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; Figure 4 c is the relationship between the TGF-b / SMAD signaling pathway and the occurrence and development of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma), about 75% of the patients have mutations in the p53 / cellcyclesignaling and Ras / PI3Ksignaling signaling pathways.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com