A kind of method utilizing lipase to catalyze the synthesis of dihydromyricetin monoester compound
A lipase-catalyzed dihydro and dihydromyricetin single technology, which is applied in fermentation and other fields, can solve the problems of seldom reported hydroxyl esterification on flavonoid aglycones, poor oil solubility of dihydromyricetin molecules, and difficulties in hydroxyl esterification reactions, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of reducing production cost, retaining antioxidant activity, and easy continuous production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] (1) Dissolve dihydromyricetin in 2 mL of organic solvent, and then add vinyl acetate (the initial concentrations of dihydromyricetin and vinyl acetate are 20 and 500 mmol / L, respectively), and then add 500 U of immobilized Aspergillus niger HGD0823 lipase was reacted for 24 hours at a temperature of 35°C and a shaker speed of 200r / min.
[0030] (2) After the reaction, the reaction solution is centrifuged, the supernatant is taken, the solvent is recovered, and the obtained solid is the product containing dihydromyricetin monoester.
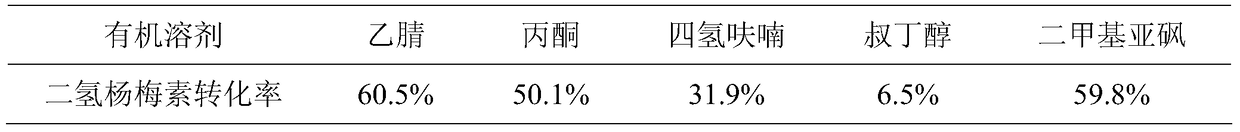
[0031] The organic solvents used in this example are acetonitrile, acetone, tetrahydrofuran, tert-butanol, and dimethyl sulfoxide, respectively. In different organic solvents, the conversion rate (measured by HPLC) of dihydromyricetin under the catalysis of immobilized Aspergillus niger HGD0823 lipase is shown in Table 1.
[0032] Table 1. The conversion rate of dihydromyricetin in different organic solvents
[0033]
Embodiment 2
[0035] (1) Dissolve dihydromyricetin in 2 mL of acetonitrile, and then add vinyl acetate after all the dissolution (the initial concentrations of dihydromyricetin and vinyl acetate are 20 and 500 mmol / L, respectively), and then add 500 U of lipase, The reaction was carried out for 24 hours under the conditions of a temperature of 35° C. and a shaker rotation speed of 200 r / min.
[0036] (2) After the reaction, the reaction solution is centrifuged, the supernatant is taken, the solvent is recovered, and the obtained solid is the product containing dihydromyricetin monoester.
[0037] The lipases used in the present embodiment are free lipases respectively: Penicillium salmonella casei lipase (LPC), Rhizopus sinensis lipase (Lipase RC), Pseudomonas cepacia lipase (PCL), porcine pancreatic lipase (PPL), Rhizopus niger lipase (Lipase RN), Penicillium extensa lipase (PEL), Aspergillus niger HGD0823 lipase; immobilized lipase: Lipozyme IM TL, Lipozyme IM RM, Novozym435, immobiliz...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com