Self-collimating grating interferometer with high optical subdivision structure
A grating interference and self-collimation technology, applied in the field of grating interferometers, can solve the problems of insufficient use of gratings, high grating design requirements, low optical subdivision multiples, etc. high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Example 1: A measuring beam
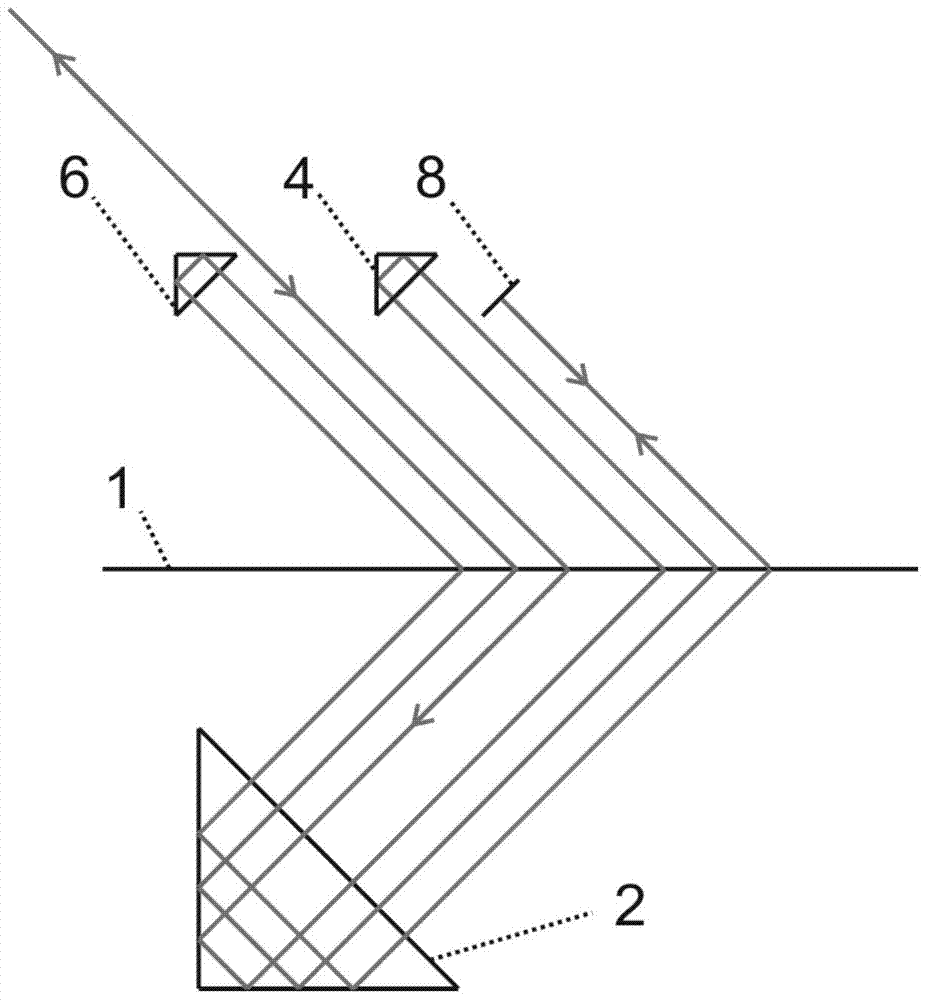
[0025] see figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of Embodiment 1 of the high optical subdivision structure of the self-collimating grating interferometer of the present invention
[0026] A highly optically subdivided structure of a self-collimating grating interferometer with only one measuring beam as figure 1As shown, it is mainly used in the grating interferometer where the measuring beam and the reference beam form interference fringes. It can be seen from the figure that the high optical subdivision structure of the self-collimating grating interferometer of the present invention includes: a grating scale 1 , a first right-angle prism 2 , a second right-angle prism 4 , a third right-angle prism 6 , and a first mirror 8 . After the measurement beam is incident on the grating scale 1 at the m-order Bragg angle for the first time, it is diffracted by the grating scale. Parallel to the incident light incident on the right-angl...
Embodiment 2
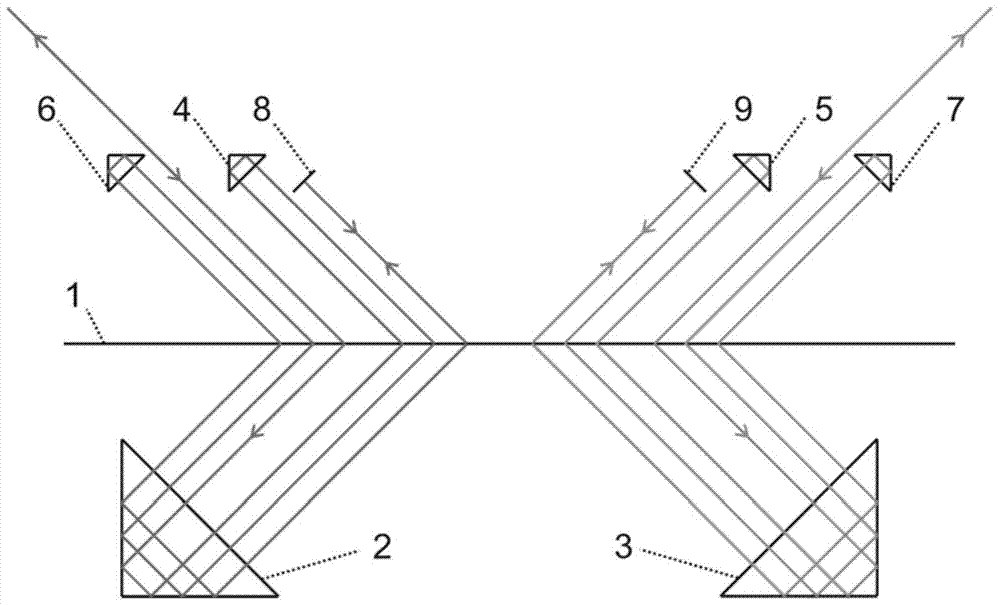
[0028] The highly optically subdivided structure of the self-collimating grating interferometer with two measuring beams is as follows: figure 2 As shown, it is mainly used in a grating interferometer in which two beams of measuring light form interference fringes. The structure includes: a grating scale 1, a first rectangular prism 2, a second rectangular prism 4, a third rectangular prism 6, a fourth rectangular prism 3, a fifth rectangular prism 5, a sixth rectangular prism 7, a first reflector 8, Second reflector 9. Compared with the high optical subdivision structure of the self-collimating grating interferometer when there is only one measuring beam, the fourth right-angle prism 3 , the fifth right-angle prism 5 , the sixth right-angle prism 7 and the second reflection mirror 9 are added. At this time, the fourth right-angle prism, the fifth right-angle prism, the sixth right-angle prism, and the second reflector are respectively placed symmetrically with the first rig...
Embodiment 3
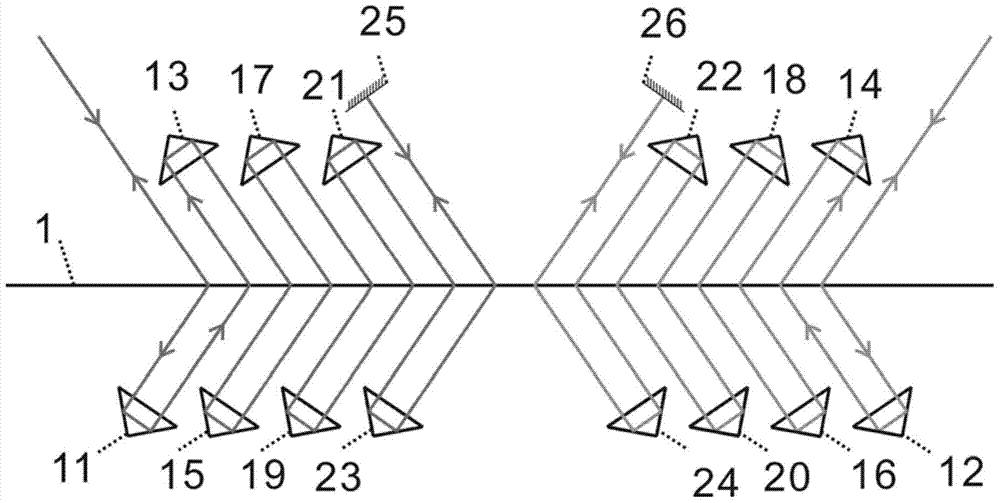
[0030] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the high optical subdivision structure of another self-collimating grating interferometer with two measuring beams. The first measuring beam is incident on the grating scale 1 at the m-order Bragg angle, and passes through the first right-angle prism 11, the grating scale 1, the second right-angle prism 13, the grating scale 1, the third right-angle prism 15, the grating scale 1, the fourth Right-angle prism 17, grating scale 1, the fifth right-angle prism 19, grating scale 1, the sixth right-angle prism 21, grating scale 1, the seventh right-angle prism 23, grating scale 1, the -m order diffracted light at this moment is vertically incident on the first On a reflector 25, the light beam returns along the original path, and finally coincides with the first initial incident measurement beam, and forms the first outgoing measurement beam in a reverse direction opposite to the first initial incident measurement beam;
[0031] Similar ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com