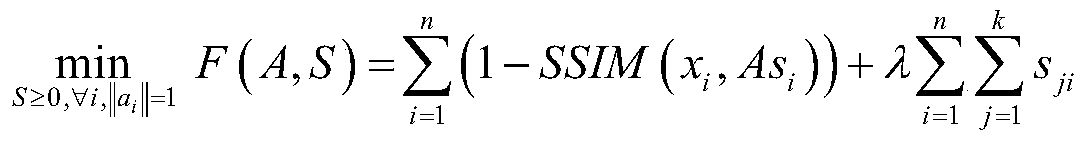Image Classification Method Based on Non-negative Sparse Coding Based on Structural Similarity
A technology of non-negative sparse coding and structural similarity, which is applied in the field of image classification of non-negative sparse coding, can solve problems that do not meet the visual characteristics of the human eye, cannot evaluate the structural similarity between the reconstructed image and the original image well, and does not fully Considering the visual characteristics of the human eye and other issues to achieve the effect of improving quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
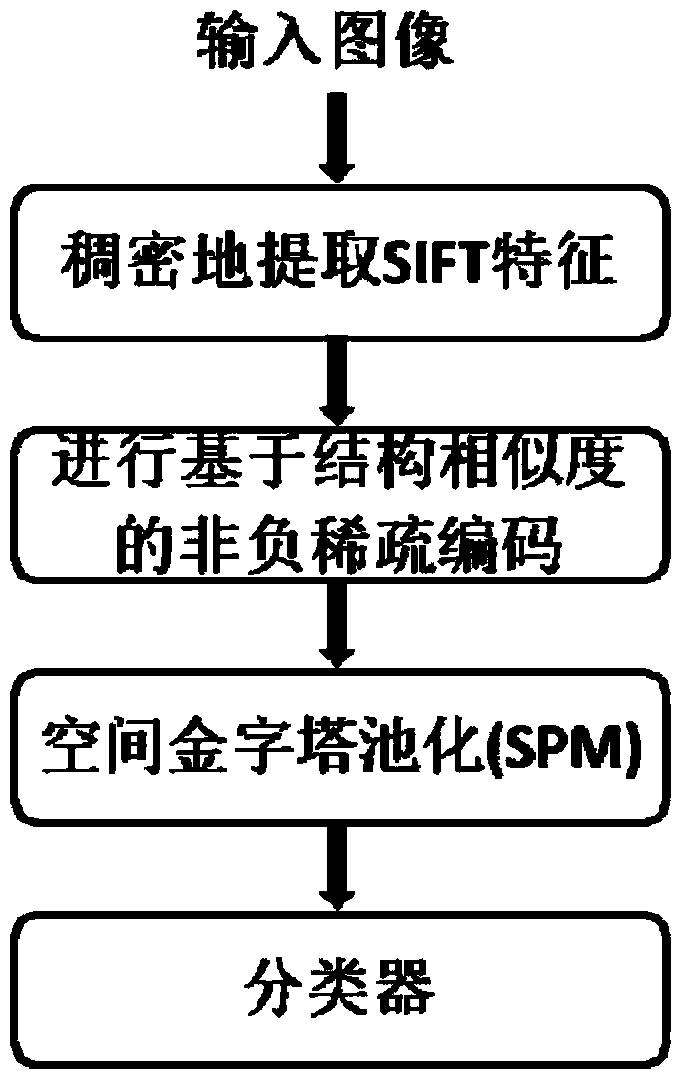
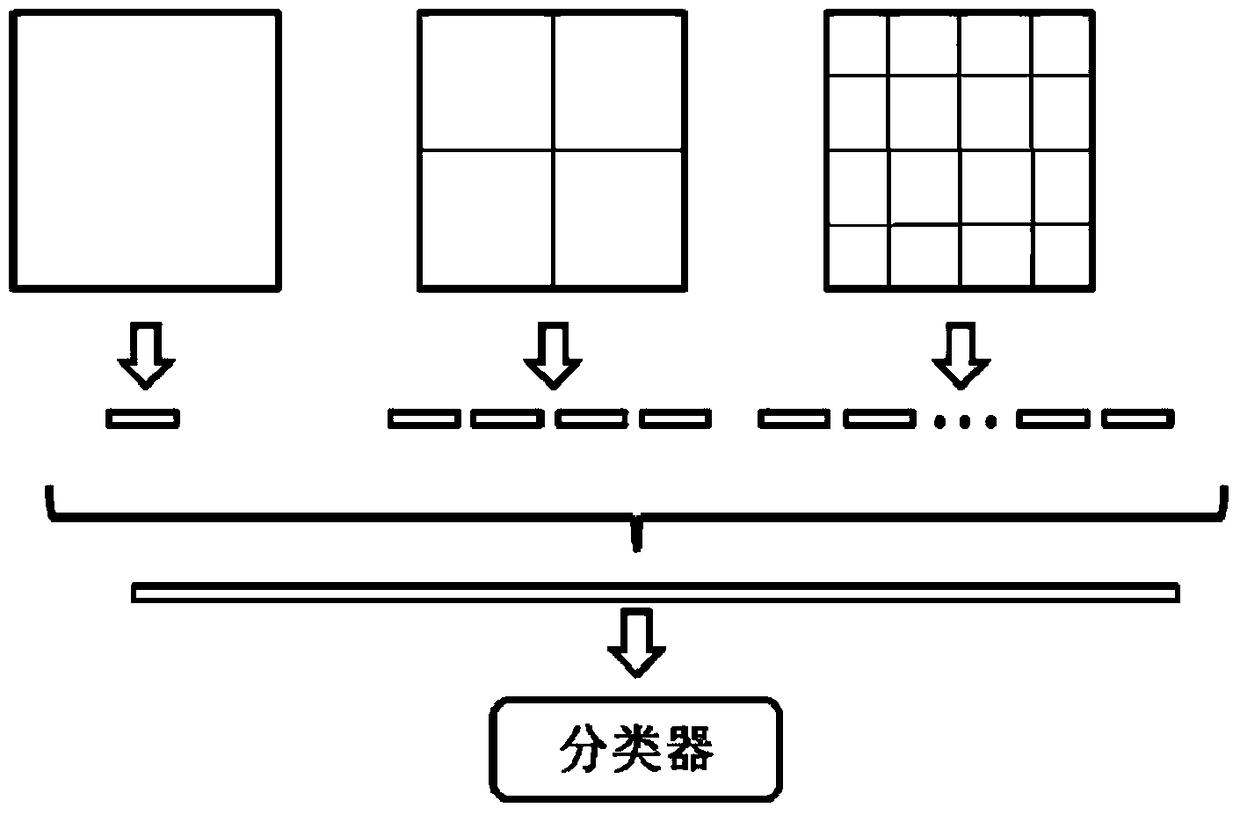
[0046] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0047]The present invention attempts to find the corresponding sparse coding from the perspective of structural similarity. The present invention introduces structural similarity as an important measure of information retention, and then adds non-negative sparse constraints to provide a non-negative sparse code based on structural similarity. Coding model. The reason why non-negativity of encoding is required is that non-negative encoding has better stability in application.
[0048] Given signals x and y, x,y ∈ R N , the definition of structural similarity is as follows:
[0049]
[0050] where x i is the ith component element of signal x, y i is the ith component element of signal y, σ x and σ y Represent the standard deviation of signals x and y, respectively, σ x,y Indicates the covariance of signals x and y, 01 ,C 2 <<1 Two...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com