Assessment method for latent anchor damage caused by ships to submarine cables, and control system
A technology for ships and submarine cables, applied in the field of potential anchor damage assessment methods and management and control systems, to achieve the effect of widening dimensions and facilitating formulation and implementation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
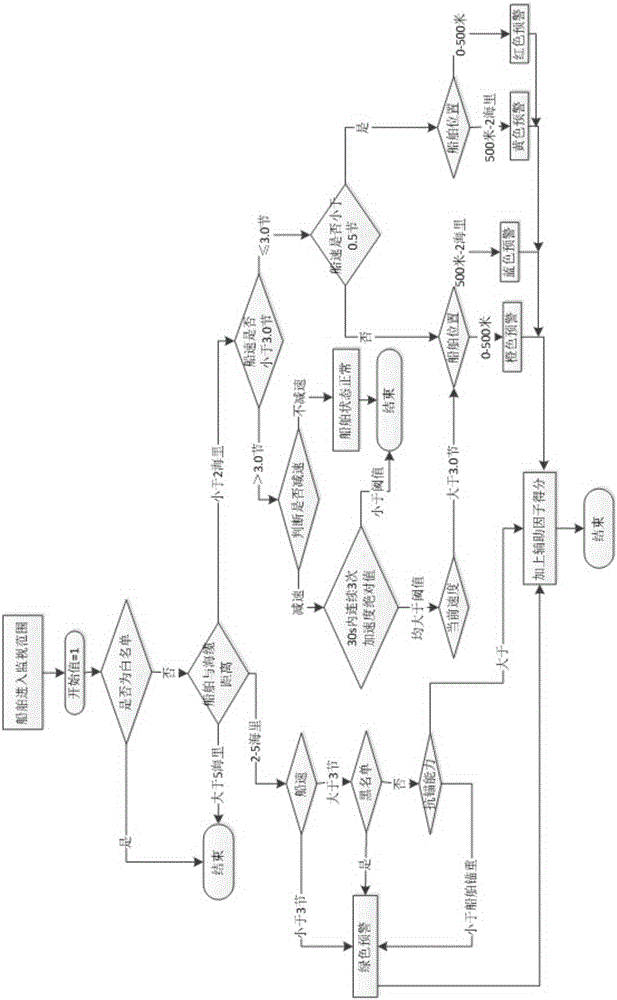
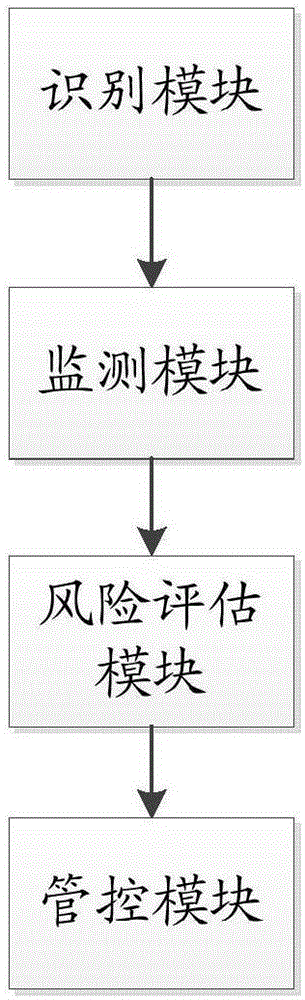
[0046] Such as Figure 1-3 As shown, a method for assessing the potential anchor damage of a ship to a submarine cable, including:
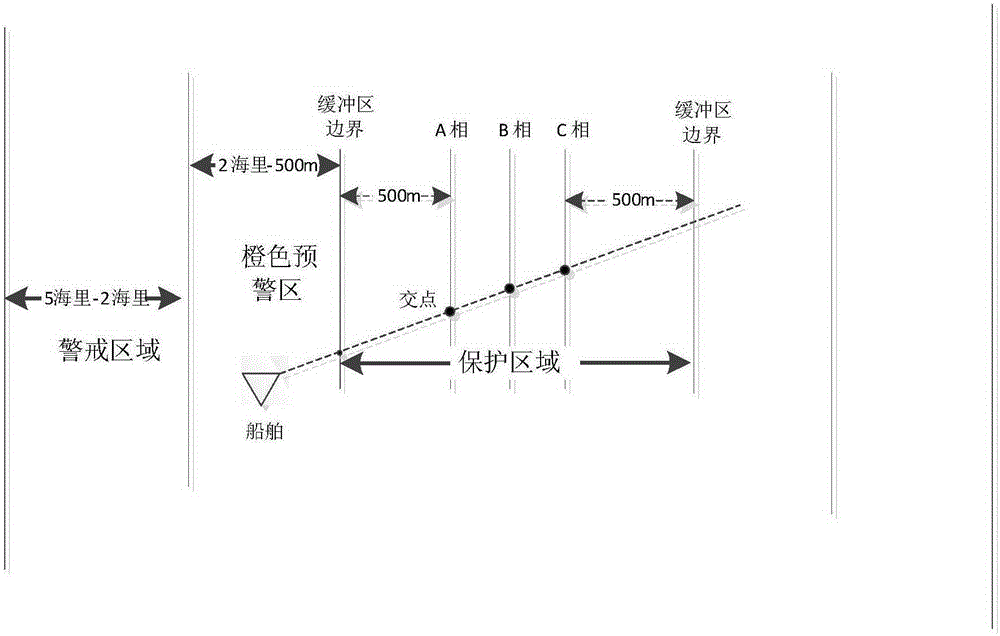
[0047] Step A, identifying ships entering the preset monitoring range, which includes the protection area of the submarine cable and the surrounding warning area;
[0048] Step B, monitoring the distance from the ship to the submarine cable and the speed of the ship, and calculating several speed variations of the ship when navigating in the warning area and the protection area;
[0049] Step C, determining the basic risk level of the ship to the submarine cable according to the distance, ship speed and speed variation.
[0050] Specifically, step C may include:
[0051] S10, if the obtained distance is greater than the boundary value of the warning area, it is determined that the ship has no potential anchor damage to the submarine cable;
[0052] S20, if the obtained distance is less than or equal to the boundary value of the warning area ...
example
[0070] Example: The cargo ship named "MINHANG6" (MMSI: 123456789), within 1.8 nautical miles to 700 meters from the west side of phase A of the submarine cable, from 07:05 to 07:08, the speed of the ship dropped rapidly from 8 knots to 3 knots, From 07:08 to 07:15, the speed of the ship slowly decreased from 3 knots to 0.5 knots, and from 07:15 to 07:23, the speed of the ship decreased from 0.5 knots to 0 knots.
[0071] 1. The system judges that "MINHANG6" has entered the ship identification area (within 5 nautical miles on both sides of the submarine cable), and the system starts to monitor and identify each data element;
[0072] 2. Determine whether the ship is whitelisted. (That is, to determine whether the ship has a history of breaking down in the submarine cable monitoring area before, or whether the ship is a non-threatening friendly ship that has reported in advance). After judging that it is not a white list, go to step 3.
[0073] 3. After judging, the relative p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com