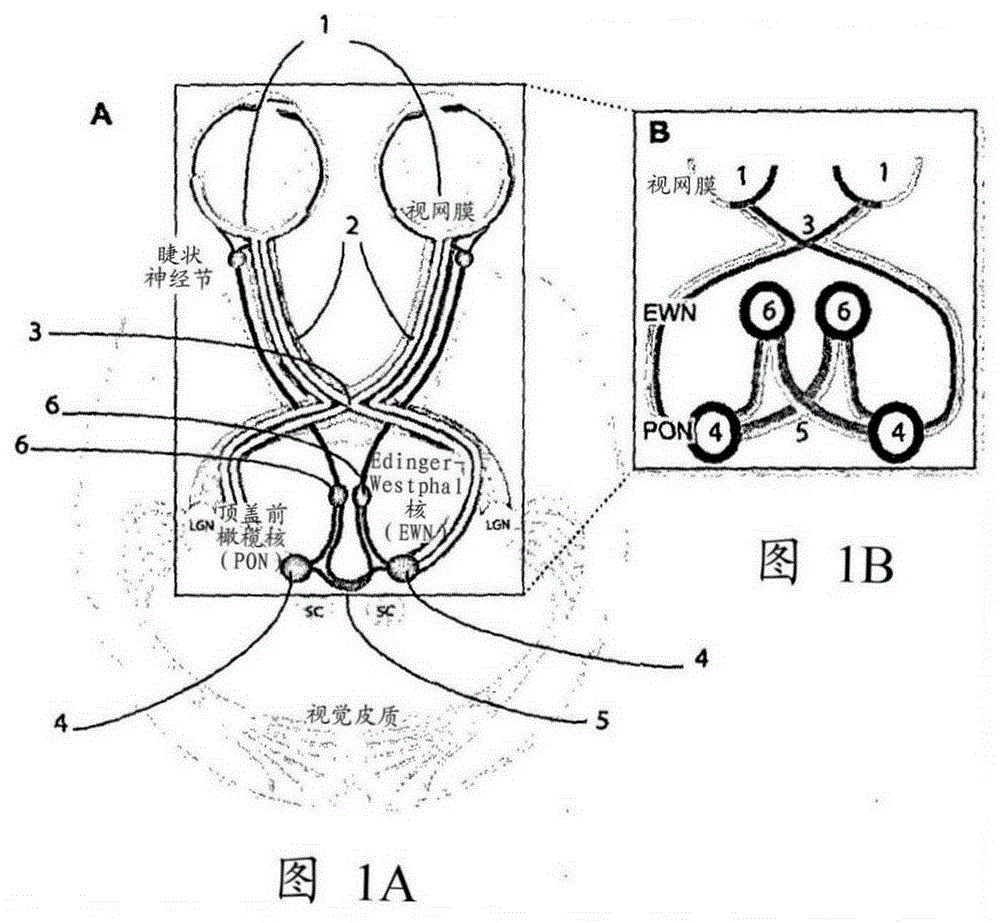
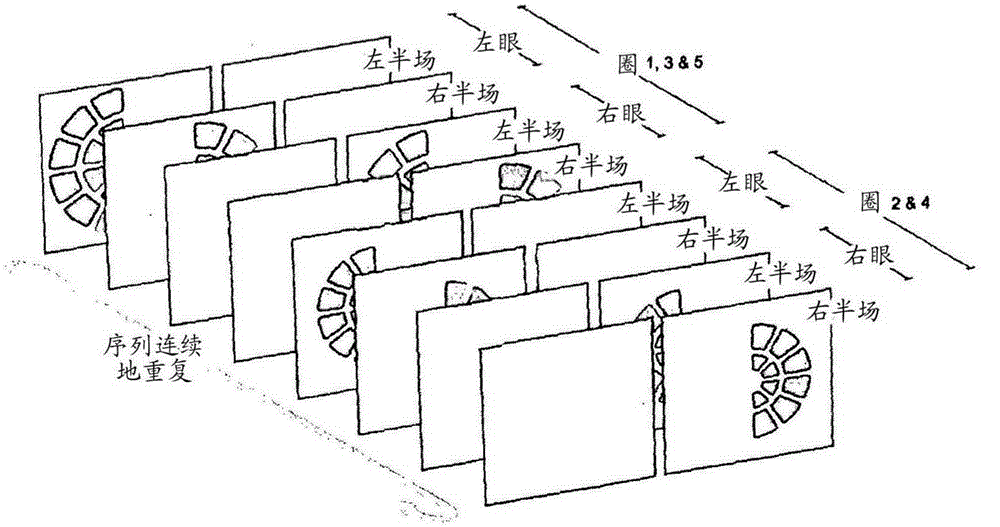
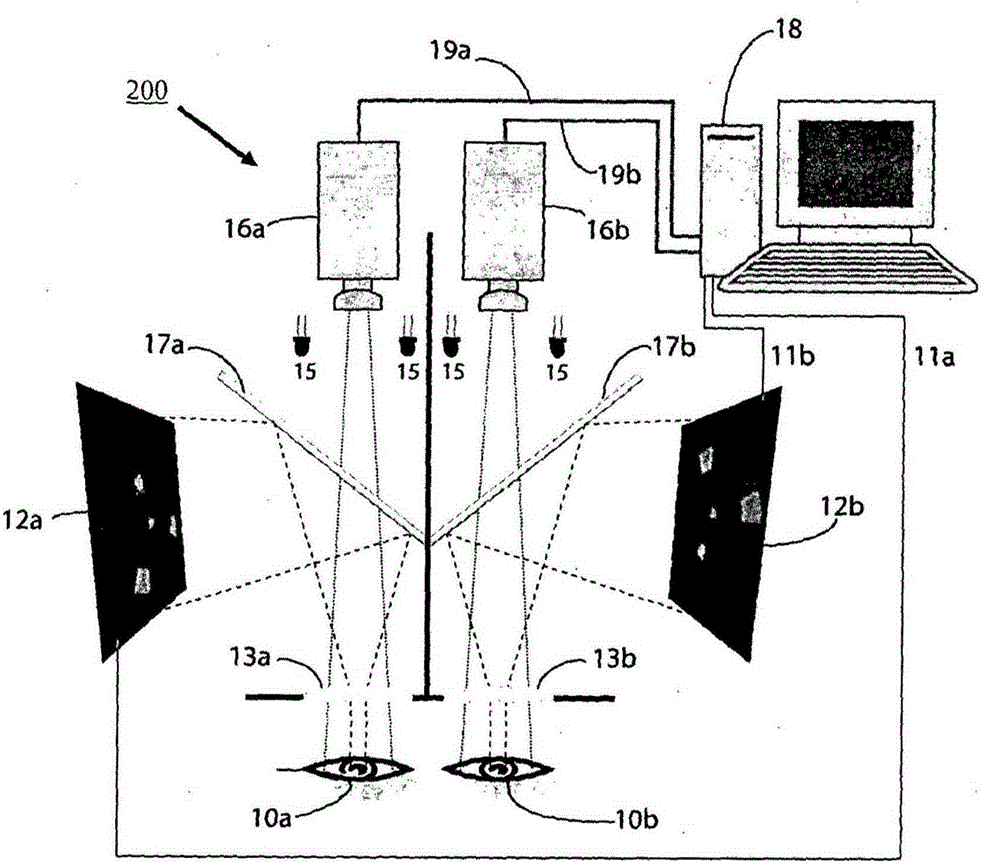
Clustered volley method and apparatus
A clustering, pupillary technique applied in the field of assessing the operation of the visual sensory system, capable of solving problems such as non-existence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0100] Example 1 - Improved SNR for normal subjects
[0101] International PCT Patent Publication WO / 2005 / 051193 describes a spatially sparse multifocal stimulation type. The idea disclosed in this document is that there is a gain control operation within the retinal part of the visual nervous system. Most of the sensory parts of the brain lie on sheets of neural tissue that are often folded to fit within the skull, forming similar gyri and sulci to the human brain. The sensory part of the brain with retinal re-presentation contains a sensory brain map of the visual field on its surface. Other types of sensory fields were also mapped in different parts of the brain slice. Within this re-rendering, there is the possibility that the gain control can interact on-chip in a short range. Retinal mapping implies that average gain control can affect responses to stimuli in adjacent regions of the visual field. International PCT Patent Publication WO / 2005 / 051193 shows that such reg...
example 2
[0122] Example 2 – Clustered salvo stimuli in glaucoma
[0123] Investigate the relative diagnostic efficacy for distinguishing normal subjects from patients with open-angle glaucoma. The three wide-area stimuli in Table 3, namely Yold, Ynew and RGnew, are 150cd / m 2 variable. As before, all three stimulation types had an average stimulation interval of 4 seconds per field. Use FA-II achromatic visual field examination (SITA-FAST), matrix 24-2 visual field examination, Heidelberg spectral domain optical coherence tomography (OCT), slit lamp biomicroscopy, and applanation tonometry to confirm the subject's diagnostic status. Subjects were required to pass the manufacturer's criteria for false positives, negatives, and loss of fixation on visual field examination. Exclusion criteria for all subjects included acuity below 6 / 12, distance refraction greater than ±6 diopters or greater than 2 diopters of cylinder. Normal subjects have little to no relation to glaucoma. The study...
example 3
[0136] Example 3 – Clustered salvo stimulation in macular degeneration
[0137] Versions of the three macular-directed stimulus types using Table 4 to compare the diagnostic efficacy of old spatially sparse stimuli and SteadyOld for the detection of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), with two new clustered stimuli FlickNew and SteadyNew, of which 44 Stimulus areas were presented to the central 30 degrees of each field of view. Stimuli are yellow, similar to Form 4, but have a maximum brightness of 288cd / m in their active state 2 , present at 10cd / m 2 on the background. Table 8 summarizes the patient and age-matched normal control subject statistics. All subjects were examined for the glaucoma study above, exclusion criteria were similar. In addition, color retinal pictures were taken using a non-mydriatic fundus camera with a 45-degree field of view.
[0138] Form 8
[0139] subject group
number of subjects
number of men
Age±SD years
norm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com