A rapid post-ripening fermentation method based on the characteristic flavor of Mucor-type tempeh
A post-ripening fermentation and mucormycotic technology, which is applied in the direction of food science to achieve the effect of improving the characteristic flavor, shortening the fermentation cycle, and the method is simple and easy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0017] Example 1: Tempeh aged for 2 years by natural fermentation (naturally mature tempeh)
[0018] Bean selection: Soybeans are used as raw materials, and soybeans are required to be full of particles. Soaking: Soak soybeans in water for 5-6 hours and drain. Cooking: Drained soybeans were steamed at 121°C for 30 min. Cooling inoculation: After the cooked soybeans are cooled to 40°C, inoculate 0.5% of Mucor koji according to the mass of soybeans, and cultivate at 10-15°C for 7 days to make fermented fermented fermented koji blanks. Mixing materials: After making the koji blank, add 12% NaCl, 3% edible starch and 5% white wine according to the quality of the koji blank. Post-ripening fermentation: Put the mixed koji into an airtight container, and naturally ferment and age for 2 years.
example 2
[0019] Example 2: Tempeh with enhanced fermentation and heat preservation for 30 days (enhanced fermented tempeh)
[0020] Bean selection: Soybeans are used as raw materials, and soybeans are required to be full of particles. Soaking: Soak soybeans in water for 5-6 hours and drain. Cooking: Drained soybeans were steamed at 121°C for 30 min. Cooling inoculation: After the cooked soybeans are cooled to 40°C, inoculate 0.5% of Mucor koji according to the mass of soybeans, and cultivate at 10-15°C for 7 days to make fermented fermented fermented koji blanks. Mixing materials: After making the koji blank, add 12% NaCl, 3% edible starch and 5% white wine according to the quality of the koji blank. Fermentation after inoculation with salt-tolerant microorganisms: the mixed koji blanks (calculated as 1000g) are simultaneously inoculated into the yeast CGMCC 3791 (2.3×10 6 CFU / g), Candida CGMCC 3790 (4.7×10 7 CFU / g) and Tetraphylococcus halophilus CGMCC 3792 (4.3×10 7 CFU / g), f...
example 3
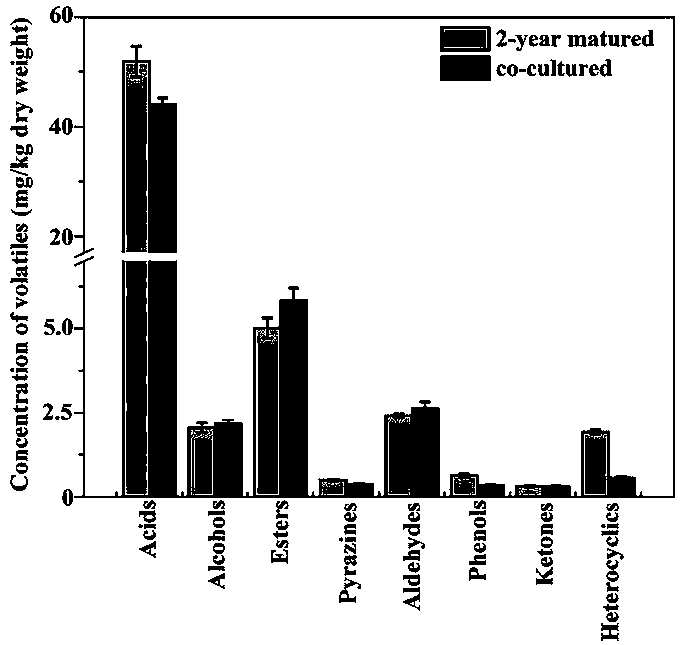
[0021] Example 3: Comparison of volatile components of naturally matured and fortified fermented tempeh
[0022] Eight types of volatile compounds were detected by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for naturally matured and enhanced fermented tempeh. Among them, the contents of acids, esters and heterocyclic compounds in the two kinds of tempeh have little difference, while alcohols, aldehydes, phenols, ketones, pyrazines and furans which have a greater contribution to the characteristic flavor of tempeh Compounds were not significantly different ( figure 1 ).
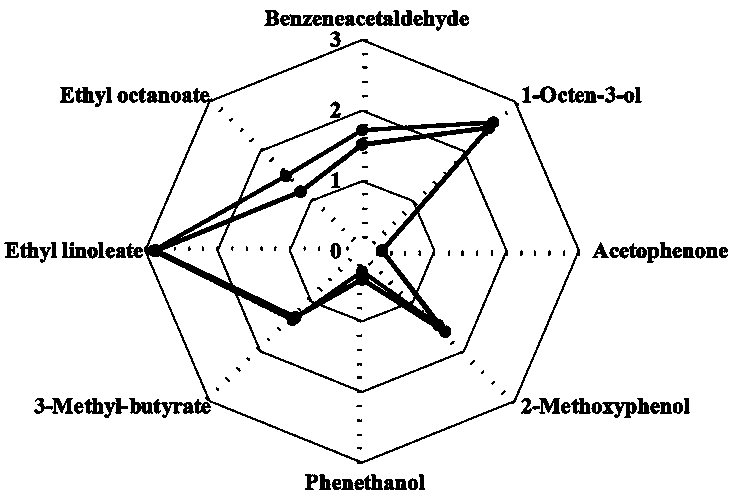
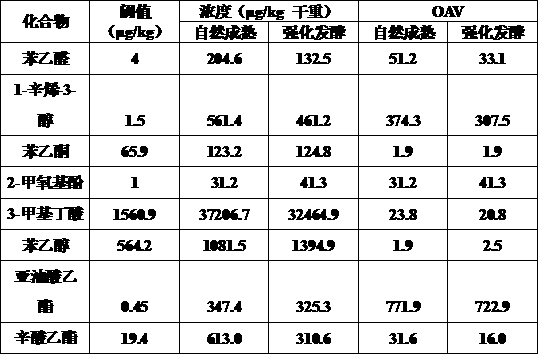
[0023] Eight volatile components that contribute to the characteristic flavor of tempeh were selected for odor activity value analysis (OAV), and the results are shown in Table 1. Among them, the OAV of ethyl linoleate, which imparted the sweet and oily flavor of tempeh, was the largest, and the OAVs of natural ripening and intensive fermentation were 771.9 and 722.9, res...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com