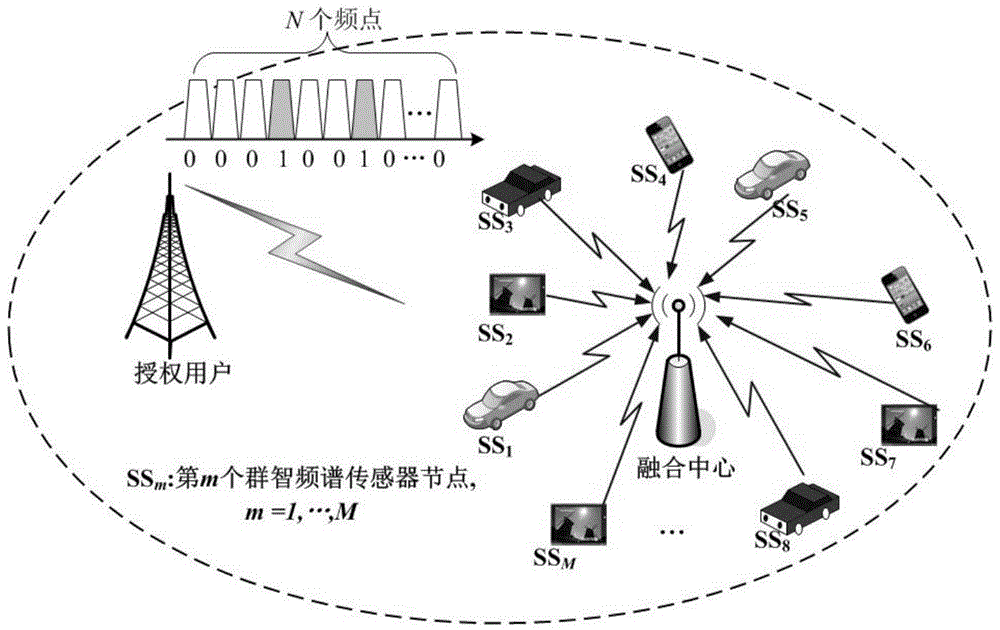
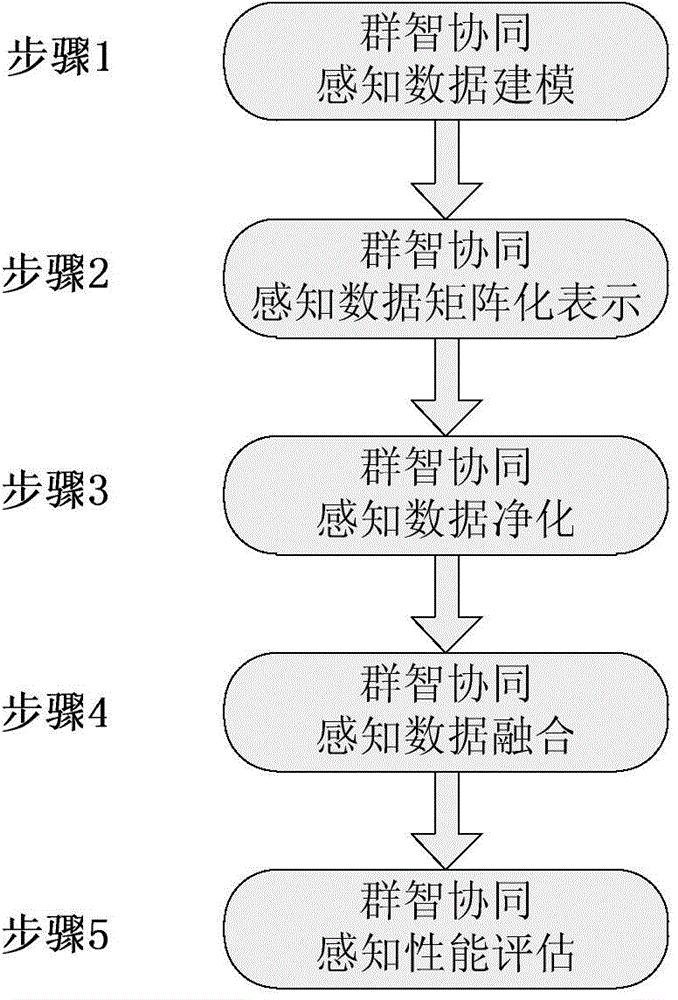
Crowd-sourcing cooperative spectrum sensing method based on data cleaning
A collaborative spectrum sensing and data purification technology, applied in the field of cognitive radio, can solve problems such as limited spectrum sensing accuracy and stability, difficulty in guaranteeing spectrum sensing data quality, and sensing data falsification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
comparative approach 1
[0094] Comparison scheme 1: The fusion center does not perform data purification, that is, skips step 3 of the present invention for swarm intelligence collaborative spectrum sensing data purification, and directly uses the data reported by swarm intelligence spectrum sensor nodes to perform fusion judgment according to step 4. The reference of this comparison scheme is "J.Ma, G.Zhao, and Y.Li, "Softcombinationanddetectionforcooperativespectrumsensingincognitiveradionetworks," IEEETransactionsWirelessCommunications, vol.7, no.11, pp.4502-4507, Nov.2008."
comparative approach 2
[0095] Comparison scheme 2: The fusion center changes "step 3 crowd intelligence collaborative spectrum sensing data purification" to "eliminate all nodes reporting abnormal data", and only uses the reported data of the remaining nodes for fusion judgment. Considering that it is often difficult for the fusion center to perfectly determine which nodes may report abnormal data in practice, it is assumed that the probability of the fusion center misjudging the node type is 0.1. The reference of this comparative scheme is "W.Wang, H.Li, Y.Sun, and Z.Han, "Securing collaborative spectrum sensing against trustworthy secondary users sin cognitive radionetworks," EURASIPJournalon Advances in Signal Processing, vol.2010, 2010."
comparative approach 3
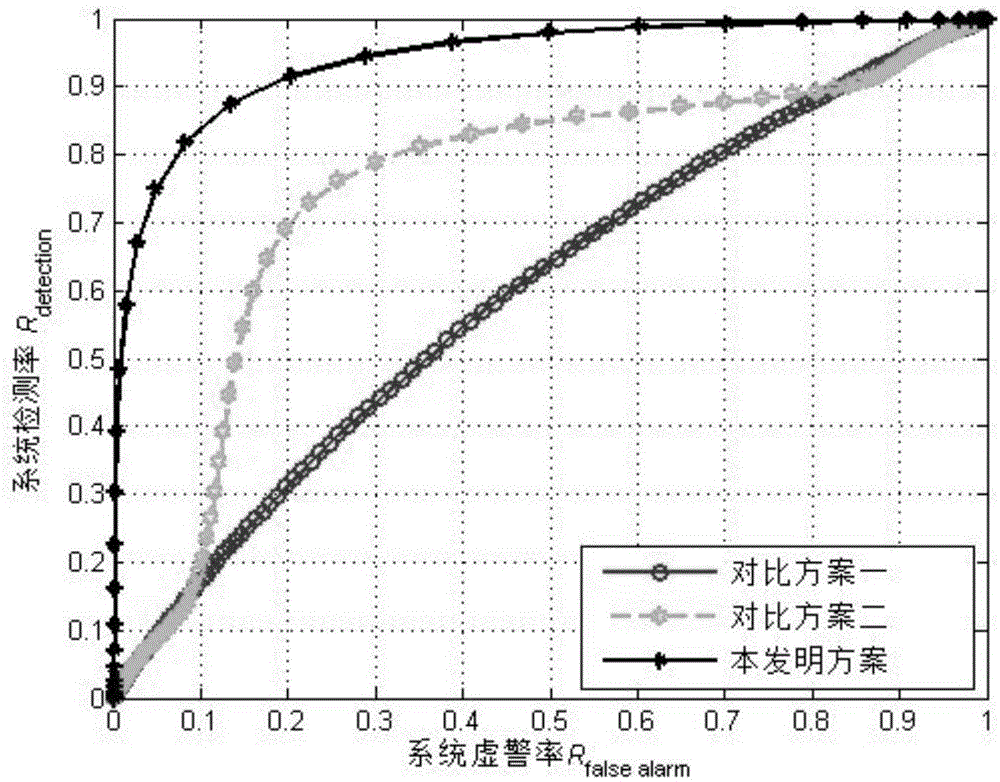
[0096] Comparison scheme three: the method for spectrum sensing based on crowd intelligence collaboration based on data purification described in the present invention.
[0097] For the three comparison schemes, image 3 The relationship curve between the system detection rate and the system false alarm rate is given, through image 3 It can be seen that: given a certain system false alarm rate R false-alarm In the case of , compared with the system detection rate R of Scheme 1 detction Very low, compared with the system detection rate R of Scheme 2 detction If it is improved, the system detection rate of the method of the present invention is greatly improved. It shows that the method of the present invention can better solve the technical problems such as the ubiquity of sensing data errors and the unavoidable falsification of sensing data in popular and portable wireless spectrum sensing devices, and obtain robust collaborative spectrum sensing performance.
[0098] Spe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com