Low-coercive-force samarium-cobalt magnet and preparation method thereof
A samarium-cobalt magnet and chemical composition technology, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, inductors/transformers/magnets, magnetic materials, etc., can solve the problem of deteriorating samarium-cobalt magnet performance, reducing the coercive force of samarium-cobalt magnets, and low-coercive force samarium-cobalt magnets Magnets and other issues, to meet customer requirements, improve overall performance, and easily saturate the effect of magnetization work
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
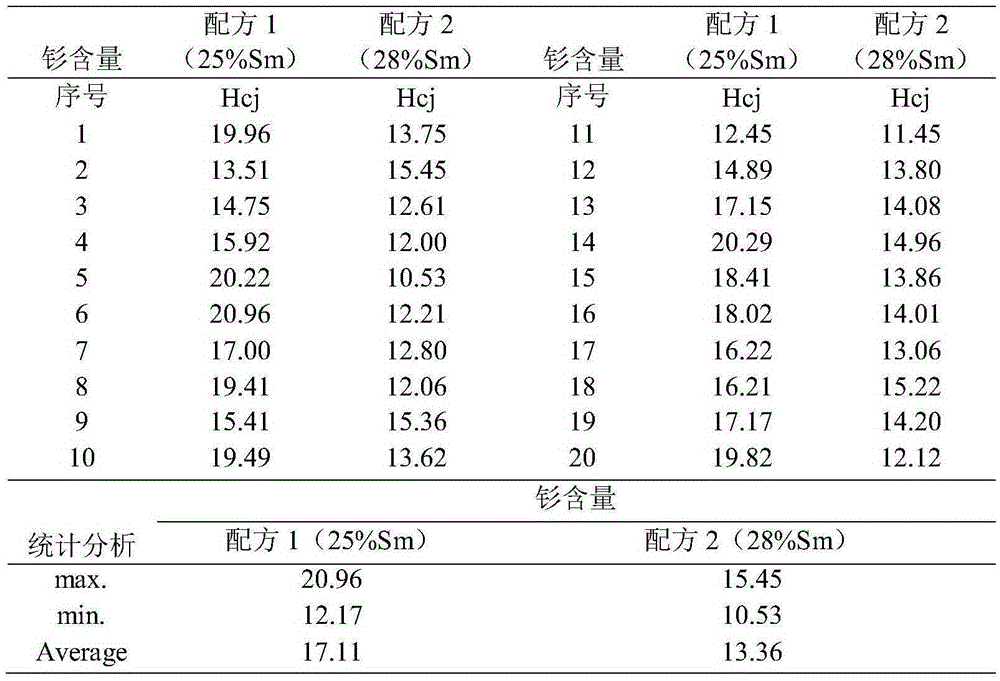
[0040] 1) According to the mass percentage: (Sm1-z RE z ) a co (1-a-b-c-d) Cu b Fe d Zr c , the value of a is: 25% and 28%, the value of Z is 0, the content of copper is 8%, the content of zirconium is: 3%, the content of iron is: 15%, and the rest is cobalt to prepare low coercive force samarium Cobalt magnet raw materials are respectively named formula 1 (a=25%) and formula 2 (a=28%) according to the difference of a value.
[0041] 2) Melting the prepared raw materials in a vacuum or protective gas environment to make alloy ingots or slabs with a thickness of 0.2-0.5mm.
[0042] 3) Coarsely crushing the alloy ingots or flakes to produce particles with a size of less than 1mm, and then ball milling the powder into 4-7μm powders under protective gas.
[0043] 4) The powder is pressed into a powder in a magnetic field greater than 1.5T, and then isostatically pressed under a pressure of 250 MPa to form a green body.
[0044] 5) Put the green body into the sintering furna...
Embodiment 2
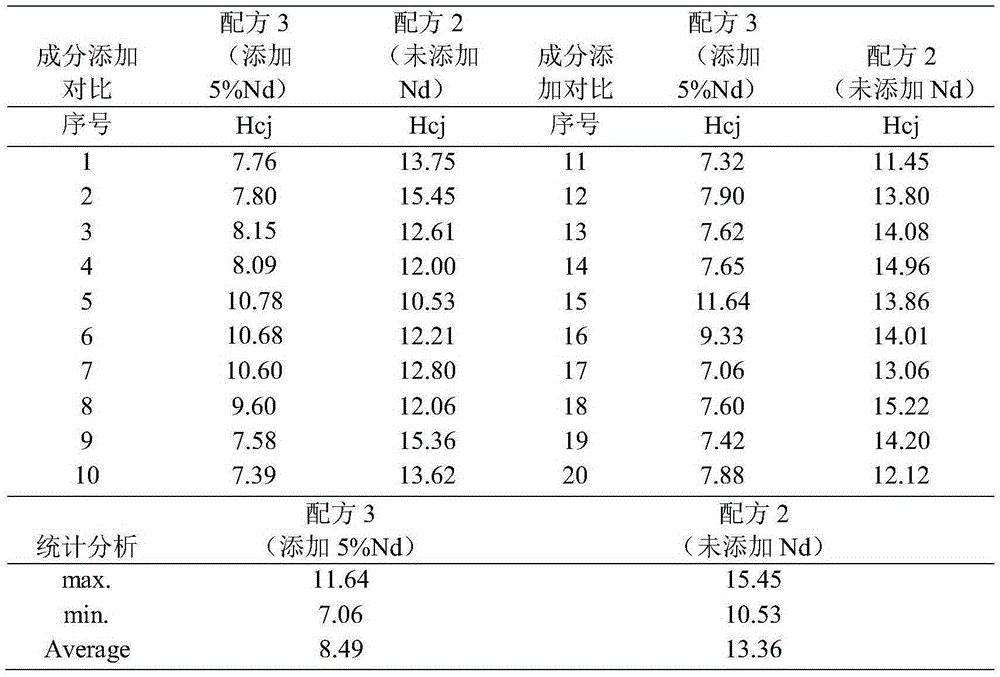
[0052] According to mass percentage: (Sm 1-z RE z ) a co (1-a-b-c-d) Cu b Fe d Zr c , the value of a is: 28%, the value of RE is Nd, the value of Z is 0% and 17.86%, the content of copper is 8%, the content of zirconium is: 3%, the content of iron is: 15%, and the rest is cobalt. Raw materials for low coercivity samarium cobalt magnets. The difference between Example 2 and Example 1 is that the composition and dosage of RE are different. The added Nd content is used as the difference point, and they are divided into two groups, which are recorded as formula 3 (adding 5% Nd: Z=17.86%, replacing with Nd The total amount is 5% Sm, the same below), formula 2 (not added). All the other preparation processes are the same as in Example 1.
[0053] The samarium-cobalt magnets prepared according to formula 3 and formula 2 in Example 2 were sampled and tested, and the magnetic properties of the products are shown in Table 2.
[0054] Table 2 Changes in magnetic properties after...
Embodiment 3
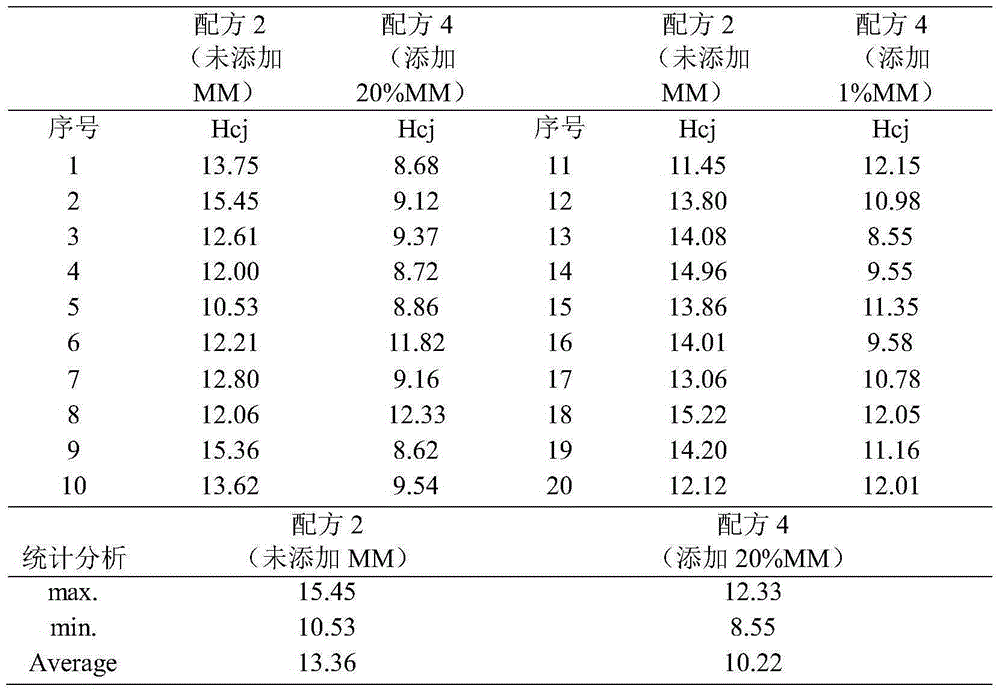
[0058] According to mass percentage: (Sm 1-z RE z ) a co (1-a-b-c-d) Cu b Fe d Zr c , the value of a is: 28%, RE is MM, and MM is mixed rare earth, which is the 194025A grade specified in GB / T4153-2008. The value of Z is 0% and 20%, the content of copper is 8%, the content of zirconium is 3%, the content of iron is 15%, the rest is cobalt, and the raw material of low coercivity samarium cobalt magnet is prepared. Taking the amount of MM added as a difference point, they were divided into two groups, which were recorded as formula 4 (add 20% MM, Z=20%, that is, replace 20% Sm with MM quality, the same below), and formula 2 (not added). The preparation process of the samarium cobalt magnet is the same as that in Example 1.
[0059] The corresponding samarium cobalt magnet samples were prepared by repeating the formula 4 and formula 2 for many times, and these samarium cobalt magnets were sampled and tested to test their intrinsic coercive force. The results are shown in T...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Intrinsic coercive force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Intrinsic coercive force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com