Electric heating system with continuously adjustable power and its control method
A heating system and electric heating technology, applied in heating methods, electric heating devices, lighting and heating equipment, etc., can solve the problems of unadjustable electric heating power and large pressure difference of the heat pump system, so as to reduce the input power and increase the input power. , the effect of reducing the input power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] In this example, an air-conditioning system is taken as an example to specifically illustrate the content of the present invention.
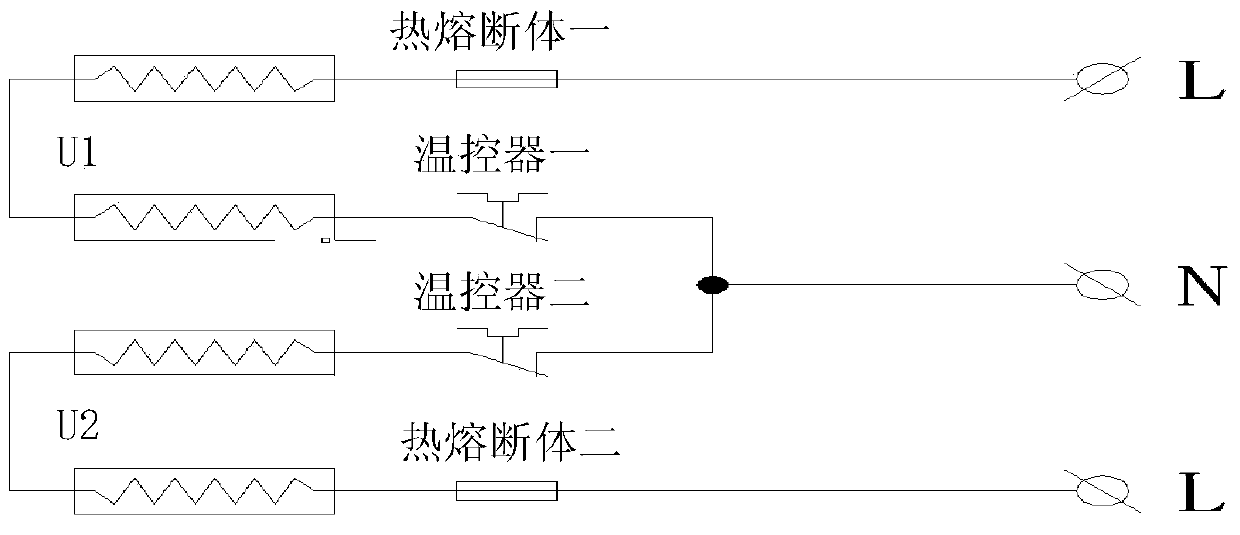
[0060] First of all, in order to increase the heat dissipation area and facilitate installation, the electric heating used in the air conditioner of this example adopts a U-shaped structure. The specific structure is as figure 1 As shown, it includes thermal fuse 1, U-shaped heating pipe U1, thermostat 1, thermal fuse 2, U-shaped heating pipe 2 U2, and thermostat 2. One end of the thermal fuse 1 is connected to the AC power supply The live wire end is connected, the other end of thermal fuse one is connected with one end of U-shaped heating pipe one, the other end of U-shaped heating pipe U1 is connected with one end of thermostat one, and the other end of thermostat one is connected with thermostat one. One end of the two is connected to the zero line end of the AC power supply, the other end of the thermostat two is connected to one en...
Embodiment 2
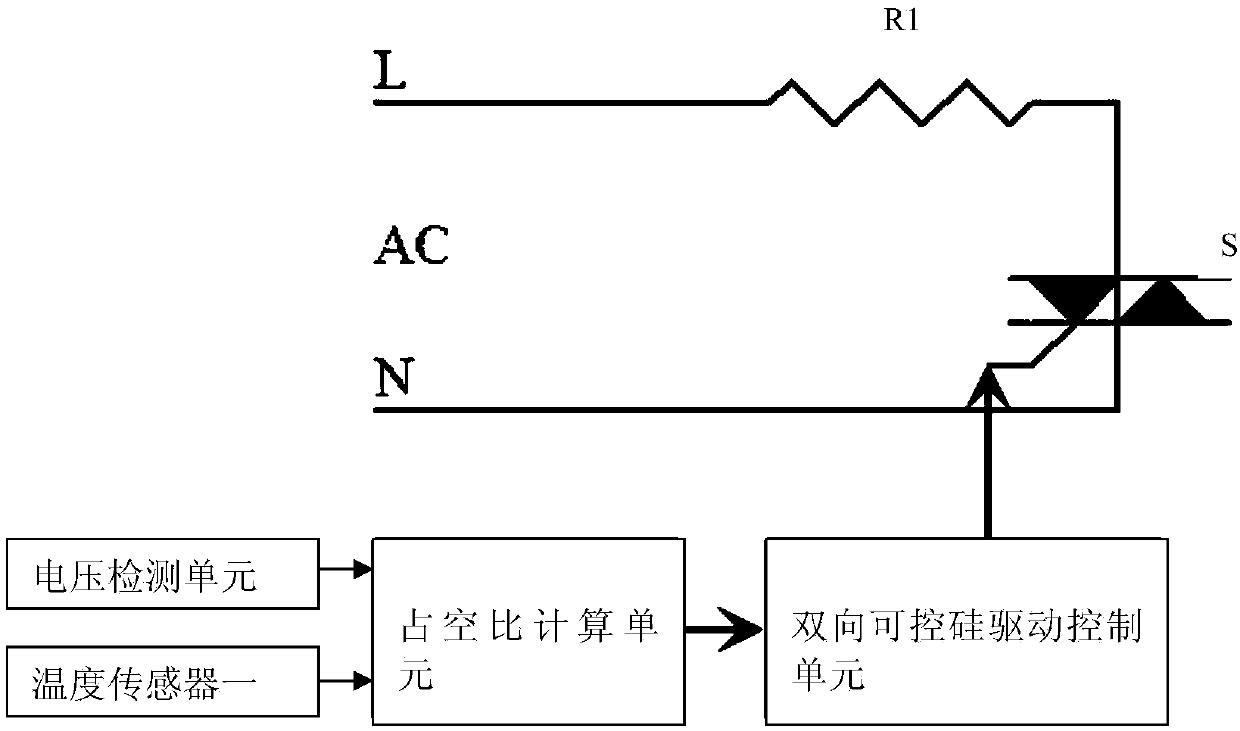
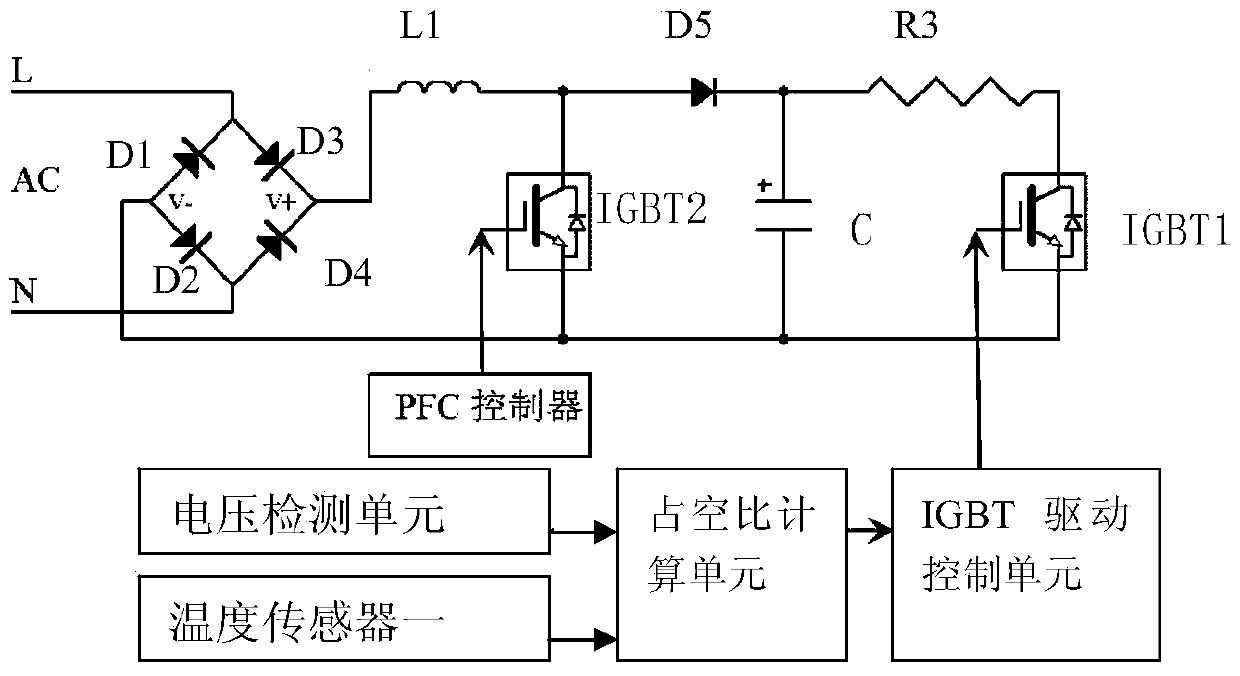
[0065]On the basis of Embodiment 1, in order to further ensure the accuracy of real-time duty cycle calculation, this example also includes a temperature sensor one, which is connected to the duty cycle calculation unit; the temperature sensor one is used to detect The real-time temperature of the electric heating circuit is transmitted to the duty cycle calculation unit; the duty cycle calculation unit is used to calculate the real-time temperature difference according to the real-time temperature of the electric heating circuit and the target temperature, and combine the real-time input voltage value and the real-time temperature difference according to the real-time temperature difference and The real-time duty ratio is calculated from the real-time power difference, and the real-time duty ratio is proportional to the real-time temperature difference and the real-time power difference; the duty ratio modulation circuit is used to modulate the output power of the power module ...
Embodiment 3
[0070] This example is based on the first and second examples, and solves the problem that the heating element of the air conditioner is easily deformed when the temperature is too high.
[0071] In order to solve the above problems, this example also includes a temperature sensor two, which is connected to the duty cycle calculation unit; the temperature sensor two is used to detect the temperature of the electric heating circuit and transmit it to the duty cycle calculation unit unit; the duty ratio calculation unit is used to compare the temperature of the electric heating circuit with the preset upper limit of the temperature of the electric heating circuit, when the temperature of the electric heating circuit is higher than the preset upper limit of the temperature of the electric heating circuit, The system reduces the current system operating duty cycle value according to the preset reduction amplitude; it is also used to compare the temperature of the electric heating c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com