A Simplified Risk Assessment Method for Nuclear Power Plant Based on Logical Equivalence Fault Tree
A technology of risk assessment and logical equivalence, applied in electrical testing/monitoring, program control, instrumentation, etc., can solve problems such as excessive computing resource requirements, long time consumption, and impossibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] The nuclear power plant risk assessment method based on logical equivalent fault tree simplification of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0042] 1. Identify several basic events that affect the reliability of nuclear power plants, such as valve bursts, overheating, etc.
[0043] 2. Determine the logical relationship between the basic events determined in the previous step, use gates to represent the logical relationship, and build a fault tree with these basic events and gates, and the nodes of the fault tree are basic events and gates.
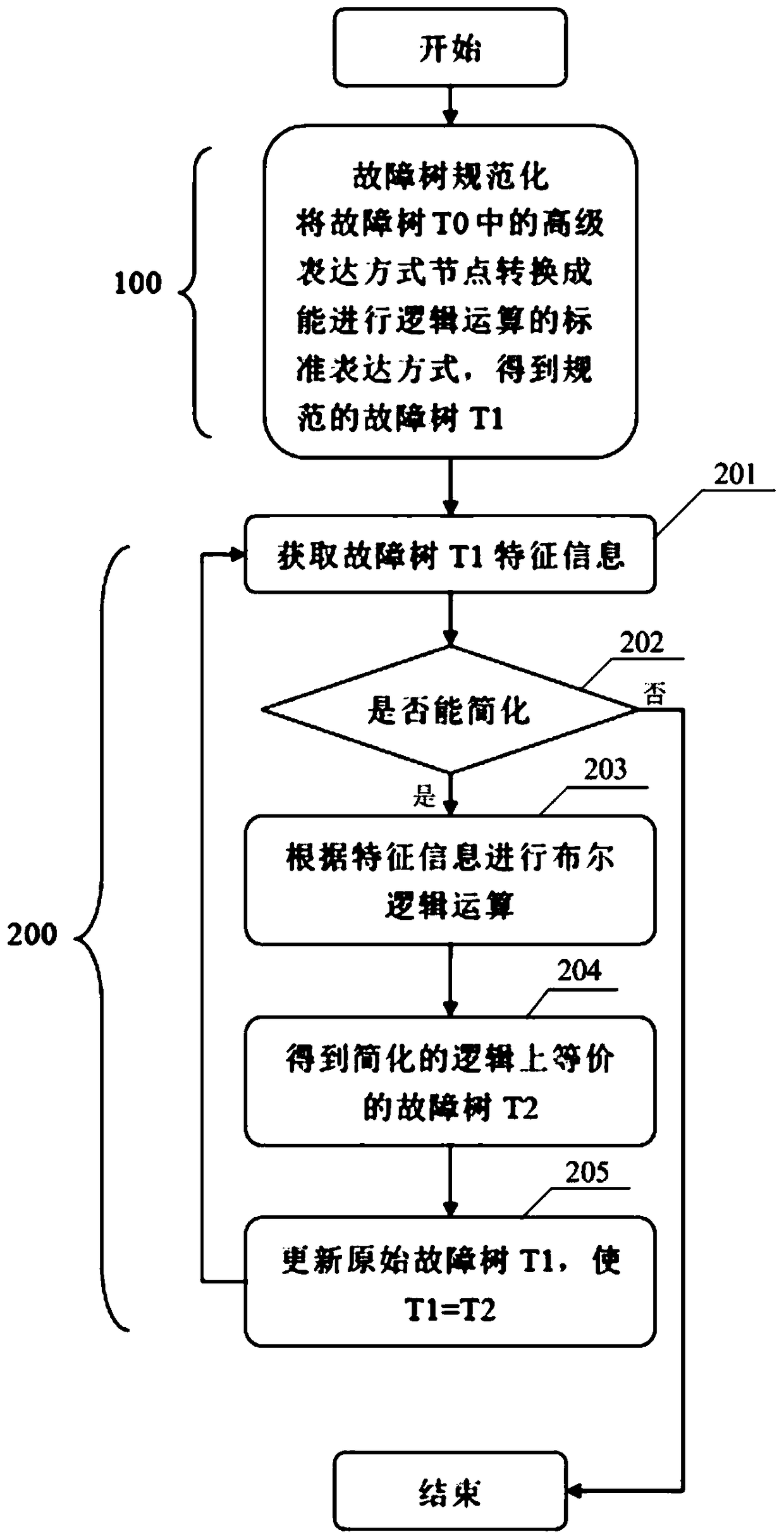
[0044] 3. Simplify the fault tree, such as figure 1 As shown, specifically include:
[0045] In step 100, each node of the fault tree T0 is traversed to obtain a normal expression form of the fault tree T0, that is, a fault tree T1 is obtained.
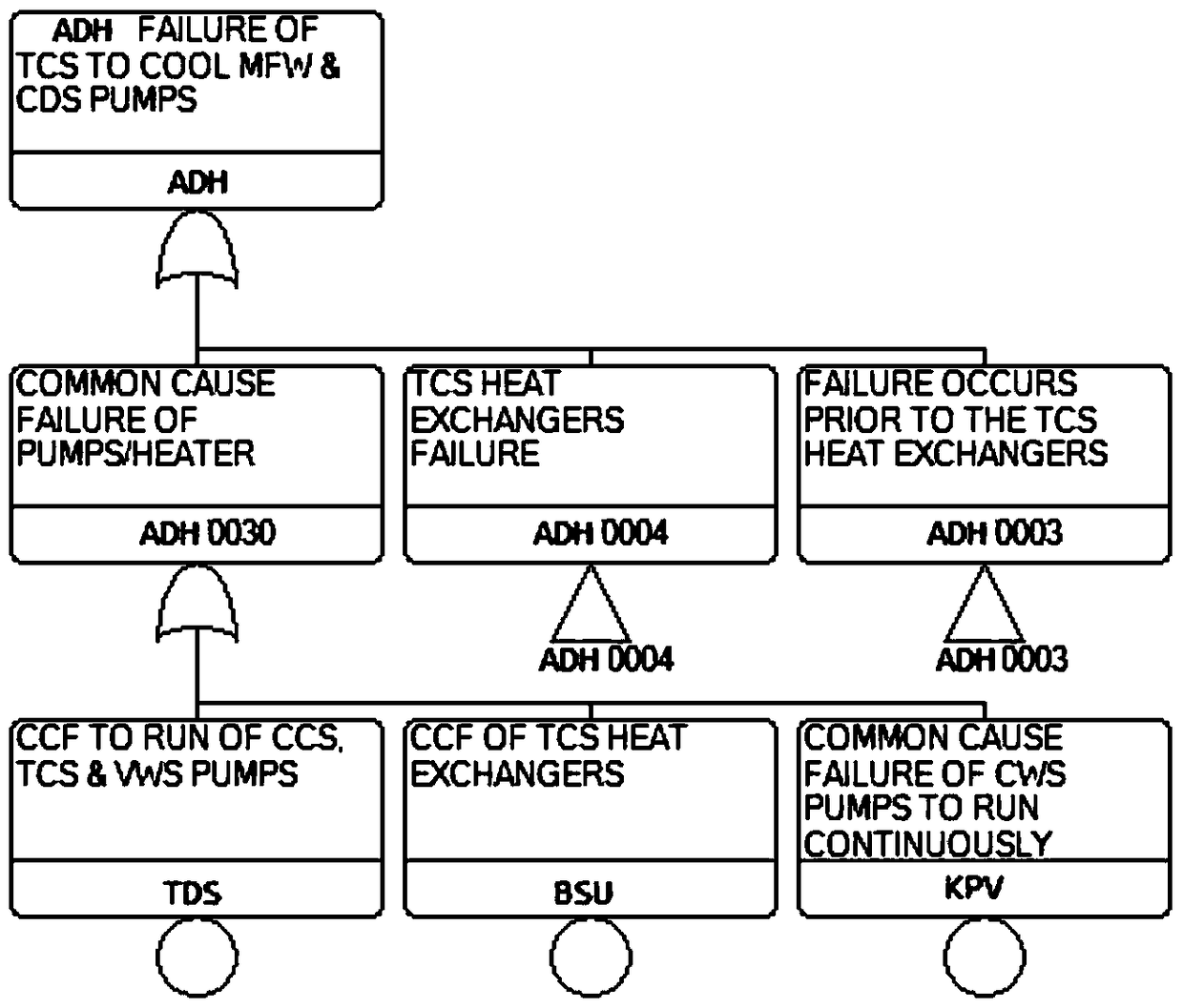
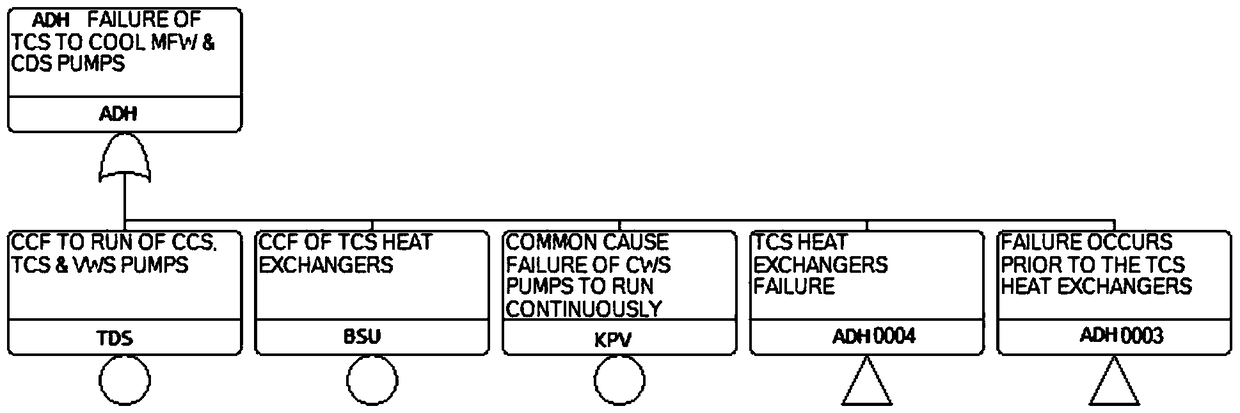
[0046] Step 200, obtain the characteristic information of the fault tree T1 and perform logical operations on the fault tree T1 according to the characteristic informati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com