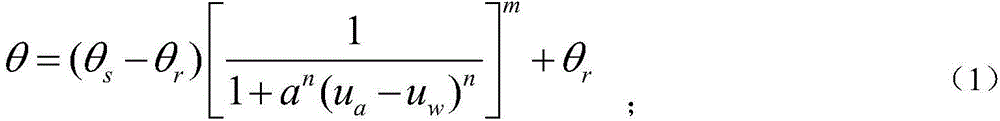Method for clay inter-particle pore equivalent pore size
A particle and pore size technology, applied in the field of geotechnical engineering, can solve problems such as unspecified quantitative methods and limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0057] A method for the equivalent pore size of pores between clay particles, specifically carried out according to the following steps:
[0058] step 1,
[0059] Firstly, clay-containing soil samples were prepared for soil-water characteristic test, and a complete soil-water characteristic curve was obtained by fitting equation (1) through MATLAB, expressed in terms of mass water content. The fitting formula is as follows:
[0060] θ = ( θ s - θ r ) [ 1 1 + a n ( u a - u ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com