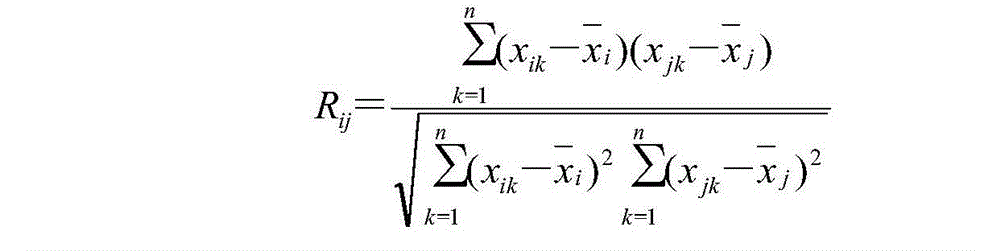Method for identifying type and characteristic of crude oil through near-infrared spectrum
A technology of near-infrared spectroscopy and crude oil, applied in the direction of material analysis, measuring devices, instruments, etc. through optical means, can solve problems such as unidentifiable, limited application range, and mixing, and achieve the effect of improving the success rate of identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0048] Establishment of near-infrared spectral database of crude oil samples
[0049] 655 representative crude oil samples were collected, and the crude oil varieties basically covered the world's major crude oil producing areas. Measure the near-infrared spectrum of the crude oil sample, perform second-order differentiation on it, and select 6076.0~5556.0cm -1 and 4628.0~4000.0cm -1 For the absorbance in the spectral range, the near-infrared spectrum matrix X of crude oil samples is established. The dimension of X is 655×289, where 655 is the number of samples collected for crude oil, and 289 is the number of sampling points for the near-infrared spectrum absorbance.
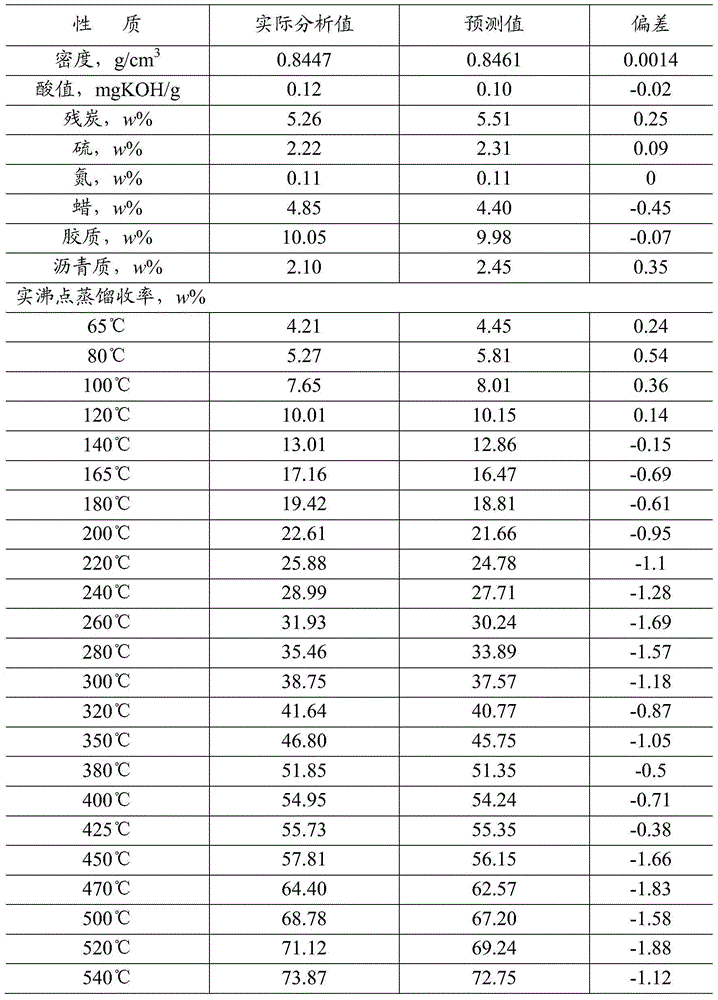
[0050] The density, acid value, carbon residue, sulfur, nitrogen, wax, colloid, asphaltene, and real boiling point distillation data (TBP, cumulative mass yield of 23 temperature points: 65°C, 80°C , 100°C, 120°C, 140°C, 165°C, 180°C, 200°C, 220°C, 240°C, 260°C, 280°C, 300°C, 320°C, 350°C, 380°C, 400°C, 425°C...
example 2
[0053] The following examples use the method of the present invention to identify unknown petroleum samples.
[0054] (1) Establish the spectral vector of crude oil to be identified
[0055] Measure the near-infrared spectrum of unknown crude oil sample A (intermediate base crude oil) according to the same conditions as the establishment of the near-infrared spectrum database of crude oil, and perform second order differentiation on its near-infrared spectrum, taking 6076.0~5556.0cm -1 and 4628.0~4000.0cm -1 The absorbance in the spectral range constitutes the spectral vector x of the crude oil to be identified A , whose dimension is 1×289.
[0056] (2) Identify unknown crude oil species in the established near-infrared spectral library of crude oil samples
[0057] For the near-infrared spectrum matrix X and the crude oil spectrum vector x to be identified A , respectively from 4000.0cm -1 Take a corresponding section of the spectral interval as the moving window, and th...
example 3
[0070] (1) Establish the spectral vector of crude oil to be identified
[0071] Measure the near-infrared spectrum of unknown crude oil sample B (paraffin-based crude oil) according to the same conditions as the establishment of the near-infrared spectrum database of crude oil, and perform second-order differentiation on its near-infrared spectrum, taking 6076.0~5556.0cm -1 and 4628.0~4000.0cm -1 The absorbance in the spectral range constitutes the spectral vector x of the crude oil to be identified B , whose dimension is 1×289.
[0072] (2) Identify unknown crude oil species in the established near-infrared spectral library of crude oil samples
[0073] Crude oil spectrum vector x to be identified B , according to the example 2 (2) step method, calculate its mobile correlation coefficient with each crude oil sample spectrum in the near-infrared spectrum matrix X of crude oil sample one by one, calculate the identification parameter Q. The calculated crude oil No. 323 clos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com