Two-motor driven variable-stiffness elastic joint of robot
A technology driven by dual motors and elastic joints, applied in manipulators, manufacturing tools, joints, etc., can solve the problems of inability to achieve linearly adjustable stiffness characteristics, waste of stiffness adjustment motor power, and inability to adjust stiffness, etc., to improve energy utilization The effect of high efficiency, elimination of mechanical shock, and fast real-time response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] The embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below. This embodiment is implemented on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation methods and specific operating procedures are provided, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following implementation example.
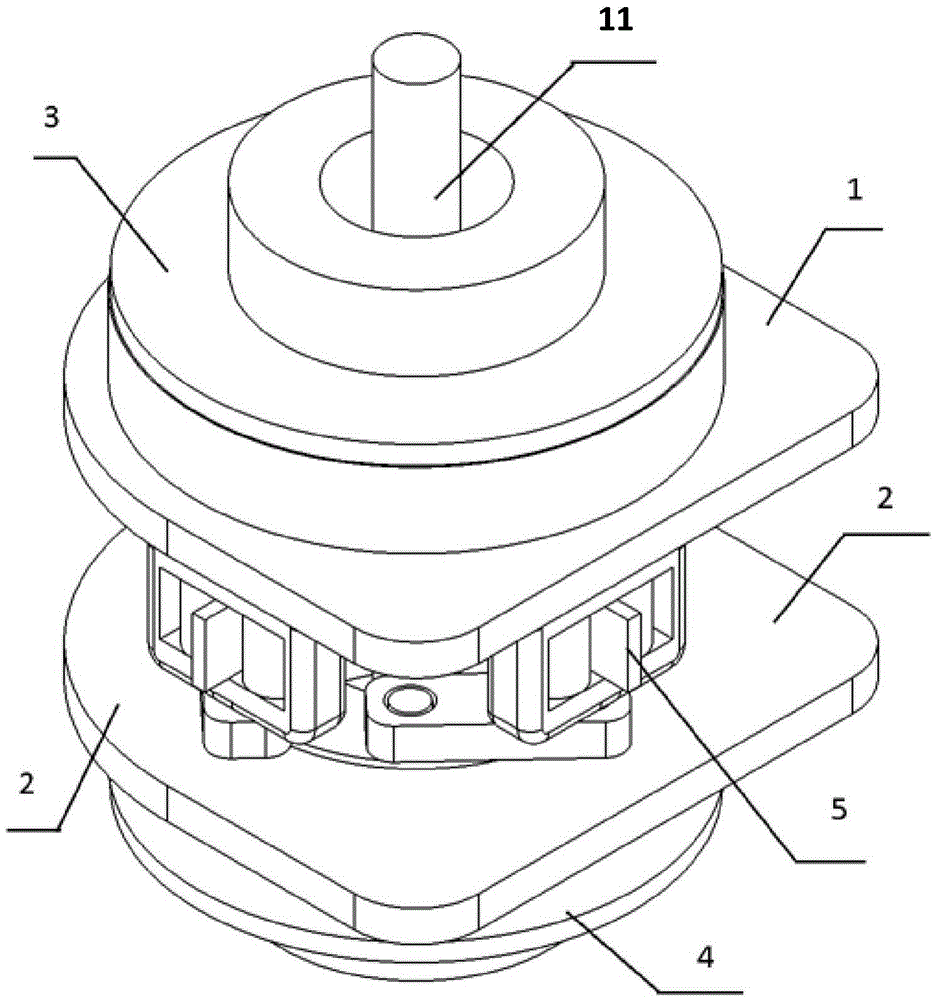
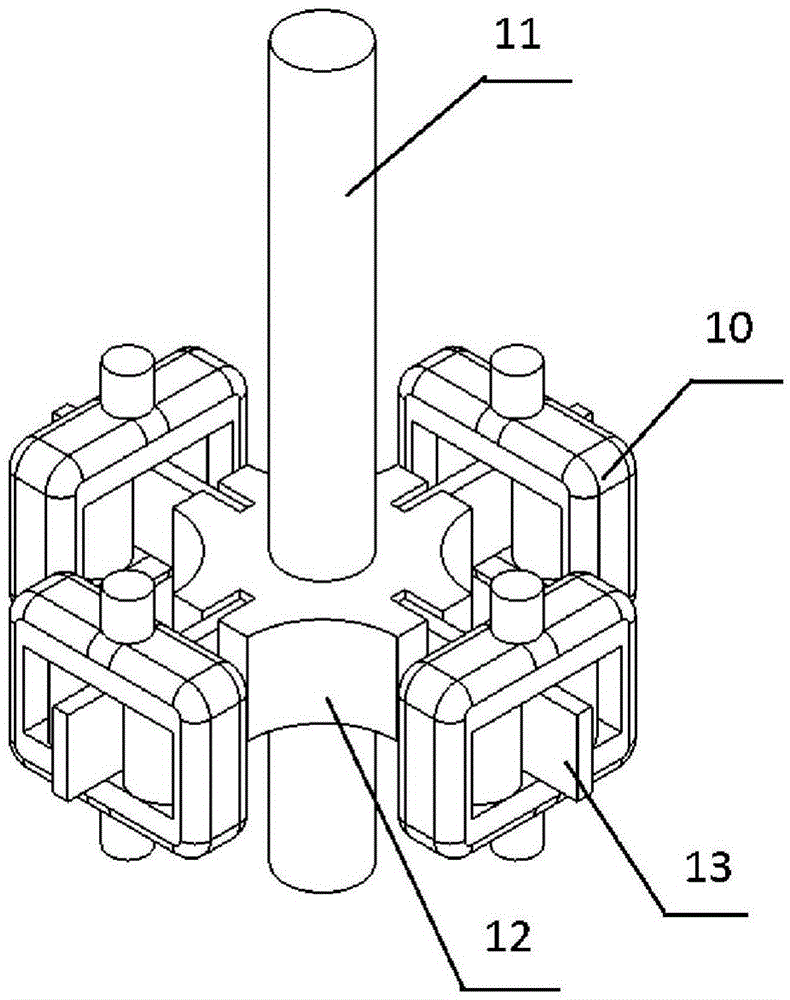
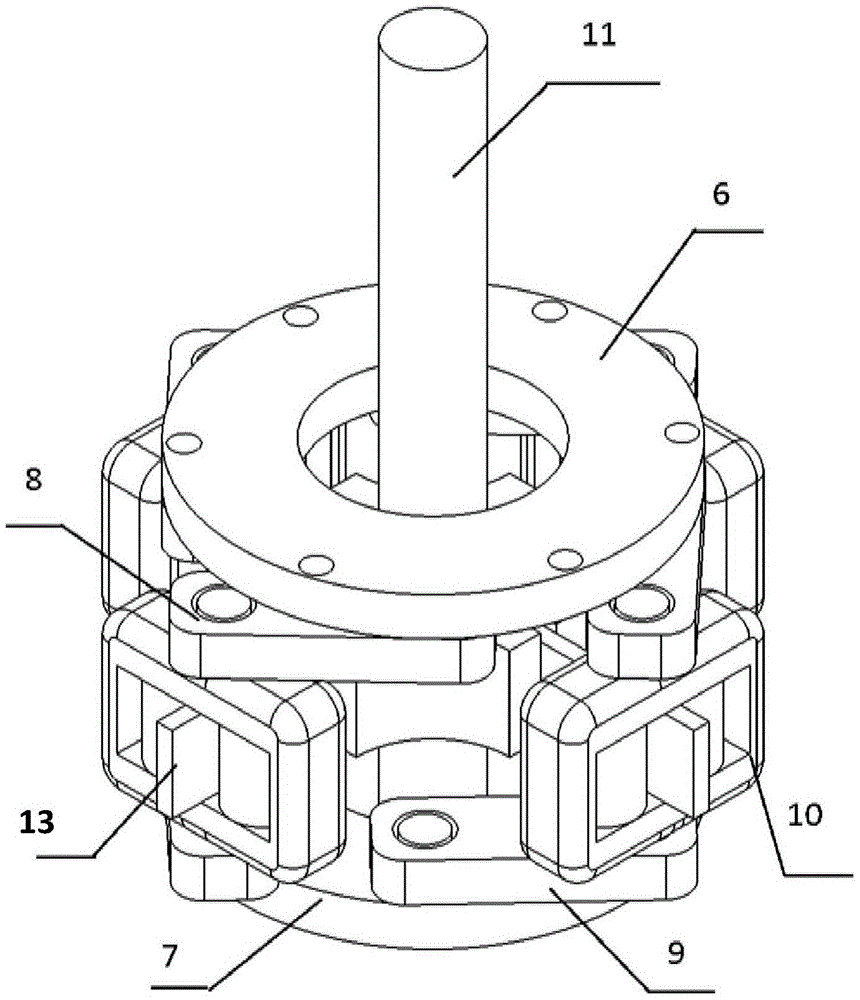
[0023] like Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, a dual-motor-driven robotic variable stiffness elastic joint includes an output shaft 11 located on the same axis of rotation, a flexible transmission mechanism 5, and a driving end. The driving end includes two coaxially driving connections connected to the flexible The hollow shaft drive motors at both ends of the transmission mechanism 5, the drive end also includes fixing plates respectively arranged at the two ends of the flexible transmission mechanism 5 for fixing two hollow shaft drive motor housings; the output shaft 11 and The middle part of the flexible transm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com