Spacecraft product final assembly precision measuring method based on workpiece coordinate system
A technology of precision measurement and coordinate system, applied in measurement devices, instruments, optical devices, etc., can solve the problems of cubic mirrors occupying load weight, difficult to process cubic mirrors, low measurement efficiency, etc., to save satellite launch costs and reduce occupation. The effect of load weight and improved measurement efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0046] The method for measuring the accuracy of the assembly of spacecraft products based on the workpiece coordinate system includes the following steps:
[0047] Step 1. Establishment of the public coordinate system:
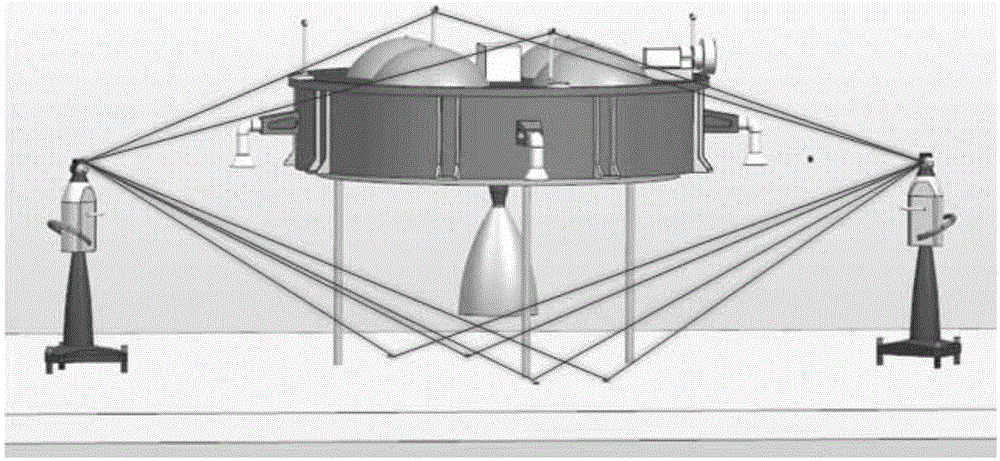
[0048] For the main body of the spacecraft that needs to detect the installation accuracy of the components, select several public reference points on the surface of the main body of the spacecraft, select several public reference points on the reference object plane where the main body of the spacecraft is currently located, and select a number of public reference points on the surface of the main body of the spacecraft. An optical reflector, that is, a target ball, is set on the 4-6 public reference points in the points;
[0049] respectively in A 1 and A 2 Position setting laser tracker a 1 and a 2 ;Adjust the laser tracker a through the cooperation of the laser tracker and the target ball 1 Obtain public fiducials on the laser tracker a 1 Coordinate ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0056] The specific process of the assembly accuracy of the detection part assembly described in step 3 of the present embodiment is as follows:
[0057] Set multiple target balls on the surface of the component to be inspected many times, set the measurement mode of the laser tracker to the stable point scanning mode, and pass the laser tracker a 1 and a 2 Cooperate with the target ball to scan the components of the part to be detected;
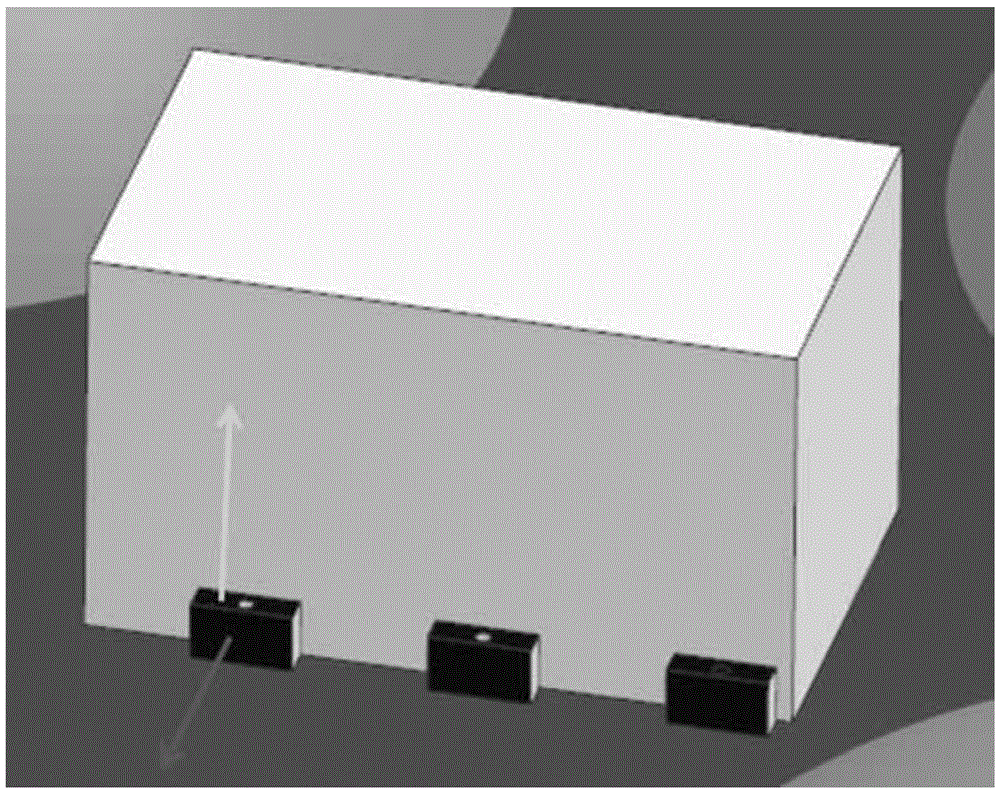
[0058] (1) As shown in Figure 3(a) and (b), if the component to be detected is a cube, combine the measured points and use the SpatialAnalyzer software to perform least squares surface fitting to obtain the normal of the plane, and calculate The angle between the normal line and the corresponding coordinate axis of the reference coordinate system is used to judge the installation accuracy of the components to be detected;
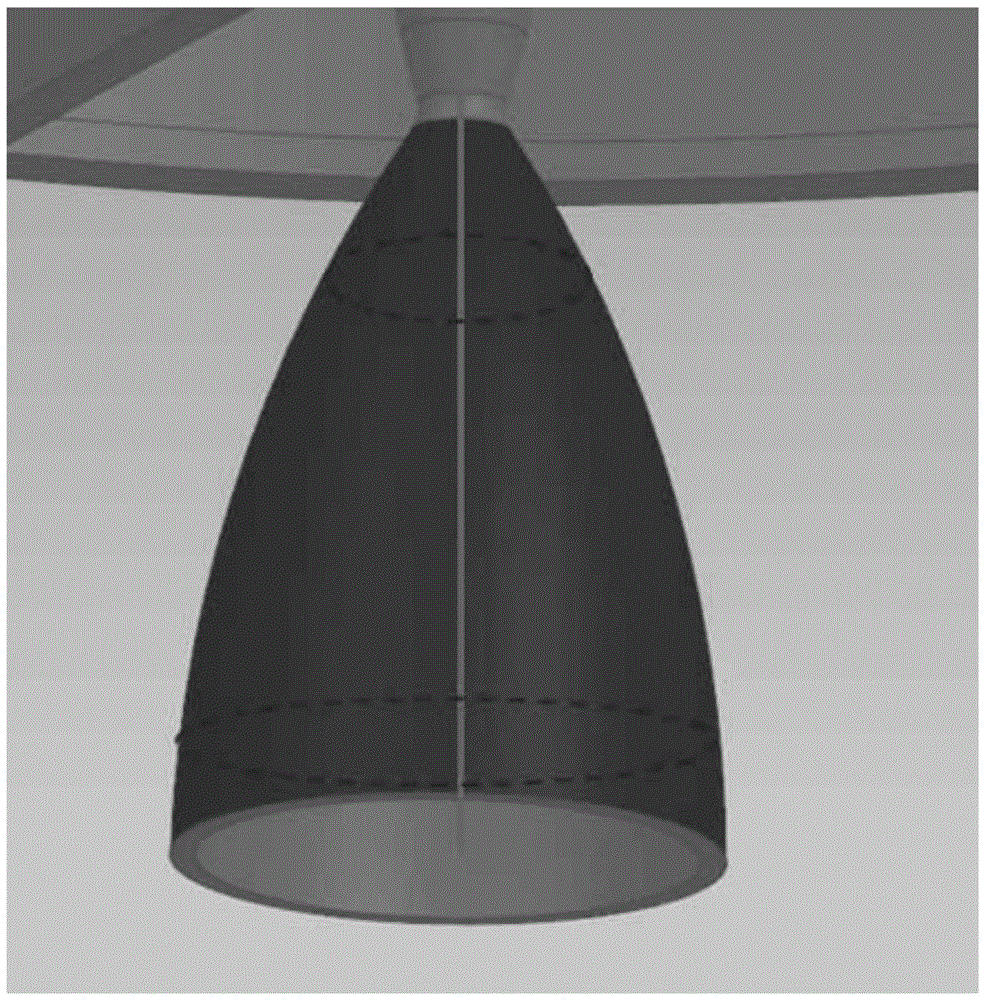
[0059] (2) If the component to be tested is a cylinder or a cone (such as a nozzle with a throat diameter, etc.), not...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0061] The specific process of detecting the axis installation accuracy of the component to be detected described in (2) of this embodiment is as follows:
[0062] The setting mode of the laser tracker is the point triggered by the geometry. The point triggered by the geometry is the name of the point collection mode of the SpatialAnalyzer software. Points, the points collected outside the plane are automatically eliminated; make the circular measurement object of the cylinder or the flat end face of the vertebral body, as shown in Figure 4 (a) and (b), set multiple target balls on the circular circumference of the flat end face on, or move the target ball on the circular circumference of the flat end surface for measurement, using the laser tracker a 1 and a 2 The obtained points are combined, and the circle fitting is carried out to obtain the center of the circle; the target ball is moved or set around the circumference of the circular contour surface with a flat end surfa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com