Distribution network traveling wave fault positioning method based on multi-terminal data
A technology of traveling wave fault and locating method, applied in fault location, fault detection according to conductor type, measurement of electricity and other directions, can solve problems such as equipment safety hazards, distortion, and equipment complexity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] It should be noted that, in the case of no conflict, the embodiments in the present application and the features in the embodiments can be combined with each other. The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples.
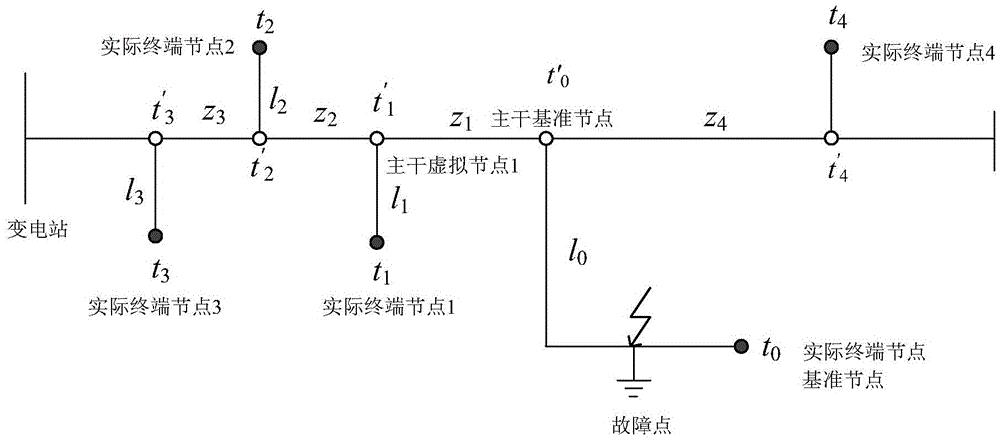
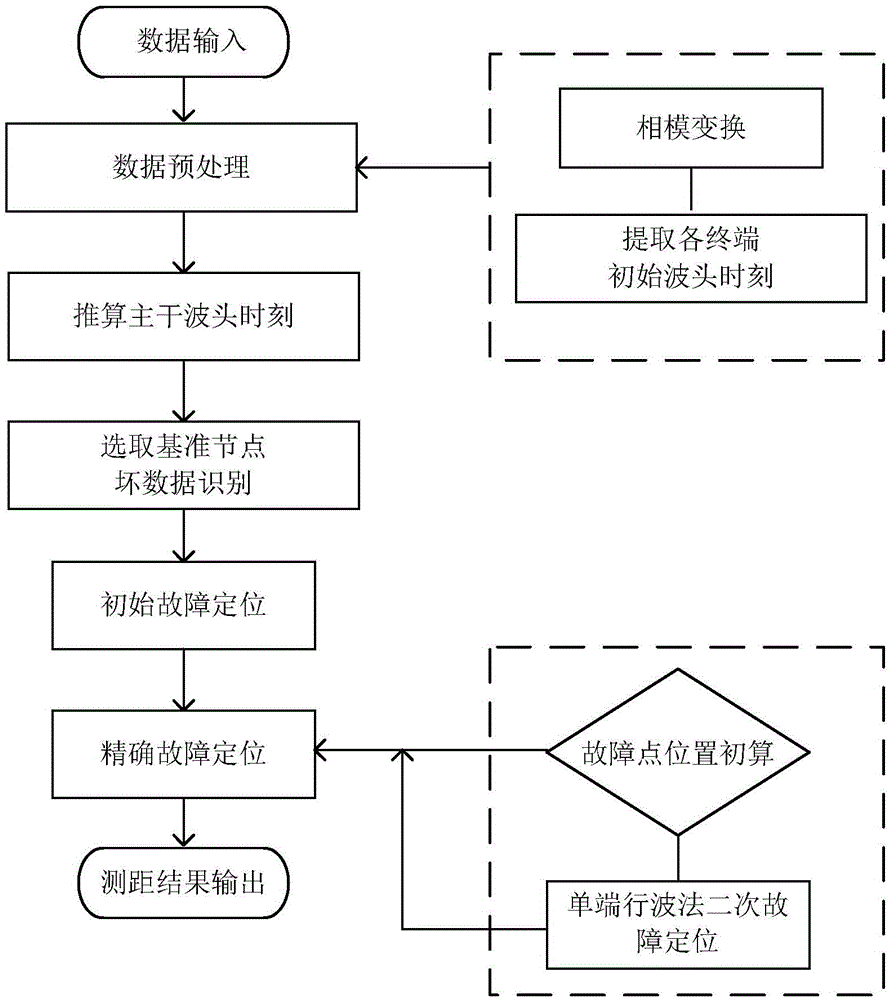
[0031] According to the distribution network traveling wave fault location method of the present invention, the measurement terminal is used, and its terminal nodes are located at the end positions of all branch lines of the distribution network. figure 1 , the method includes the following steps: step S10 of calculating the initial wave head time of each terminal node; calculating the fault of each virtual node corresponding to each terminal node on the trunk line according to the initial wave head time of each terminal node and line length data Step S12 of the initial wave head time; step S14 of determining the reference node on the trunk line according to the wavelet transform modulus value ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com