Compensation method of compensation capacity of pure active three-phase imbalance load
A technology for compensating capacity and balancing load, applied in reactive power compensation, reactive power adjustment/elimination/compensation, reduction of multiphase network asymmetry, etc. , the lack of power grid compensation capacity and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0039] Embodiment 1: The compensation method for pure active three-phase unbalanced load compensation capacity described in this embodiment, the method includes the following steps:
[0040] Step 1. Use the three-phase positive sequence voltage to supply power to the three-phase unbalanced load, and obtain the effective value of the neutral point voltage of the three-phase unbalanced load, which are respectively and
[0041] in, is the phase voltage of the system, is a phase-to-ground voltage, is b phase-to-ground voltage, is the phase-to-ground voltage of c, j is the imaginary component;
[0042] Using the formula:
[0043]
[0044] Obtain the ab phase line voltage respectively bc phase-to-line voltage and ca phase line voltage
[0045] According to the formula:
[0046]
[0047] Obtain the load current of the ab branch in the delta connection respectively The load current of the bc branch and the load current of the ca branch
[0048] In th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0075] Specific implementation mode two: refer to figure 1 and figure 2 Describe this embodiment in detail. This embodiment is a further description of the compensation method for the pure active three-phase unbalanced load compensation capacity described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, in step 3, according to the three-phase balance compensation method , to obtain three-phase compensated reactive power, respectively at P 1 ab ≥P 1 bc ≥P 1 ca ≥0,P 1 ab ≥P 1 ca ≥P 1 bc ≥0,P 1 bc ≥P 1 ab ≥P 1 ca ≥0,P 1 bc ≥P 1 ca ≥P 1 ab ≥0,P 1 ca ≥P 1 ab ≥P 1 bc ≥0 or P 1 ca ≥P 1 bc ≥P 1 ab Under any two conditions in ≥0, the specific process of selecting the phase with the largest compensation power among the three-phase compensation reactive power is:
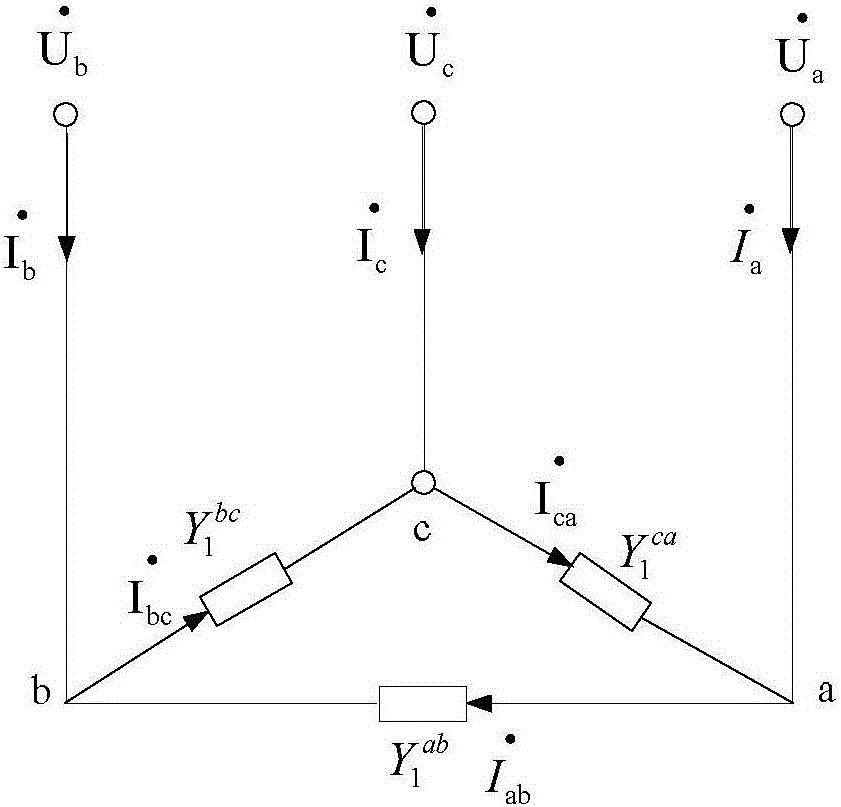
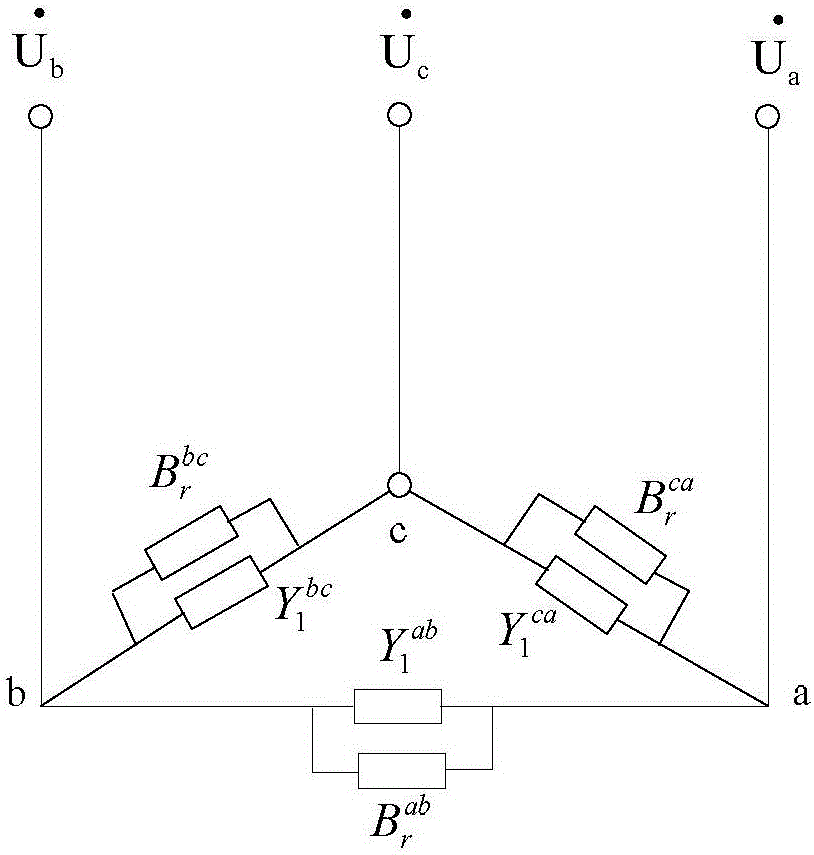
[0076] Assuming the supply voltage is balanced, the load Y 1 ab , Y 1 bc and Y 1 ca Represented by a network connected by triangles:
[0077]
[0078] According to the principle of three-phas...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0100] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment is to further explain the compensation method of the pure active three-phase unbalanced load compensation capacity described in specific embodiment one. In this embodiment, in step four, the load that needs to be compensated in step two Multiply the compensation coefficient K as the actual negative sequence capacity that needs to be compensated, and compare the actual negative sequence capacity that needs to be compensated with the maximum value of the total compensation capacity in the three-phase system in step 3. When the actual negative sequence capacity that needs to be compensated When the difference between the sequence capacity and the maximum value of the total compensation capacity in the three-phase system is greater than or equal to zero, the specific process for obtaining the compensation coefficient K greater than or equal to 2 is:
[0101] at P 1 ab ≥P 1 bc ≥P 1 ca ≥0 and P 1 ca ≥P 1 bc ≥P 1 ab Under t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com