A Secure Dot Product Realization Method in Chip
An implementation method and point-multiplying technology, applied in the protection of internal/peripheral computer components, etc., can solve the problem of inability to attack the means of immunity, and achieve the effect of improving security and resisting side-channel attacks.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
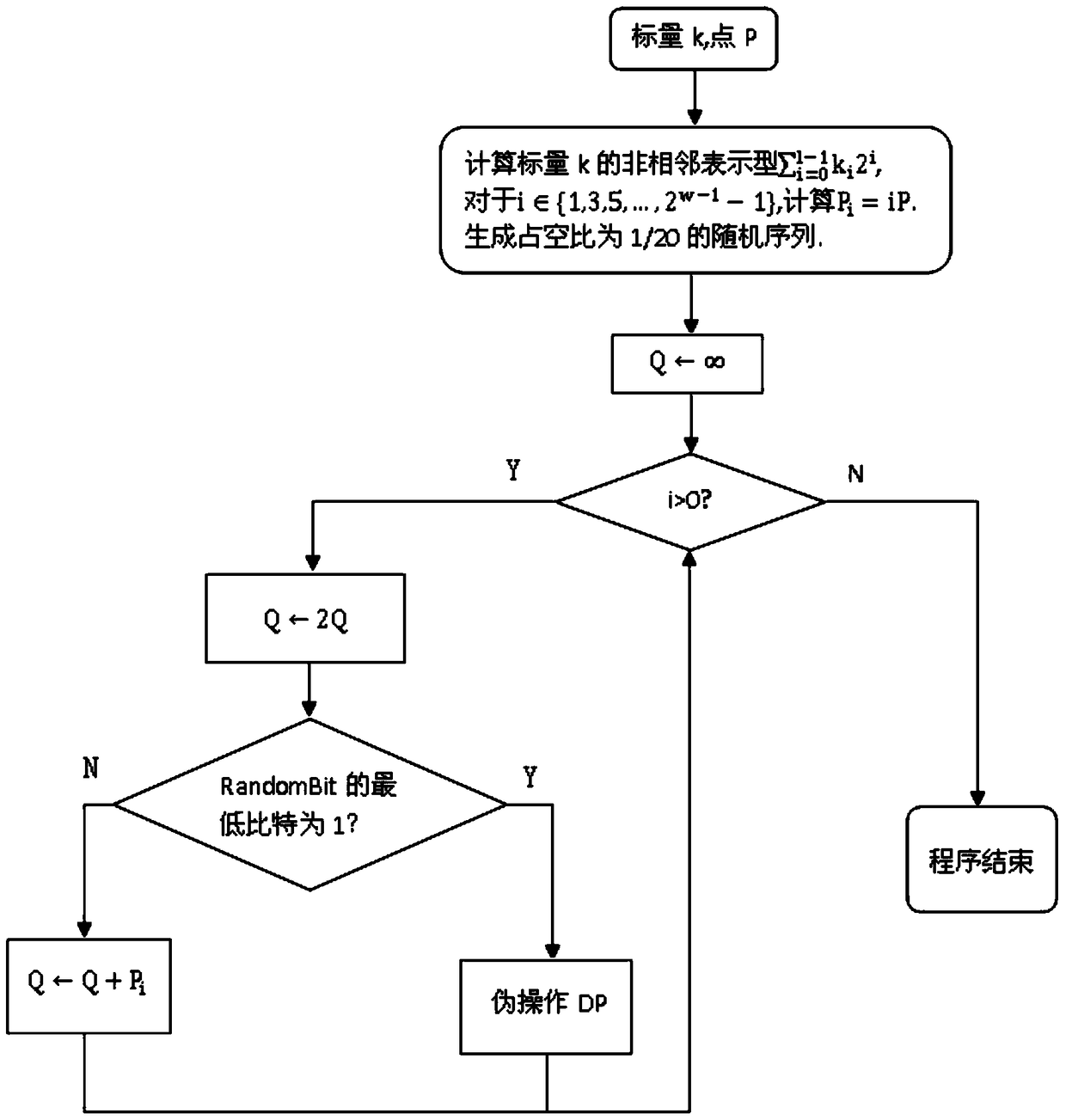
[0030] The secure point product implementation method in the chip, when a software or hardware cryptographic device potentially subject to SCA attack, DFA attack, and TA attack runs the elliptic curve cryptosystem, in the case of needing to perform point product operation, add In the process of point-fold iteration, the following steps are performed:
[0031] Step 1, read scalar k and elliptic curve point P for point multiplication operation;
[0032] Step 2, generating a random bit sequence with a duty ratio of 1 / N;
[0033] Step 3. Calculate the non-adjacent representation of the scalar k For i ∈ {1, 3, 5, ..., 2 w-1 -1}, calculate P i =iP;
[0034] Step 4, Q←∞;
[0035] Step 5, for i from 1-1 to 0, repeat execution;
[0036] Step 5.1, Q←2Q;
[0037] Step 5.2, if the lowest bit of RandomBit is 1, then execute the dummy operation DP, RandomBit>>1; otherwise, if k i ≠0, and k i >0, then otherwise,
[0038] Step 6. Return to Q.
[0039] The generation of the ran...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com