Stereo Matching Method Based on Segmented Intersection Tree
A stereo matching and cross-tree technology, used in image analysis, image enhancement, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of poor stability of matching algorithms, differences in parallax results, distortion, etc., to ensure similarity, improve accuracy, and enhance robustness. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
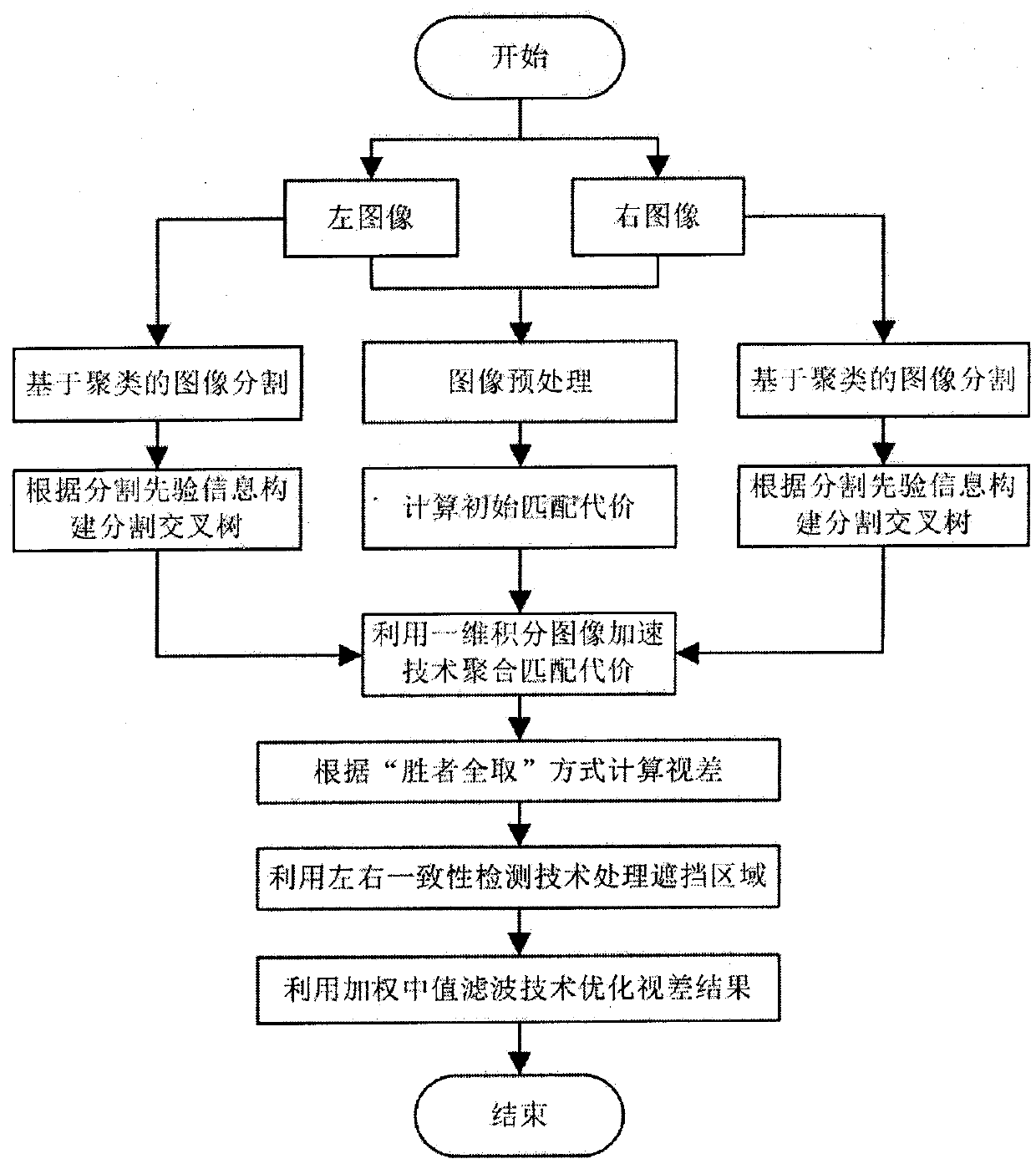
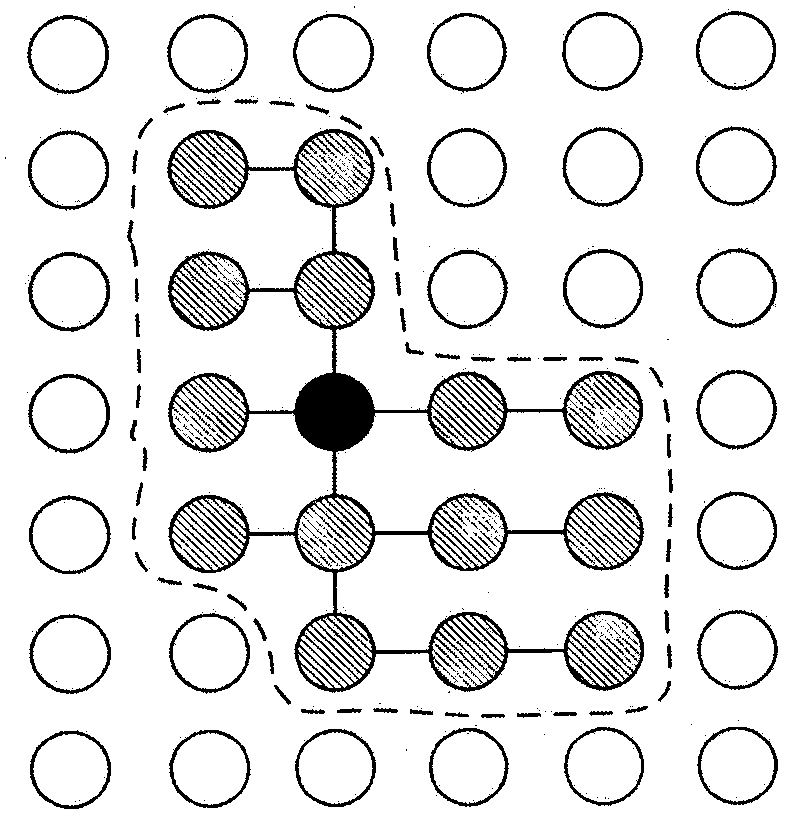
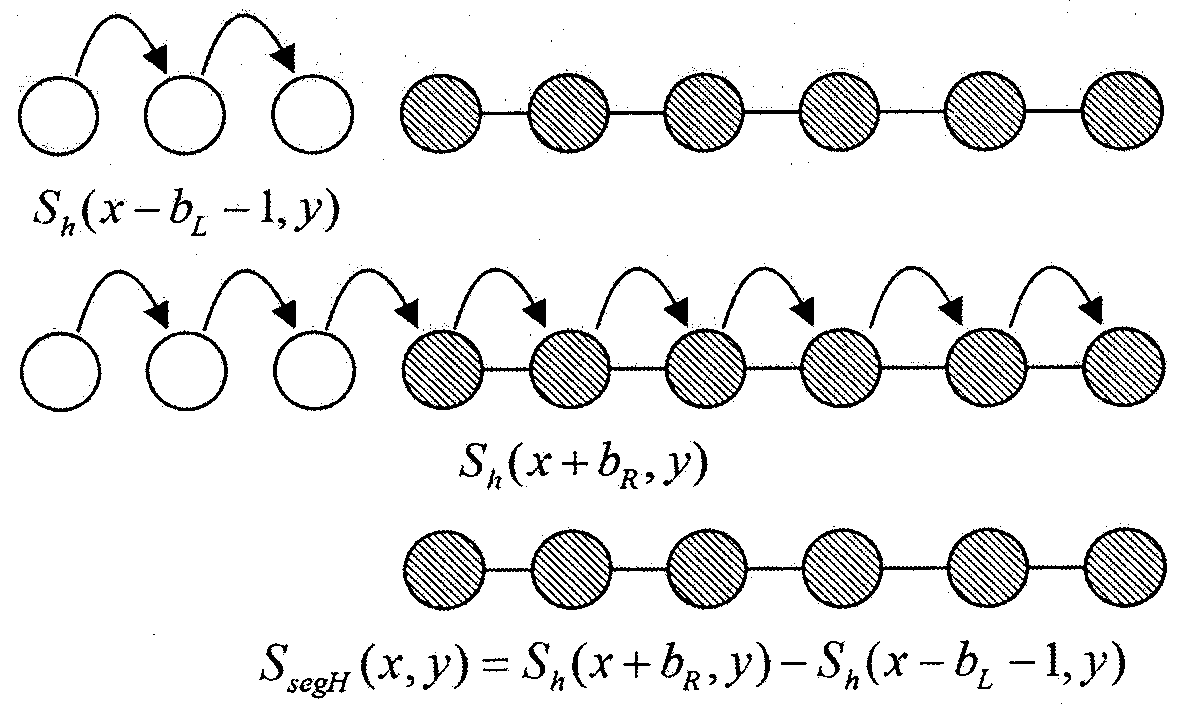
[0045]A stereo matching method based on segmentation cross tree, the method includes six steps, the first step uses Gaussian filter technology to preprocess the left and right stereo images, the second step calculates the initial matching cost, and the third step is each of the left and right stereo images The pixel points to be matched construct a segmentation cross tree. The fourth step uses the one-dimensional integral image acceleration technology to aggregate the initial matching cost in the support area of the segmentation cross tree. The fifth step calculates the disparity according to the "winner takes all" method. The sixth step is based on For the disparity results of the left and right stereo images, the disparity results are corrected by using the left and right consistency detection technology and the weighted median filter technology respectively.
[0046] First, the initial matching cost is calculated according to the pixel gray level information, the gradient ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] In the stereo matching method based on the segmentation cross tree described in embodiment 1, the first step is to perform convolution operation on the original left and right stereo images according to the Gaussian template, and its calculation formula is as follows:
[0049]
[0050] In the formula, G(i, j) represents a Gaussian template with a size of m×m, * represents a convolution operation, I′(x, y) represents the gray value of a pixel (x, y) in the initial image, and I( x, y) represents the gray value of the (x, y) pixel in the image after filtering and denoising.
[0051] The purpose of the preprocessing is to ensure the smooth progress of the subsequent steps, and to ensure that the noise of the stereoscopic image is reduced as much as possible after the preprocessing is completed.
Embodiment 3
[0053] In the stereo matching method based on the segmentation cross tree described in embodiment 1, the second step is to calculate the initial matching cost according to the disparity search range, the gray information of the left and right stereo images, the gradient information of the horizontal and vertical two main directions, and calculate the function To truncate the absolute difference function, the initial matching cost is stored in a 3D disparity space map C raw (x, y, d), its calculation formula is as follows:
[0054]
[0055] In the formula, I L (x, y) represents the gray value of the (x, y) pixel in the reference image after preprocessing, I R (x, y) represents the gray value of the (x, y) pixel in the matched image after preprocessing; α ( Indicates the gradient value of the function in the x direction, Represents the gradient value of the function in the y direction, τ 1 , τ 2 and τ 3 denote grayscale, horizontal and vertical gradient cutoff threshold...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com