Positive Sequence Impedance Differential Protection Method for Distribution Networks Containing IBDG with Braking Characteristics
A positive-sequence impedance and differential protection technology, which is applied in the direction of automatic disconnection emergency protection devices, emergency protection circuit devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of limited applicability, protection refusal to operate, and the change law of equivalent impedance on the back side of the protection Complicated and other problems, to improve the action characteristics, reduce the load branch, and ensure the effect of reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] The present invention is described in detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
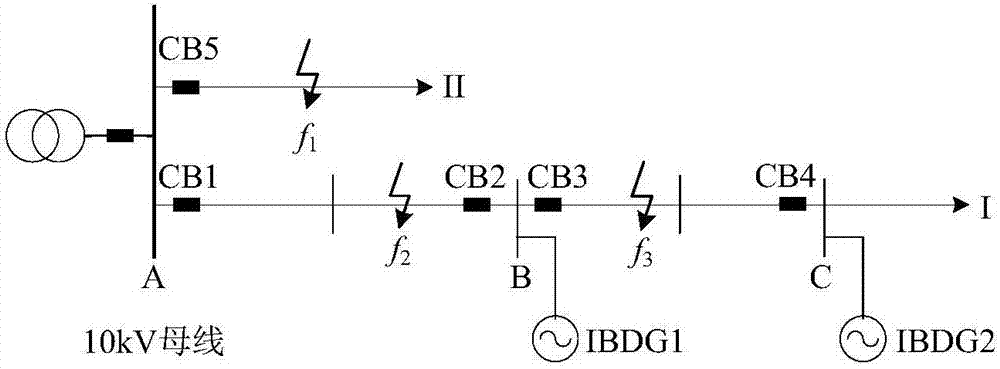
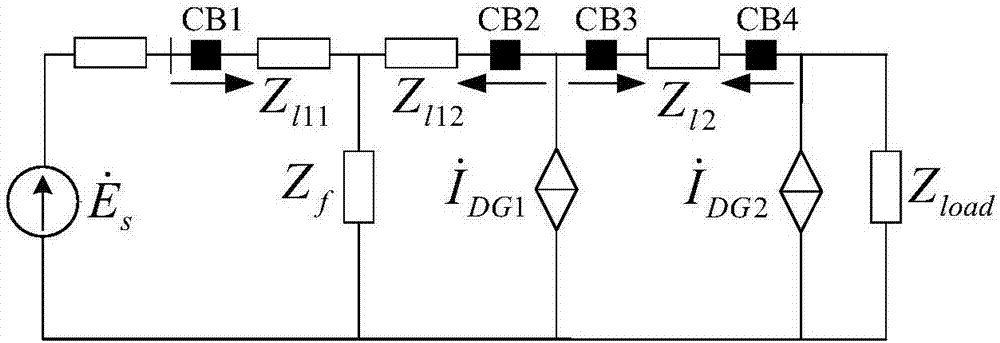
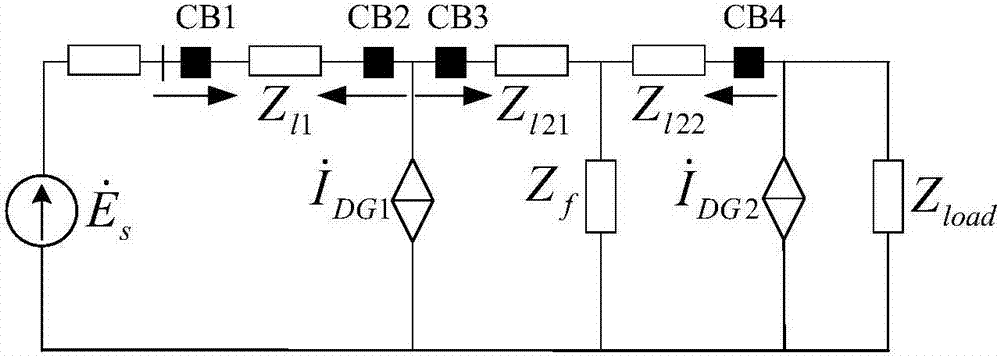
[0047] A positive-sequence impedance differential protection method for distribution networks with IBDG with braking characteristics, such as Figure 4 shown, including:
[0048] Install current transformers on the upstream and downstream sides of each distributed power access point on the active distribution network feeder, and use the voltage transformer at the grid-connected point of the distributed power to collect and protect the three-phase current and three-phase current at the installation site in real time. voltage; use the instantaneous value of three-phase current to determine the fault in the distribution network, and protect and start the fault processing program; determine the initial time of the fault, store the fault data of one cycle before and after the initial time of the fault, and compare the three-phase current amplitude before and after the fault value, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com