A method for calibrating the actual temperature of the substrate surface in molecular beam epitaxy
A molecular beam epitaxy, substrate surface technology, applied in thermometers, thermometer test/calibration, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problems of large test errors, increased equipment complexity, cost, and difficulties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
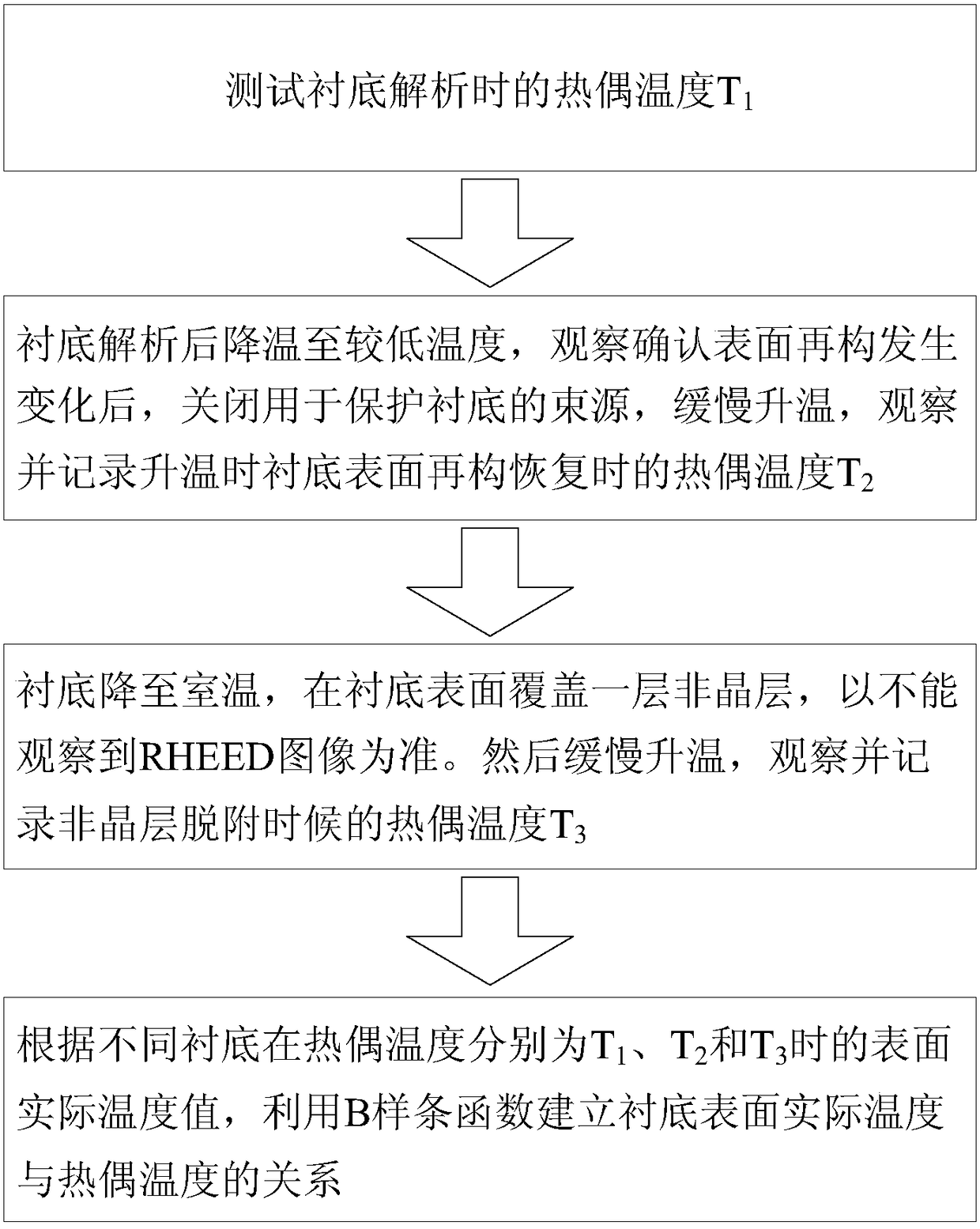
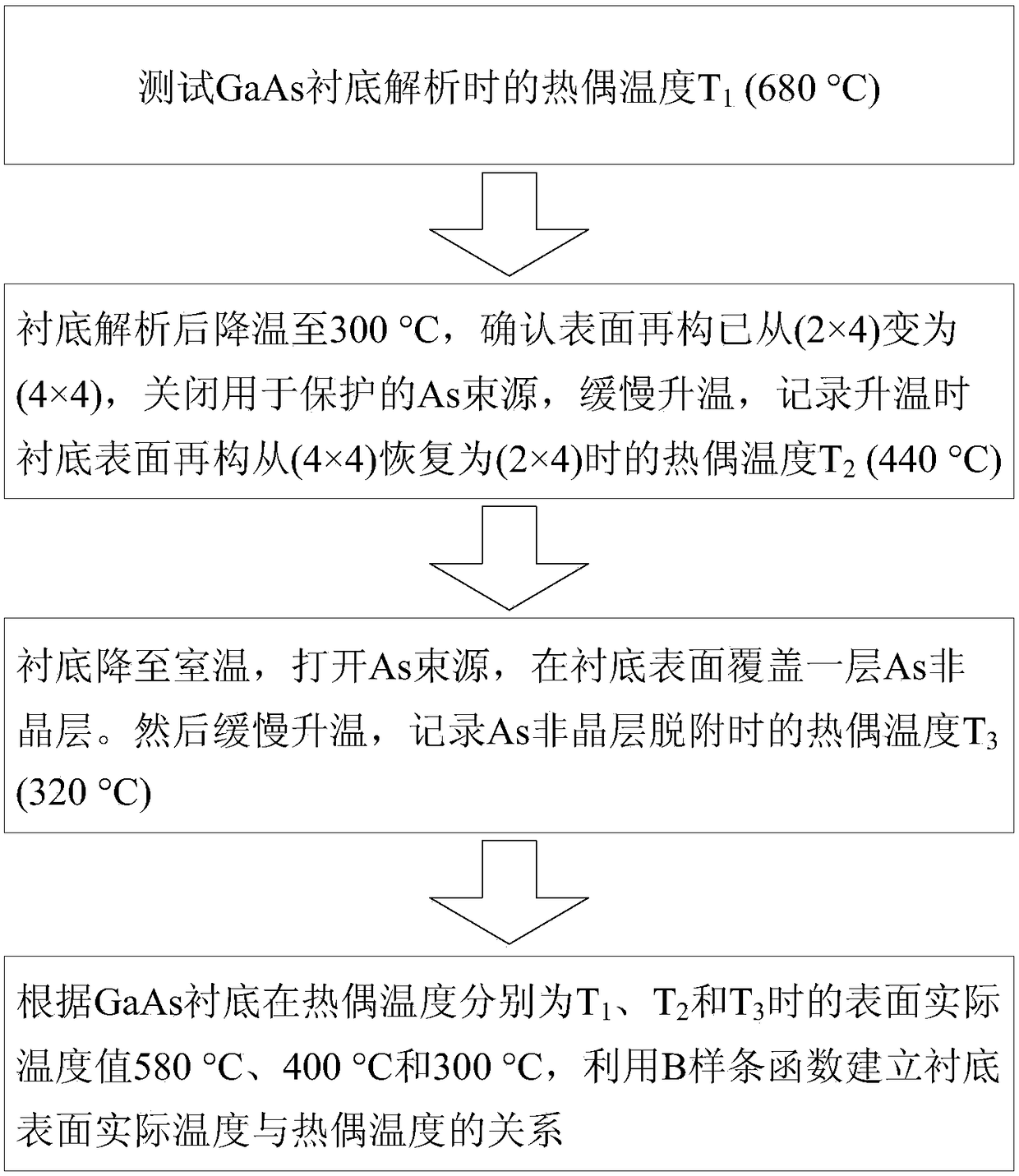
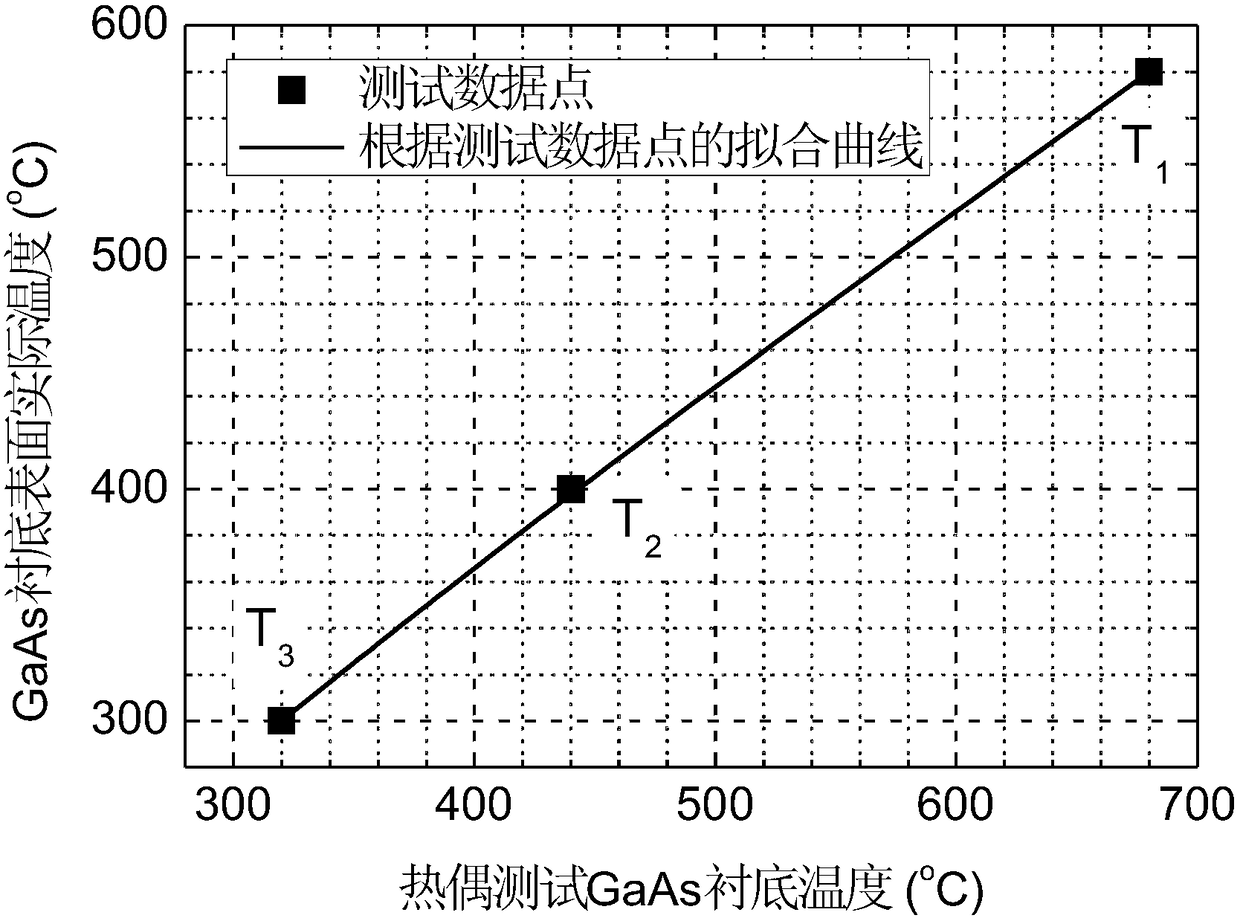
[0032] This embodiment provides a GaAs substrate as an example to illustrate the method of calibrating the actual temperature of the GaAs substrate surface in molecular beam epitaxy, such as figure 2 As shown, the method steps are as follows:
[0033] (1) Test the thermocouple temperature T during GaAs substrate analysis 1 , taking 680°C as an example;
[0034] (2) After the substrate is analyzed, the temperature is lowered to 300°C, and the substrate surface reconstruction has been confirmed to have changed from (2×4) to (4×4) by RHEED observation, and the As beam source used to protect the substrate is turned off, and then the temperature is raised. The heating rate is 0.1°C / s, observe the change of the substrate surface reconstruction when the temperature rises, and record the thermocouple temperature T when the surface reconstruction recovers from (4×4) to (2×4) 2 , taking 440°C as an example;
[0035] (3) Lower the substrate to room temperature, turn on the As beam so...
Embodiment 2
[0041] This embodiment provides an InP substrate as an example to illustrate the method of calibrating the actual temperature of the InP substrate surface in molecular beam epitaxy, such as Figure 4 As shown, the method steps are as follows:
[0042] (1) Test the thermocouple temperature T when analyzing the InP substrate 1 , taking 530°C as an example;
[0043](2) After substrate analysis, cool down to 250°C, observe with RHEED to confirm that the substrate surface reconstruction has changed from (2×4) to (4×4), turn off the P beam source used to protect the substrate, and then raise the temperature, The heating rate is 0.1°C / s, observe the change of the substrate surface reconstruction when the temperature rises, and record the thermocouple temperature T when the surface reconstruction recovers from (4×4) to (2×4) 2 , taking 350°C as an example;
[0044] (3) Lower the substrate to room temperature, turn on the P beam source to the maximum, and leave it for more than half...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com