Device for the transcutaneous implantation of epicardial pacemaker electrodes
An epicardial and pacemaker technology, applied in the field of devices used for percutaneously implanting epicardial pacemaker electrodes, can solve problems such as narrow pericardial space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
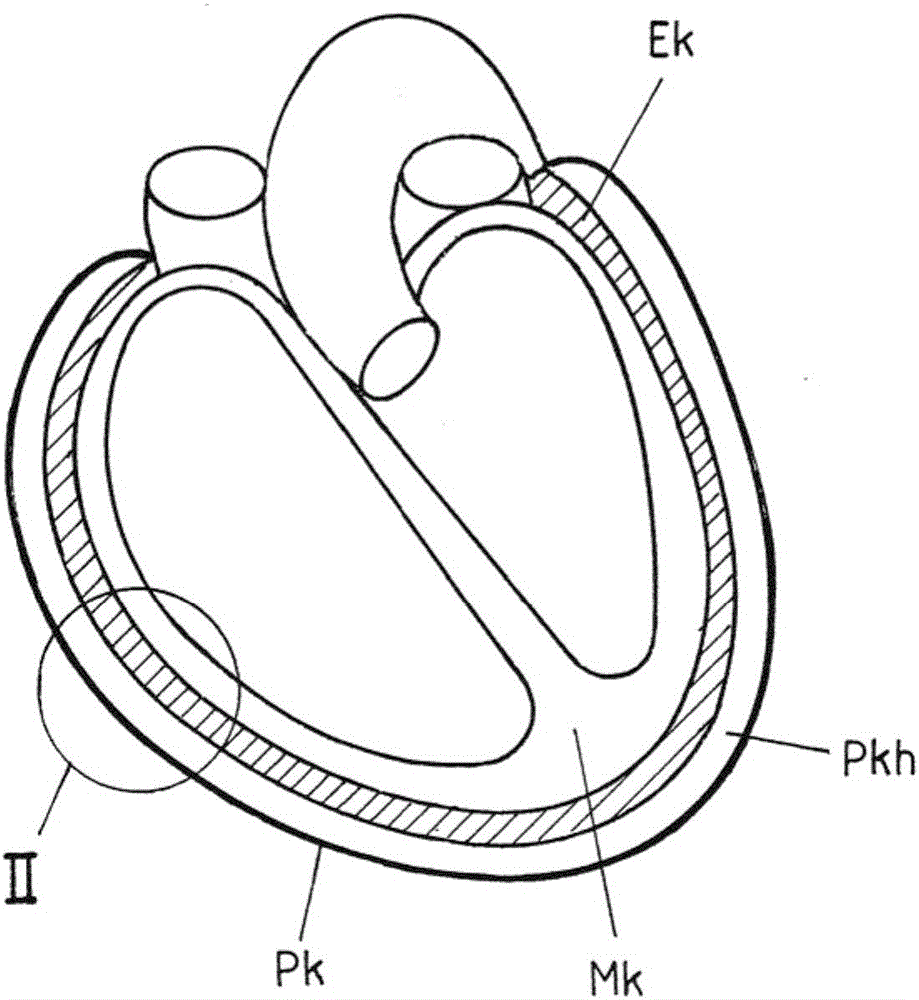
[0046] figure 1 Schematic cross-sectional view showing a double-walled pericardium with: the pericardium Pk forming the outer valve of the pericardium; the epicardium Ek forming the inner valve of the Mk); and the fine gap formed between the epicardium Ek and the pericardium Pk, i.e. the pericardial cavity or pericardial space Pkh, which serves as a fluid for the sliding membrane to fill.
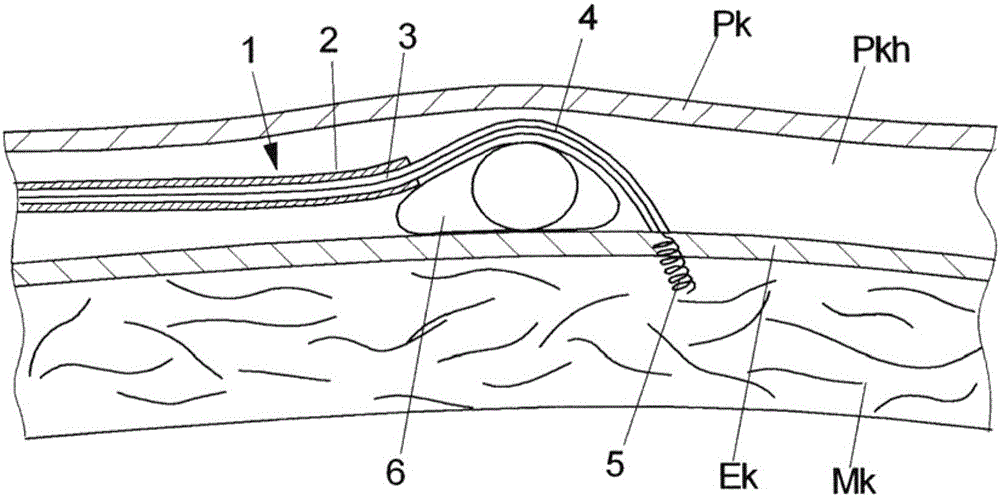
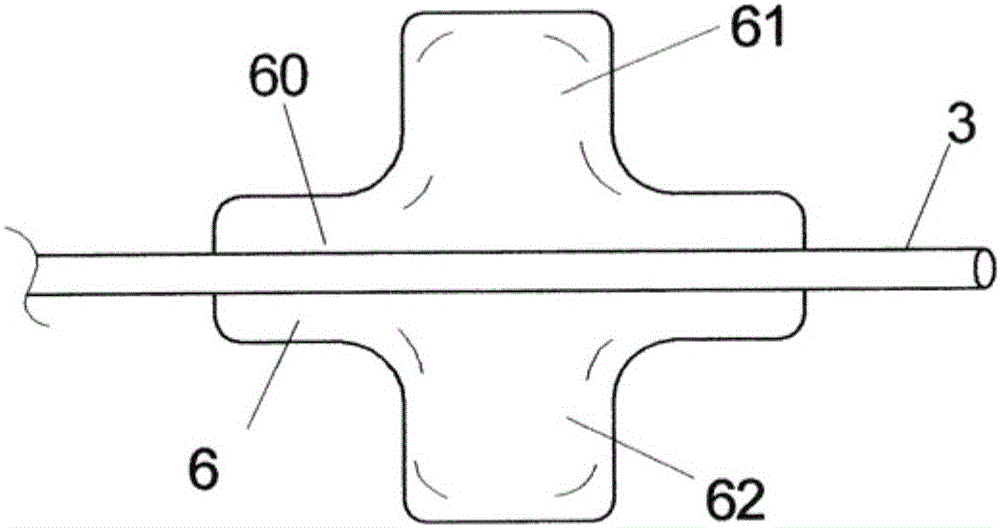
[0047] figure 2 Shown in enlarged view according to figure 1 Region II of the pericardium Pk, epicardium Ek, and the pericardial space Pkh formed between the pericardium Pk and epicardium Ek and the myocardium Mk of the heart connected to the epicardium Ek. In order to implant the epicardial pacemaker electrode 4, the implantation catheter 1 is introduced percutaneously or transthoracically into the pericardium space Pkh after puncturing the pericardium Pk and moves along the pericardium space Pkh until it reaches the threshold for implantation. Optimal implantation site for epicardial...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com